![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
From what if the tunica vaginalis derived? |
Processus vaginalis |
|
|
Which layer of the tunica albuginea contains blood vessels? |
Tunica vasculosa in the inner, loose CT |
|
|
What extends inwards to form septa in the testes? |
Tunica albuginea |
|
|
How many seminiferous tubules are in each lobule? |
1-4 |
|
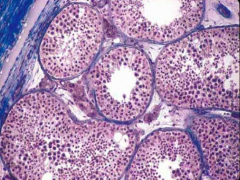
Identify |
Seminiferous tubules |
|
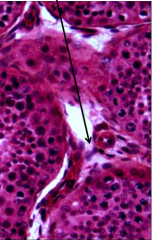
Identify arrow |
Leydig cells (Interstitial) |
|
|
Where are myoid cells located? |
Tunica Lamina Propria |
|
|
What do myoid cells do? |
Peristaltic contraction |
|
|
What cells are found in the seminiferous epithelium? |
Sertoli cells and spermatogenic cells |
|
|
What do Sertoli cells secrete? |
Inhibin --> inhibits FSH secretion Androgen bind protein --> binds testosterone |
|
|
What makes up the blood-testis barrier? |
Sertoli cells' tight junctions |
|
|
What do Leydig cells secrete? |
Testosterone |
|
|
How many days does it take to go from spermatogonia to spermatozoa? |
~74 days |
|
|
Spermatogenesis process |
Dark A spermatogonia --> Pale A spermatogonia --> Type B spermatogonia --> Primary spermatocytes --> secondary spermatocytes --> Spermatids --> Spermatozoa |
|
|
Which sperm cells are diploid? |
Spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes |
|
|
Which sperm cells are haploid? |
Secondary spermatocytes, spermatids and spermatozoa |
|
|
Sertoli cell function |
Support, protect and nourish developing spermatozoa |
|
|
What receptors do Leydig cells have? |
LH receptors |
|
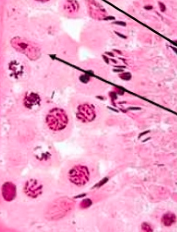
Identify arrow |
Sertoli cell |
|
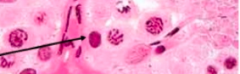
Idenitfy arrow |
Dark spermatogonia |
|
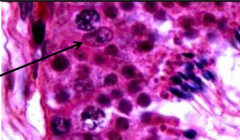
Identify arrow |
Sertoli cell |
|
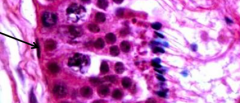
Identify arrow |
Myoid cell |
|
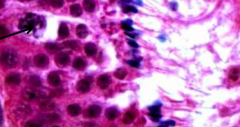
Identify arrow |
Primary spermatocyte |
|
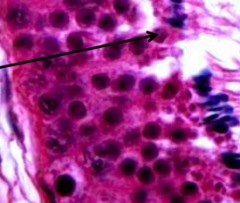
Identify arrow |
Spermatid |
|
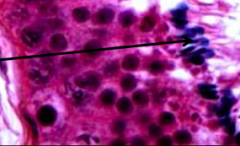
Identify arrow |
Spermatozoa |
|
|
Rete testis epithelium |
Simple cuboidal to low columnar |
|
|
Straight tubules epithelium |
Simple cuboidal with microvilli and flagella |
|
|
What does the efferent ductule connect? |
Rete testis to epididymis |
|
|
Efferent ductule epithelium |
Pseudostratified columnar Tall cells with cilia Short cells with microvilli |
|
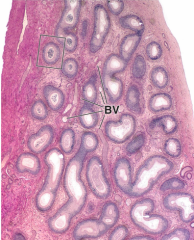
Identify |
Epididymis |
|
|
Which duct/tubule contains smooth muscle? |
Epididymis |
|
|
What do the principle cells of the epididymis secrete? Why? |
Glycerophosphocoline --> decapacitates sperm |
|
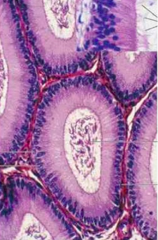
Identify |
Epididymis (Notice smooth muscle) |
|
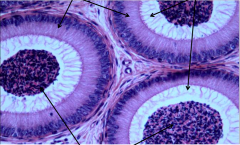
Identify area |
Epididymis (Notice pseudostratifed columnar with stereo cilia) |
|
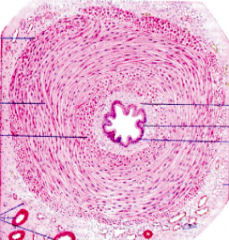
Identify |
Vas Deferens (Notice three layers of smooth muscle) |
|
|
What do the seminal vesicles secrete? |
Fructose and prostaglandins |
|
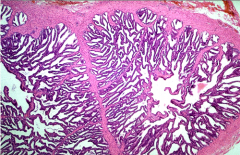
Identify |
Seminal vesicle |
|
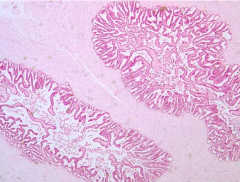
Identify |
Seminal vesicle |
|
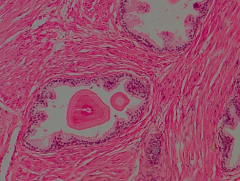
Identify |
Prostate |
|
|
What is the function of the blood-testis barrier? |
To protect spermatogenic cells from an autoimmune response |

