![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Stability of joints |
Articulating surfaces |
|
|
How would you examine the hip joint
|
Patient supine position |
|
|
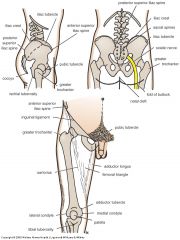
Lateral view of inominate
|
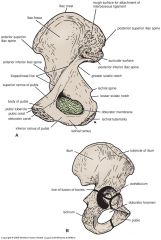
|
|
|
Femur landmarks
|
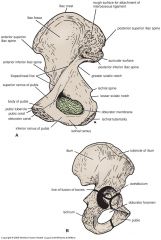
|
|
|
Surface landmarks
|
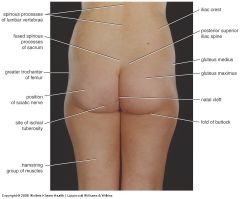
|
|
|
Surface landmarks anterior
|
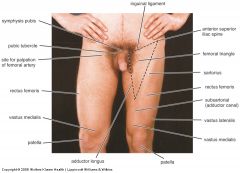
|
|
|
Synovial joint
|
|
|
|
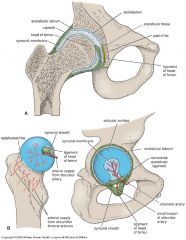
Location and anatomy
|
|
|
|
Lateral view of hip joint
|
|
|
|
Anterior thigh muscles
|
Flexor a of the hip |
|
|
Pectineus
|
Or: superior ramus of pubis
In: pectineal line infer to lesser trochanter Femoral nerve: l2 l3 Adducts flexes thigh Assists medial rotation |
|
|
Iliopsoas
|
Iliacus
Psoas major Papas minor All flex thigh at hip joint and stabilises hip joint |
|
|
Iliacus
|
Or: iliac crest, ala of sacrum, iliac fossa
In: lesser trochanter, tendon of psoas major. Femoral nerve l2 l3 |
|
|
Psoas major
|
Or: T12-l5 veterbrae
In: lesser trochanter of femur Lumbar nerves l1 l2 l3 |
|
|
Psoas minor
|
Or: t12-l1
In: pectineal line Lumbar nerves l1-l2 |
|
|
Sartorius
|
Or: asis
In: sup. medial surface of tibia Femoral nerve l2 l3 Hip joint: flexes, abducts and laterally rotates thigh Knee joint: flexes leg, medially rotates leg when knee is flexes. |
|
|
Anterior flexor muscles
|
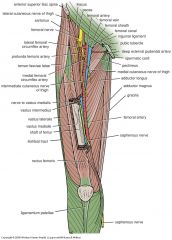
|
|
|
Anterior extensor muscles
|
Quadriceps femoris
|
|
|
Quadriceps fenoris
|
Rectus femoris
Vastus lateralis Vastus medialis Vastus intermedius |
|
|
Quadriceps common traits
|
Via common tendinous
Independent attachments to base of patella Femoral nerve l2 l3 l4 Extend leg at knee Rectus steadies hip joint and helps iliopsoas flex thigh |
|
|
Rectus femoris
|
Origin: Aiis
Sup. to acetabulum |
|
|
Vastus femoris
|
Gr. trochanter
Lateral lip of linea aspera |
|
|
Vastus medialis
|
Intertrochanteric line and medial lip of linea aspera
|
|
|
Vastus intermedius
|
Anterior and lateral surfaces of shaft of femur
|
|
|
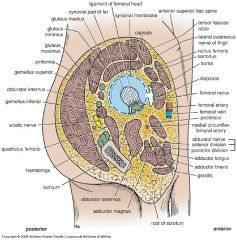
Medial muscles of thigh
|
Adductor group
All supplied by obtrusive nerve except hamstring Next layer of muscles under anterior muscles |
|
|
Medial muscles
|
Adductor longus |
|
|
Adductor longus
|
Or: body of pubis inferior to pubic crest |
|
|
Adductor brevis
|
Or: body and inferior ramus pubis |
|
|
Adductor magnus
|
2 parts: adductor and hamstrings
|
|
|
Adductor Magnus adductor
|
Or: inferior ramus of pubis
In: gluteal tuberosity, linea aspera Obturator nerve posterior branches Flexes thigh |
|
|
Adductor Magnus hamstrings
|
Or: ishial tuberosity |
|
|
Gracillus
|
Or: body and inferior ramus of pubis |
|
|
Obturator externus
|
Or: margins of obturator Foramen |
|
|
Actions of adductor
|
Pull thigh medially, toward or past median plane. |
|
|
Testing of medial thigh muscles
|
Individual is supine |

