![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
three causes of PID
|
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
• Chlamydia • Actinomyces |
|
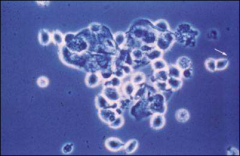
what
|
trich, Frothy discharge
• Fishy odor |
|
|
histo of LSC
|
Squamous hyperplasia associated with inflammation
|
|
|
what is BOWENOID PAPULOSIS
|
Multiple small erythematous/white macules/papules
– Both sexes, young – F: VIN III – HPV 16, often regress |
|
|
histochemical stains for extramammary paget's
|
Mucin, PAS +
|
|
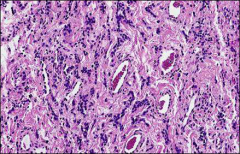
what, histo fx, ihc
|
angiomyofibroblastoma:
histo: Well circumscribed • Alternating hyper and hypocellular zones • Thin-walled vessels • Stromal cells, wavy collagen strands ihc: Vimentin, desmin, CD 34, ER, PR+ |
|
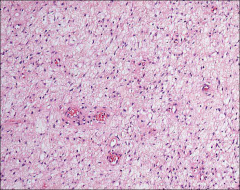
what, ihc
|
aggressive angiomyxoma: all hypocellular, rbc extravascation, infiltrative border, thin and thick-walled blood vessels
SMA, HHF 35, ER / PR + |
|
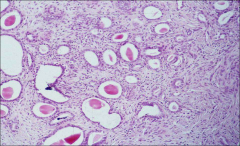
what
|
mesonephric remnants: mesonephric remnants; stroma is "just around these" CD10+
|
|
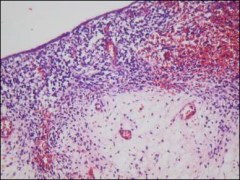
what
|
botryoid rhabdo: note cellular condensation with cambium - less aggressive than other embryonal rhabdo
|
|
|
HPV 6, 11 viral protein
|
Koilocytosis related to viral E4
|
|
|
viral proteins of HPV16, 18
|
Only early E6, E7 genes expressed
• Integration of viral DNA • E6 binds P53 • HPV E7 interacts with Rb protein |
|
|
ihc to distinguish endocervical from endometrial ca
|
endocervical adenoca: p16, cea
endometrial: vimentin, CK+, bcl2 random: if mits towards lumen, endocervical (mits usually more basal in endometrium) |
|
|
what is glassy cell carcinoma
|
adenosquamous ca (very aggresive, eos in background)
barrel shaped cx |
|
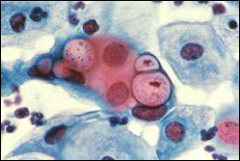
what
|
chlamydia
|
|
|
infectious cause of acute endometritis
|
Group A streptococci
|
|
|
review dating?
|
dating endometrium
exodus: day 6-10 of endometrium (seen in pap) |
|
|
what is Stein Leventhal syndrome
|
PCOS
|
|
|
cytology background endometrial ca
|
watery diathesis?
|
|
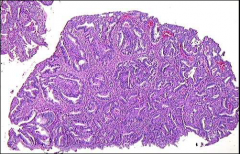
what, uterus
|
apa - note smooth muscle in polyp, usu > 2cm, often squamous morules
|
|
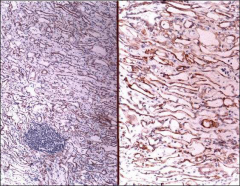
what
|
adenomatoid tumor
|
|
|
endometrial ca with poor prognoses
|
- serous papillary
- clear cell - scca |
|
|
significance of p53 in endometrial ca
|
associated with more aggressive subtypes
|
|
|
ihc for endometrial stroma sarcoma
|
• Beta catenin overexpression
• CD 10 + • ER / PR +, if low grade ESS Vimentin + • Actin – focally + • Desmin – |
|
|
expected mit count for uterine leiomyosarcoma
|
>10/10hpf
|
|
|
tumor arising from endometriosis
|
clear cell
endometrial hope i have this right |
|
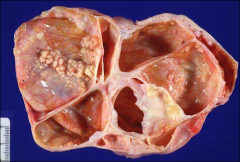
what
|
serous tumor; 30-50% bilateral
|
|
|
for borderline tumors of ovary, how much invasion is allowed (so not to call invasive)
|
microscopic focus ,3 mm/10mm2 allowed
|
|
|
implants from borderline tumors
|
noninvasive: - superficial, stuck on surface
can be desmoplastic but still appear stuck on invasive: deep, retraction seen |
|
|
name two types of mucinous ovarian tumors and describe clinical implications
|
intestinal type: most are this, if malignant, worse prognosis
mullerian type: more often bl, more often a/w em-osis |
|
|
ck 7 and ck 20 stains for serous and mucinous tumors of peritoneum
|
serous 7+20-
mucin7+20+ |
|
|
origin of peritoneal mucinous, serous
|
check this!!!
|
|
|
criteria for delineating btwn endometrial ca vs. mixed
|
if >10% of something else, call mixed
|
|
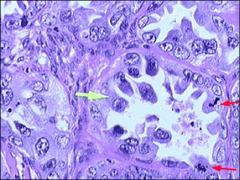
what, histology
|
clear cell carcinoma: hobnail nuclei, bulge into lumen, Pleomorphic macronucleoli
|
|
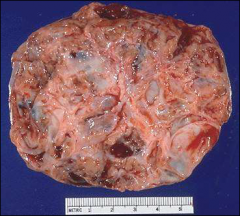
what, ovary
|
granulosa cell tumor
|
|
|
ihc for granulosa cell tumor
|
Inhibin
• Calretinin • Vimentin • WT1 • CD 99 • S100 • CD56 • SF1 (steroidogenic factor) |
|
|
cytogenetics on granulosa cell tumor
|
FOXL2 gene abnormality on xsome 3
|
|
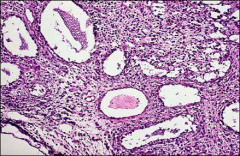
what
|
juvenile granulosa cell tumor
very mit active, excellent prognosis ddx: germ cell, hypercalcemia small cell histo: Irregular macrofollicles • Mitoses common • Larger, rounded nuclei • No nuclear grooves • Abundant leutinized cytoplasm • Pleomorphism, atypia |
|
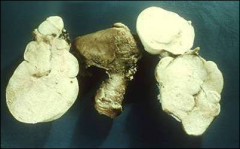
what, syndrome
|
fibroma, meigs
if fibroma/thecoma: produce estrogen thecoma component will be oil red O + |
|
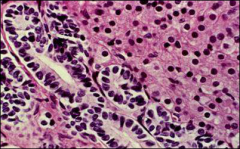
what
|
sertoli -leydig
|
|
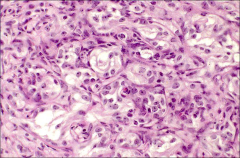
what
|
sertoli cell tumor
|
|
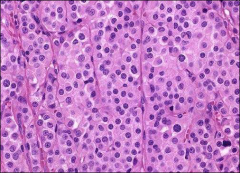
what
|
leydig cell tumor, look for reinke's
|
|
|
Most common ovarian cancers in
children |
Germ cell tumors
|
|
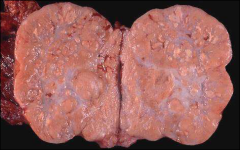
what
|
dysgerminoma
|
|
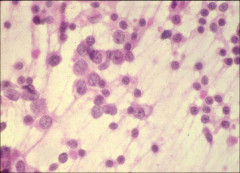
what
|
dysgerminoma
|
|
|
ihc for dysgerminoma
|
PLAP
– CD117 (membrane staining) – D2-40 – OCT4 – SALL4 – NANOG – CK (minimal) – EMA - |
|
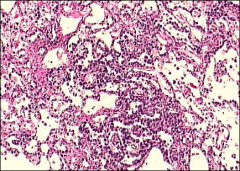
what, histo and ihc
|
yolk sac tumor
histo: Lace-like reticular network, Schiller Duvall body ihc: AFP, Glypican 3, SALL4, CK + |
|
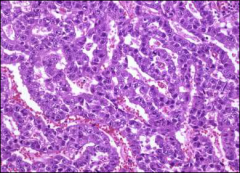
what, ihc
|
embryonal ca
Epithelial, glandular features • Keratin +, CD 30 +, OCT ¾ + NANOG, SALL4, SOX2 + |
|
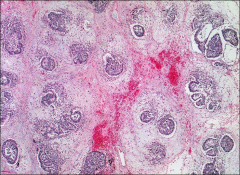
what
|
polyembryoma
|
|
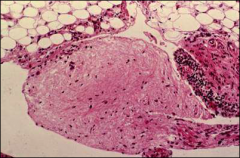
what
|
gliiomatosis peritonei - doesn't come from germ cell itself
|
|
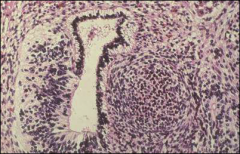
what
|
immature teratoma
|
|
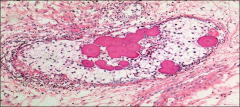
what
|
gonadoblastoma
|
|
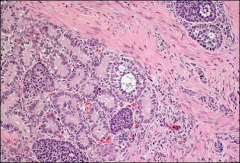
what
|
gynadndroblastoma (sertoli and granulosa)
|
|
|
carcinosarcoma in ovary vs. endometrium -most common heterolgous component
|
ovary - cartilage
endometrium - rhabdo |
|
|
common tumors to ovary
|
Colon
• Breast • Stomach • Pancreas • Leukemia • Lymphoma |
|
|
which has better prognosis de novo chorio or postpartum
|
postpartum
(ovarian chorioca has worst prognosis) |

