![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
103 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
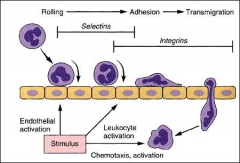
RAT
|
SIT
|
|
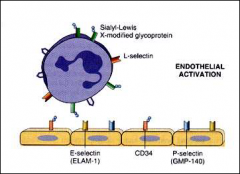
for review
|
binding factors
|
|
|
adhesion mediated by
|
Mediated by integrins ICAM-1 and VCAM-1
|
|
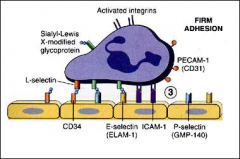
for review
|
review
|
|
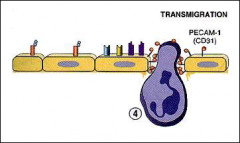
transmigration
|
just review
|
|
|
for phagocytosis: recognition and attachment
|
Opsonins (IgG and C3) coat target
|
|
|
phagocytosis o2 dependent killing
|
O2 dep: Reactive O2 species in lysosomes
|
|
|
for phagocytosis: O2 independent killing
|
O2 indep: Bactericidal permeability agents, lysozyme,
MBP, lactoferrin |
|
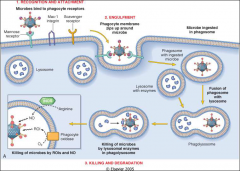
for phagocytosis
|
steps
|
|
|
LAD 1 defect
|
•B chain of CD11/CD18 integrins
|
|
|
LAD 2 defect
|
Sialylated oligosaccharide
|
|
|
CGD defect
|
defective chemotaxis:
•NADPH oxidase (membrane) - x linked •NADPH oxidase (cytoplasm) - AR |
|
|
MPO deficiency defect
|
Absent H2O2 system, cant make HCL
•no problem w infections |
|
|
Chediak-Higashi syndrome defect
|
Lysosomal defect
|
|
|
Thermal injury, DM, CA, sepsis acquired immunologic defect
|
Chemotaxis
|
|
|
Dialysis, DM - acquired immunologic defect
|
Adhesion
|
|
|
Leukemia, anemia, sepsis, DM,
neonates, malnutrition - acquired immunologic defect |
•Phagocytosis & microbicidal activity
|
|
|
clinical findings in LAD1 (defect in CD11/CD18 integrins on polys)
|
Neutrophils can roll but do not stick
• Recurrent bacterial infections • Inflammatory lesions lack neutrophils • But, ↑ neutrophils in the circulation |
|
what
|
chediak-higashi: defect in lysosome so large lysosomal vesicles
|
|
|
mutation in chediak-higashi
|
Mutation in LYST lysosomal trafficking regulator gene
|
|
|
other problems in Chediak Higashi besides defect in phagocytosis
|
any cell with granules including melanosomes (ocular albinism); EBV lymphoproliferative d/o
|
|
|
clinical scenario: Young, men with infections and granulomas at autopsy
– recurrent catalase + bacterial and fungal infections think: |
CGD (xlinked, defect in NADPH oxidase system)
|
|
|
Nitoblue tetrazolium reductase test negative: think
|
CGD
Inability to reduce NBT – reduced O2 consumption, reduced H2O2 and O2- production |
|
|
deficiencies in Membrane Attack Complex (MAC C5-9), leaves you vulnerable to what:
|
encapsulated
Neisseria, Strept, H. influenzae, Listeria INSL (insulated/encapsulated) |
|
|
which complement components mediate vasodilation
|
C3a and C5a
|
|
|
which complement mediates activation of arach. acid pathway (lipoxygenase)
|
C5a
|
|
|
which complement mediates Leukocyte activation, adhesion and chemotaxis
|
C5a
|
|
|
which complement acts as opsonin
|
C3b
|
|
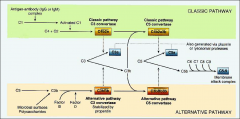
complement activation
|
for review
|
|
|
what is Decay accelerating factor
|
acts to destabilize convertases that activate complement
|
|
|
what dz occurs where defect in DAF and can't turn off complement
|
PNH
you cannot turn off the complement system -RBCs are destroyed and platelets bind to complement -Hemolytic anemia and thrombosis |
|
|
how does AA get out of cell membrane
|
phospholipases
|
|
|
what are the two pathways of AA metabolism
|
lipooxygenase and cyclooxygenases
|
|
|
Cyclooxygenases synthesize
|
Prostaglandins
Thromboxanes |
|
|
Lipoxygenases synthesize
|
Leukotrienes
Lipoxins |
|
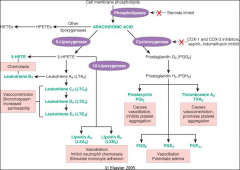
where steroids and asa act
|
for review
|
|
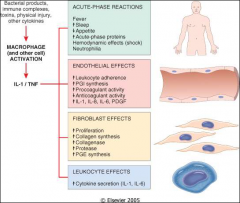
effect of TNFa and IL1
|
review
|
|
|
mediators released by macs
|
Tox. O2
Proteases Collagenases Chemotx factors Coag factors AA metabolites NO PDGF FGF TGF |
|
|
czome for Familial retinoblastoma
|
13
|
|
|
NF 1 and 2 czomes
|
17 and 22
|
|
|
four tumors of turcot's syndrome
|
(colon, breast, ovary & brain
|
|
|
dna repair defects (4 syndromes)
|
Xeroderma pigmentosa (XP) – 9,19,11,16,13
• Ataxia-telangiectasia – 11q22.3 • Bloom’s syndrome – 15q26.1 • Fanconi’s anemia – 9,16,3,6 |
|
|
two signal transduction oncoproteins
|
ras (GTP binding)
• abl (non-receptor tyrosine kinase) |
|
|
nuclear regulatory protein oncoproteins
|
myc family
|
|
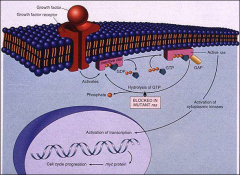
oncoproteins
|
for review
|
|
|
what kind of oncoprotein is her2/neu
|
receptor tyrosine kinases (growth factor receptor
|
|
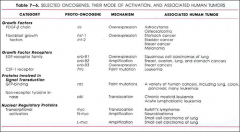
for review
|
read through
|
|
|
how is ras gene activated
|
point mutation
|
|
|
aml m2 (myeloblastic with differentiation)
|
t(8;21)
|
|
|
aml m3 promyelocytic
|
t(15;17)
|
|
|
aml m4 eo myelomonocytic with eo
|
inv 16
|
|
|
aml m5, monoblastic
|
t(9;11)
|
|
|
common translocation in all
|
t (4:11)
|
|
|
burkitt
|
t(8;14)
|
|
|
follicular
|
t(14;18)
|
|
|
b LBL - 7 recurrent translocations
|
B LBL w t(9;22)(q34;q11.2); BCR-ABL1
2. B LBL w t(v;11q23); MLL rearranged 3. B LBL w t(12;21(p13;q22);TEL-AML1 4. B LBL w hyperdiploidy 5. B LBL w hypodiploid 6. B LBL w t(5;14)(q31;q32);IL3-IGH 7. B LBL w t(1;19)(q23;p13.3)E2A-PBX1 |
|
|
good b LBL genetics
|
t(12;21) (p13;q22); TEL/AML1
• Hyperdiploid > 50 • Age 4-10 |
|
|
bad b LBL genetics
|
Hypodiploid
• t(9:22) (q34;q11.2); BCR/ABL • 11q23; MLL • t(1;19) (q 23;p13.3); PBX/E2A |
|
|
most common b LBL in infant
|
t(4;11)
|
|
|
most common b LBL translocation in child
|
t(12;21)
|
|
|
most common b LBL in adults
|
t(9;22)
|
|
|
genetics of ewings
|
T(11;22) EWS/FLI-1
T(21;22) EWS/ERG Many others EWS/Other |
|
|
genetics of DSRCT
|
T(11;22) EWS/WT-1
|
|
|
genetics of clear cell sarcoma
|
T(12;22) EWS/ATF-1, EWS/TEC
|
|
|
genetics of myxoid liposarcoma
|
T(12;16) EWS/CHOP EWS/FUS
|
|
|
genetics of alveolar soft part sarcoma
|
T(X;17) ASPL/TFE3
|
|
|
genetics of synovial sarcoma
|
T(X;18) SYT/SSX1 SYT/SSX2
|
|
|
genetics of rhabdomyosarcoma
|
T(1;13) PAX7/FKRH
T(2;13) PAX3/FKRH |
|
|
dfsp genetics
|
T(17;22) CALIA1/PDGFß
|
|
|
low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma genetics
|
T(7;16) FUS/CREB
|
|
|
tumor suppressor genes
|
Rb gene (retinoblastoma) 13q14
• p53 gene (G1 arrest apoptosis) 17p13.1 • APC gene (adenom. polyposis coli) 5q21 • NF-1 gene (neurofibromatosis) 17q11 • NF-2 gene (neurofibromatosis) 22q12 • DCC gene (deleted in colon CA) 18q21 • WT-1 gene (Wilms’ tumor) 11p13 • VHL gene (von Hippel-Lindau) 3p25 |
|
|
P62
|
liver, mallory bodies
|
|
|
P63
|
breast/prostate - myoepithelial/basal celsl
|
|
|
P53
|
gi tract, glandular dysplasia
|
|
|
trinucleotide repeat
|
Fragile X
Friedrich ataxia Spinocerebellar ataxia Myotonic dystrophy |
|
|
wiscott-aldrich sx
|
X-linked recessive
Eczema, thrombocytopenia and immune deficiency wiscite-aldrich where I, T, E |
|
|
arsenic carcinogenicity
|
skin ca
|
|
|
ebv-related cancers
|
Burkitt’s Lymphoma, especially endemic
• Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders • Nasopharyngeal CA • Hodgkin lymphomas • Primary effusion lymphoma • Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma • Aggressive NK/T cell lymphoma |
|
|
tumors and hypoglycemia: name three
|
Fibrosarcoma, solitary fibrous tumor, HCC
IGF or increased insulin |
|
|
tumor and polycythemia
|
metanephric adenoma
Renal cell carcinoma • Cerebellar hemangioblastoma • Hepatocellular carcinoma • Leiomyoma • Solitary fibrous tumor |
|
|
acanthosis nigricans + tumor
|
Gastric CA
• Lung CA • Uterine CA |
|
|
tumors in nf1 and nf2
|
Multiple NFs (plexiform NFs), schwannomas
(bilateral acoustics in 2), gliomas, pheos, somatostinomas |
|
|
tuberous sclerosis tumors and genetics
|
Chromosomes 9 & 16
• Cortical tubers, sclerosis, SEGAs, cardiac rhabdomyomas, pulm LLM, AMLs, sebaceous adenomas, ash green patches, subungual fibromas |
|
|
tumors/findings of VHL
|
RCC (bilateral)
papillary cystadenoma of pancreas, pheos • Cavernous hemangiomas/hemangioblastomas of retina, cerebellum/brainstem • Hemangiomas/cysts in pancreas, skin, liver,kKidney |
|
|
gardners tumors
|
FAP & jaw osteomas, desmoids, cysts of skin
• Soft tissue tumors (desmoplastic fibromas) |
|
|
cowden genetics and tumors
|
10q23 (same as MEN II – MEN I 11p13)
• 9q22.3 • FAP with increased risk of breast, thyroid CA • Tricholemommas |
|
|
tumors of Peutz-jeghers
|
SCTAT/Large cell calcifying Sertoli tumors
• Adenoma malignum of cervix • Increased risk of breast, lung, ovary, pancreas and uterine CA; rare malignant transformation in GI tract |
|
|
genetics and tumors of turcot syndrome
|
AR
FAP with brain tumors (astrocytomas – GBMs) • HNPCC genes • DNA mismatch/repair defect |
|
|
findings of Canada-cronkhite
|
FAP (hamartomatous polyps) with skin & nail changes
|
|
|
findings in gorlin syndrome
|
cutaneous basal cell carcinoma and
a mandible odontogenic keratocyst Intracranial calcification • Skeletal abnormalities: bifid ribs, kyphoscoliosis, calcification of falx cerebri • Distinct faces: frontal/temporopariental bossing, hypertelorism, and mandibular prognathism |
|
|
genetics of gorlin
|
Mutated PTCH gene Chr (9q)
|
|
|
findings in Werner Syndrome
|
MEN I, menin, czome 11 PPPAAT
Parathyroid adenomas/hyperplasia – Pituitary adenomas/hyperplasia – Pancreas adenomas/carcinomas/hyperplasia – Adrenal hyperplasia (note like mini II – Thyroid C-cell hyperplasia (note like mini II |
|
|
findings in sipple syndrome
|
men II, czome 10 (ret)
Parathyroid adenomas/hyperplasia Pheochromocytomas Thyroid medullary carcinomas |
|
|
menIIb
|
menIIa +with mucocutaneous ganglioneuromas and
marfanoid habitus (RET (different locus) |
|
|
minimal change dz in kidney
|
hodgkin lymphoma
|
|
|
reye
|
abnl mitochondria
|
|
|
assoc with Plummer Vinson
|
FeDA,
pulmonary hemorrhage |
|
|
assoc with multicentric castlemans
|
POEMS
|
|
|
assoc with Heinz bodies
|
G6PD, unstable
HB pyruvate kinase, sulf Hb |
|
|
mass in the lower
extremity of a female adolescent or young female adult and rhomboid crystals on EM |
alveolar soft parts sarcoma
|
|
|
calc of Hct =
|
mcv * rbc (femtoliters)
|
|
|
calc of MCH
|
= hb*10/rbc (picograms)
|
|
|
calc of • MCHC =
|
hb/hct (g/dL)
|

