![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
causes of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
|
- stone obstruction
- uti: e coli and proteus |
|
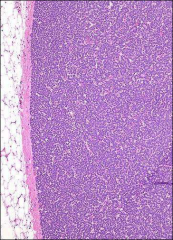
what
|
metanephric adenoma (adults, counterpart to Wilms in kids), benign
near solid looking, orderly array of tubules, can see psammoma bodies |
|
what
|
oncocytoma - on micro can have tubules within a paucicellular stroma
|
|
|
nonsporadic causes of clear cell RCC
|
VHL disease, APKD, acquired cystic kidney disease (long-term hemodialysis)
|
|
|
putative cell of origin clear cell RCC
|
Proximal convoluted tubules
|
|
|
stain chromophobe rcc
|
hale's colloidal iron
|
|
|
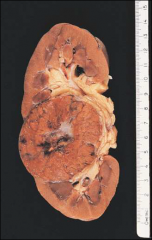
cf gross of chromophobe rcc to oncocytoma
|
same exc oncocytoma with central scar
|
|
|
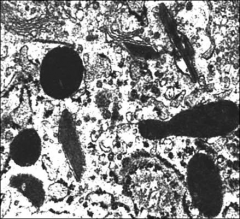
em chromophobe
|
microvescles some of which are mt
|
|
|
rcc with better prognosis than conventional
|
pap rcc, chromophobe rcc
|
|
|
rcc with worse prognosis
|
sarcomatoid
|
|
|
see medullary ca of kidney think
|
sickle cell, young black males, poor prognosis
|
|
|
clues to medullary ca microscopically
|
- high grade nuclei
- centered on medulla |
|
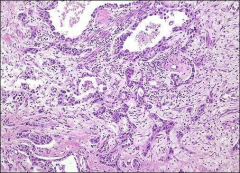
what
|
collecting duct ca
Cytoplasmic and intraluminal mucin Hobnail cells centered on medulla partially cystic, can have variable growth patterns desmoplasia |
|
what tumor
|
JGA
|
|
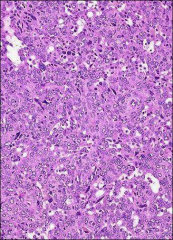
hypokalemia
|
JGA tumor, benign, hyperreninism
|
|
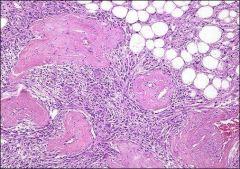
what, ihc, em
|
angiomyolipoma
mature fat, thickwalled vessels, smooth muscle HMB45, actin EM: premelanosomes |
|
|
pecoma family
|
Angiomyolipoma
• Lymphangioleiomyomatosis • Clear cell sugar tumor of lung • Clear cell myomelanocytic tumor of the falciform ligament* all assoc with TS except last one |
|
|
a michaelis gutman body is...
|
lysosomes containing bacterial degradation products
|
|
|
alt name for mesonephric adenoma
|
nephrogenic adenoma - not true neoplasm - reaction to injury
|
|
|
alt name for nephrogenic adenoma
|
mesonephric adenoma - not true neoplasm -reaction to injury
|
|
|
mass on posterior wall/dome of bladder, young woman
|
think endocervicosis
|
|
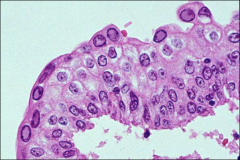
what
|
BK virus, SV40 family, DNA viruses
decoy cells (shown) and comet cells (short cytoplasmic tails) |
|
|
fish probes for urovysion
|
chromosomes 3, 7, 17, and the 9p21 locus
|
|
|
adenoca of bladder association
|
exstrophy, urachal remnants
|
|
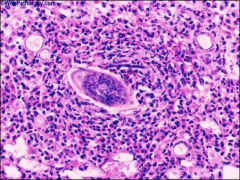
what
|
schistosomiasis, scca bladder
|
|
|
hypercalcemia and SIADH
|
small cell undifferentiated ca of bladder
|
|
|
when see basal cell hyperplasia
|
post radiation or hormone deprivation
|
|
|
stains/ihc for mucinous metaplasia
|
PSA and PAP –ve
PAS, mucicarmine and Alcian blue + |
|
|
what is atypical adenomatous hyperplasia
|
no prominent nuclei, patchy basal layer otherwise can mimic ca
|
|
|
Xanthoma of prostate
|
CD68+ cell aggregates
|
|
|
criteria for ASAP
|
3 or more glands to call ca
|
|
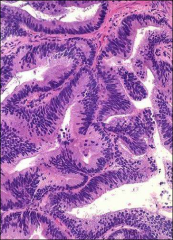
what, where, stains
|
prostatic large duct ca, (aka endometrioid ca), resembles endometrium; mass veromontanum
PSA, PAP staining |
|
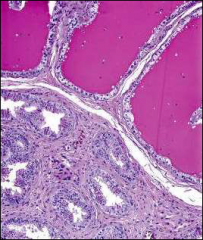
know this one, male GU - where, what, association
|
epidydimis, papillary cystadenoma, VHL!!!!!!
|
|
|
clinical setting for malignant mesothelioma in GU region
|
recurrent hydroceles,
|
|
|
strange/seemingly unique staining for malignant meso of GU tract
|
Alcian blue +, hyaluronidase sensitive
|
|
|
histo fx of GU-based malignant meso
|
epithelioid, biphasic
usually noninvasive/exophytic |
|
|
most common sarcoma of childhood? of adults?
|
- embryonal RMS for kids
- liposarcoma for adults |
|
|
5 paratesticular tumors to think about
|
-papillary cystadenoma of testis
- adenomatoid tumor - embryonal RMS - liposarcoma - malig mesothelioma |
|
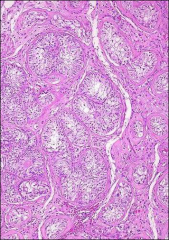
what
|
pick adenoma, a/w crptorchidism, no spermatogonia
|
|
|
ihc unique to seminoma of all the GCTs
|
cd117
|
|
|
clinical behavior of spermatocytic seminoma, specific fx to highlight in micro
|
-indolent (unless sarcomatoid component)
- polymorphic cells (varying sizes) - spireme (filamentous) nuclei |
|
|
gross of embryonal ca
|
often necrotic
|
|
|
embryonal ca - ihc unique of the GCTs
|
CD30
|
|
|
embryonal ca ihc
|
CD30, keratin, OCT3/4 and PLAP
|
|
|
alt name for yolk sac tumor
|
endodermal sinus tumor
|
|
|
key ihc for yolk sac tumor and two others and histochemical stain (1)
|
AFP
keratin, PLAP PAS+ hyaline globules |
|
|
ihc for chorioca
|
hcg and keratin
|
|
|
teratoma in boys
|
Immature form: primitive mesenchyme (neurotubules)
b9 course even with immature elements |
|
|
what sertoli cell tumor type is a/w endocrinopathies
|
large cell calcifying Sertoli cell tumor
|
|
|
when are sertoli cell tumors seen bilaterally
|
peutz-jeghers
|
|
|
key ihc for sertoli cell
|
inhibin
also keratin |
|
|
what are Charcot-Bottcher filaments
|
Spindle-shaped crystalloids seen in sertoli cells by EM
|
|
|
two syndromes a/w large cell calcifying sertoli cell tumor
|
Carneys
Peutz Jegher's |
|
|
some endocrine-related findings in carney's as well as skin fx
|
also recall LAMB/NAME
in endocrine, thought to be a ACTH-independent adrenal process Acromegaly Pituitary gigantism Hypercortisolemia Sexual precocity Spotty mucocutaneous hyperpigmentation |
|
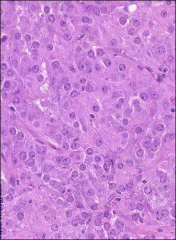
what
|
leydig cell tumor
|
|
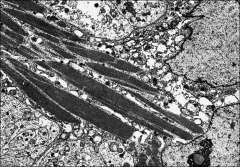
what
|
leydig cell tumor - reinke's crystals
|
|
|
ihc for leydig cell tumor
|
Inhibin +, keratin +/-
|

