![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
function of the male reproductive system |
* Functions to produce spermatozoa, seminal fluid (semen), and endocrine function
|
|
|
* Paired glands with both exocrine (spermatozoa) and endocrine (testosterone) functions |
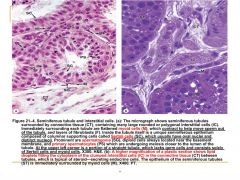
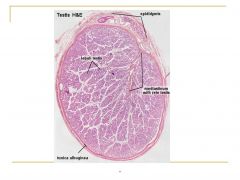
testes |
|
|

|
|
|
function of Sertoli Cells |
* protection and nourishment of spermatogenic cells |
|
|
spaces between seminiferous tubules |
* loose CT (interstitial CT):
* lymphatic and blood vessels * nervesinterstitial cells of Leydig which produce testosterone |
|
|
* Highly coiled tube about 5 m long that extends down the surface of the testis
* Functions as site of sperm storage and maturation; and absorption of water by stereocilia * Lined with pseudostratified columnar epithelium with tufts of stereocilia (long microvilli) * Absorb water * Participate in uptake and digestion of residual bodies produced during spermiogenesis * Wall has smooth muscle that move sperm toward ductus deferens |
Epididymis |
|
|
* Conducts spermatozoa from epididymis to urethra
* Is a thick walled, muscular tube (long, circ, long) * Lined with pseudostratified columnar epithelium (sparse stereocilia) * Epithelium and lamina propria (elastic fibers) are folded to allow for expansion during ejaculation * Covered by adventitia * Forms ampulla (after passing over u. bladder) |
Ductus Deferens/ Vas Deferens |
|
|
secretion of seminal vesicles |
fructose, fibrinogen, prostaglandins (among others) |
|
|
form ~70% of seminal fluid |
seminal vesicles |
|
|
* Spermiogenesis involves.. |
* development of an acrosome (from Golgi) |
|
|
* Along the BM, are most primitive cells of germinal cell population – called spermatogonia |
Spermatogenesis |
|
|
Testes |
|

|
Epididymis |
|

|
seminal vesicles |
|

|
prostrate gland |
|
|
3 bundles of erectile tissue in Penis |
2 corpora cavernosa 1 corpus spongiosum |
|
|
CT surrounding each erectile tissue |
tunica albuginea |
|

|
penis |

