![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Confucianism |
Confucianism is a way of life taught by Confucius in the 6th–5th century BC. Sometimes viewed as a philosophy, sometimes as a religion, Confucianismis perhaps best understood as an all-encompassing humanism that neither denies nor slights heaven. |
|
|
Daoism |
is a philosophical, ethical or religious tradition of Chinese origin that emphasizes living in harmony |
|
|
Laozi |
Laozi is the name of a legendary Daoist philosopher, finder of daoism |
|
|
Dao de jing |
Book written by laozi |
|
|
Opium wars |
a war between Great Britain and China thatbegan in 1839 as a conflict over the opiumtrade and ended in 1842 with the Chinesecession of Hong Kong to the British, theopening of five Chinese ports to foreignmerchants, and the grant of othercommercial and diplomatic privileges in theTreaty of Nanking. |
|
|
Taiping rebellion |
unsuccessful rebellion (Taiping Rebellion)1850–64, led by Hung Hsiu-ch'üan (HongXiuquan), who attempted to overthrow theManchu dynasty. |
|
|
Nationalist |
Someone that wants all for one |
|
|
Koumintang |
the dominant political party of China from1928 to 1949, founded chiefly by Sun Yatsen in 1912 and led from 1925 to 1975 byChiang Kaishek; the dominant party of theRepublic of China (Taiwan) since 1949. |
|
|
Sun yat sen |
1866–1925, Chinese political andrevolutionary leader communist |
|
|
Chang Kai shek |
Early in the 20th century Chiang Kai-shek fought for Sun Yat-sen's United Revolutionary League and the Kuomintang party to overthrow China's imperial dynasty. The Republic |
|
|
Mao zedong |
Former Chairman of the Communist Party of China (Hitler) |
|
|
Long march |
Long March (October 1934 – October 1935) was a military retreat undertaken by theRed Army of the Communist Party of China, |
|
|
Great leap forward |
The campaign was led by Mao Zedong and aimed to rapidly transform the country from an agrarian economy into asocialist society through rapidindustrialization |
|
|
Cultural revolution |
ocial-political movement that took place in thePeople's Republic of China from 1966 until 1976. Set into motion by Mao Zedong, thenChairman of the Communist Party of China, its stated goal was to preserve 'true'Communist ideology |
|
|
Renaissance |
14th-17th century |
|
|
Reformation |
1517 |
|
|
Mahatma Gandhi |
1893 |
|
|
Indus river valley civilization |
5500 bce |
|
|
French revolution |
1789-1799 |
|
|
Muhammed |
570-630 |
|
|
Pax romana |
27-31 bc |
|
|
Alexander the great |
356bc-324bc |
|
|
Hannibal |

|
|
|
Battle of thermoplae |

|
|
|
Mahatma gandhi |

|
|
|
Nelson mandela |

|
|
|
Martin luther |

|
|
|
Joan of arc |

|
|
|
Confucius |

|
|
|
Parthenon |

|
|
|
Colosseum |

|
|
|
Terra cotta army |

|
|
|
Mao Zedong |

|
|
|
Phidippides |

|
|
|
Buddha |

|
|
|
King David |
|
|
|
Cuneiform |
denoting or relating to the wedge-shaped characters used in the ancient writing systems of Mesopotamia, Persia, and Ugarit, surviving mainly impressed on clay tablets. |
|
|
Sparta |
an ancient Greek city in the S Peloponnese, famous for the discipline and military prowess of its citizens and for their austere way of life |
|
|
Heiroglyphics |
Egyptian hieroglyphs were a formal writing system used by the ancient Egyptians that combined logographic and alphabetic elements |
|
|
Mesopotamia |
Mesopotamia is a name for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, corresponding to modern‑day Iraq,… |
|
|
Charles Martel |
was the leader of the Frankish army at the Battle of Tours in 732, and played a key role in turning back . |
|
|
Martin luther |
Rebelled against Roman Catholic Church and started Lutheranism |
|
|
Crusades |
a medieval military expedition, one of a series made by Europeans to recover the Holy Land from the Muslims in the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries. |
|
|
Feudalism |
the dominant social system in medieval Europe, in which the nobility held lands from the Crown in exchange for military service, and vassals were in turn tenants of the nobles, while the peasants (villeins or serfs) were obliged to live on their lord's land and give him homage, labor, and a share of the produce, notionally in exchange for military protection. |
|
|
Charlemagne |
Charlemagne, also known as Charles the Great or Charles I, was King of the Franks who united most of Western Europe during the early Middle Ages and laid the foundations for modern France and Germany. |
|
|
Quran |
Muslim |
|
|
Abraham |
The unifying characteristic of Abrahamic religions is that all accept the tradition that God revealed himself to the patriarch Abraham. All are monotheistic, and conceive God to be a transcendent creator and the source of moral law. |
|
|
Five pillars |
The Five Pillars of Islam are the framework of the Muslim life. They are the testimony of faith, prayer, giving zakat (support of the needy), fasting during the month of Ramadan, and the pilgrimage to Makkah once in a lifetime for those who are able. |
|
|
4 noble truths |
the doctrines of Buddha: all life is suffering, the cause of suffering is ignorant desire, this desire can be destroyed, the means to this is the Eightfold Path. |
|
|
Nirvana |
Nirvana is a place of perfect peace and happiness, like heaven. In Hinduism andBuddhism, nirvana is the highest state that someone can attain, a state of enlightenment, meaning a person's individual desires and suffering go away. |
|
|
Torah |
The Torah, or Jewish Written Law, consists of the five books of the Hebrew Bible - |
|
|
Muhammed |
is the founder and chief prophet of Islam and the source for the Quran (Islam/Muslims) |
|
|
Mahatma gandhi |
Wins war with peace |
|
|
Jawaharla Nehru |
the first Prime Minister of India and a central figure in Indian politics for much of the 20th century. |
|
|
Sepoy rebellion |
violent and very bloody uprising against British rule in India in 1857. |
|
|
East India Company |
an English joint‑stock company, formed to pursue trade with the East Indies, but which ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and Qing China. |
|
|
Mahhamad Ali jinnah |
was a lawyer,politician, and the founder of Pakistan.[1] |
|
|
Pacific |
|
|
|
Atlantic |

|
|
|
Indian |

|
|
|
Persian gulf |
|
|
|
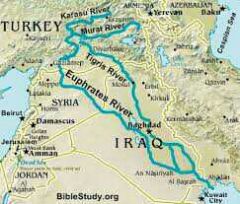
Euphrates |
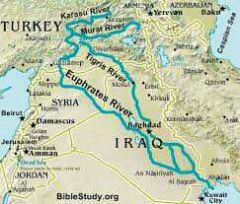
|
|
|
Tigris |
|
|
|
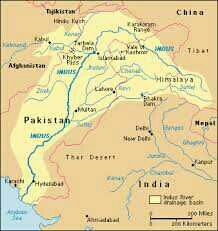
Indus |
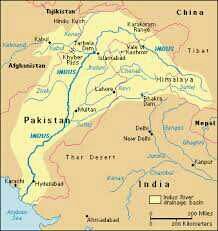
|
|
|
Ganges |
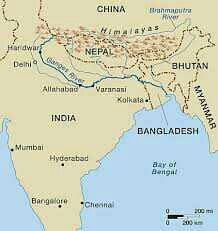
|
|
|
Yellow |
|
|
|
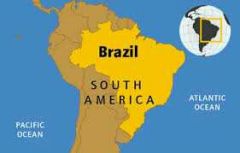
Brazil |
|
|
|
India |
|
|
|
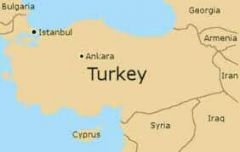
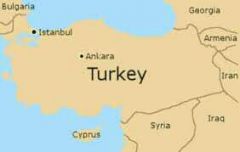
Turkey |
|
|
|
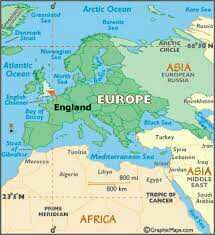
England |
|
|
|
Iran |
|
|
|
Pakistan |
|
|
|
Greece |
|
|
|
Saudi Arabia |
|
|
|
Iraq |
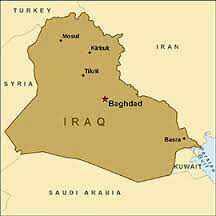
|
|
|
Japan |
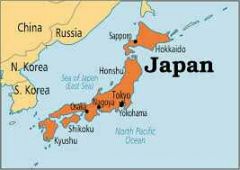
|

