![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
True vocal cord epithelium |
Stratified squamous nonkeratinized |
|
|
From where is the trachea derived? |
Primordial foregut |
|
|
What is the respiratory epithelium? |
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar |
|
|
What cell is increased in chronic inflammation? |
Goblet cells |
|
|
Trachea epithelium |
Ciliated pseudo stratified columnar with goblet cells |
|
|
Trachea lamina propria contains what fibers? |
Elastic |
|
|
What glands are present in tracheal submucosa? What do they secrete? |
Seromucous; glycoprotein |
|
|
Where are tracheal glands most prominent? |
Posterior aspect where there is no cartilage |
|
|
What cartilage makes up the C shaped rings in the trachea? |
Hyaline |
|
|
What muscle makes up the posterior aspect of the trachea to allow flexibility of the esophagus? |
Trachealis muscle |
|
|
What membrane makes up the posterior aspect of the trachea to allow flexibility of the esophagus? |
Fibroelastic membrane |
|
|
What happens to the respiratory epithelium in the intrapulmonary (secondary) bronchi? |
-Cell height decreases as bronchi diameter decreases -Reduced BL and LP |
|
|
What is now present in the intrapulmonary mucosal layers? |
Smooth muscle |
|
|
Describe the cartilage in the intrapulmonary bronchi |
Hyaline cartilage plates (not ring) arranged linearly around bronchus |
|
|
What glands are present in the submucosal layer of the intrapulmonary bronchus? |
Seromucous glands |
|
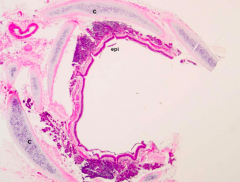
Identify the area |
Intrapulmonary bronchus (Notice the smooth muscle layer, hyaline cartilage and respiratory epithelium) |
|
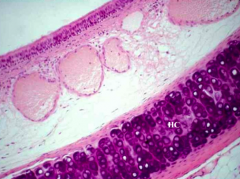
Identify the area |
Intrapulmonary bronchus (Notice cartilage plates) |
|
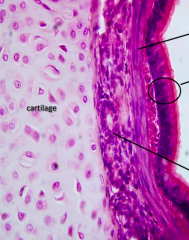
Identify the area |
Trachea (Notice hyaline cartilage, respiratory epithelium and lack of muscular layer) |
|
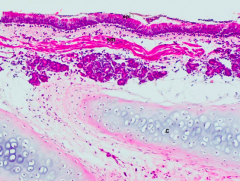
Identify the area |
Secondary (intrapulmonary) bronchus (Notice smooth muscle and cartilage plates) |
|
What epithelium is this? |
Respiratory epithelium Ciliated pseudo stratified columnar with goblet cells |
|
|
What increases and decreases as intrapulmonary diameter decreases? |
Cartilage plates get smaller Smooth muscle increases |
|
|
By what is the intrapulmonary airway surrounded? |
Alveoli |
|
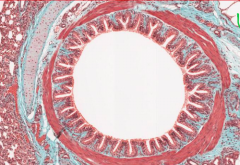
Identify |
Intrapulmonary bronchus (Notice SERRATED APPEARANCE, smooth muscle, cartilage plates and alveoli in top right corner) |
|
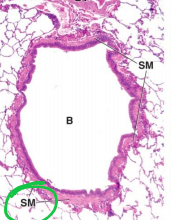
Identify area |
Bronchiole (notice smooth muscle and lack of cartilage) |
|
|
Do the bronchioles have glands? |
NO |
|
|
What epithelium is present in the larger primary bronchioles? |
Ciliated pseudo stratified columnar with goblet cells |
|
|
What epithelium is present in the smaller bronchioles ex. terminal bronchiole and respiratory bronchiole? |
Ciliated cuboidal with Clara cells (Clara cells replace goblet cells) |
|
|
Clara cell appearance |
Cuboidal cell with domed apical surface |
|
|
What do Clara cells secrete? |
Surface active agent and Clara cell protein (CC16) |
|
|
What is CC16? |
COPD and asthma marker |
|
|
Where is the first site of gas exchange? |
Respiratory bronchiole |
|
|
Describe walls of respiratory bronchiole |
Discontinuous walls interrupted by alveoli Small amount of smooth muscle |
|
|
Where do alveolar ducts terminate? |
Alveolar sac |
|
|
What cells are seen in heart failure? |
Alveolar macrophages loaded with RBCs |
|
|
Which cells predominantly line alveolar wall? |
Type I pneumocyte |
|
|
What covers type I pneumocyte surface? |
Surfactant |
|
|
How are type I pneumocytes joined? |
Occluding junctions |
|
|
What do type II pneumocytes secrete? |
Surfactant |
|
|
Type I pneumocyte function |
Blood-air barrier |
|
|
What do lamellar bodies? |
Form surfactant |
|
|
What do lamellar bodies look like? |
Mitochondria |
|
|
What does the inter alveolar septum contain? |
Collagen fibrils and elastic fibers |
|
|
What kind of capillaries are seen in the inter alveolar septum? |
Continuous |
|
|
Where are type II pneumocytes located? |
In septum |
|
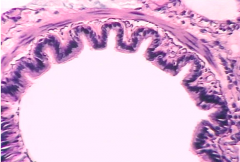
Identify |
Terminal bronchiole (Notice smooth muscle, no cartilage) |
|
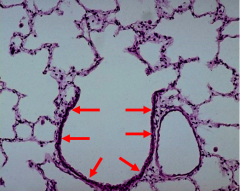
What is this region? |
Terminal bronchiole |

