![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Anatomy |
The study of structure |
|
|
|
Physiology |
Study of function |
|
|
|
Levels of organization |
1) Molecules 2) Cells 3) Tissues 4) Organs 5) Organ systems 6) Human organism |
From simple to complex |
|
|
Organ |
A group of tissues arranged to perform a particular function |
EX: Heart, lung |
|
|
Organ System |
A group of organs that help each other to perform a particular function |
There are 11 organ systems |
|
|
Integumentary System |
Provides the covering for the body, and maintains body temperature |
Skin, hair, nails |
|
|
Skeletal system |
Provides support and protection |
Bones, joints, and cartilage |
|
|
The muscular system |
Enables the body to move Skeletal muscles Cardiac muscles Smooth muscles |
Contraction/relaxation |
|
|
The nervous system |
Concerned with sensation, interpretation, integration |
Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sense organs |
|
|
Endocrine system |
Secretes hormones that help control the body activities such as growth and reproduction |
Hormones |
|
|
Circulatory system |
Transport nutrients and oxygen around the body |
The heart |
|
|
The lymphatic system |
Concerned with defense againist pathogens and and forgein substances |
Lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, lymph, lymphoid |
|
|
The respiratory system |
Takes in oxygen and excreted carbon dioxide |
Oxygen, carbon dioxide |
|
|
The digestive system |
Takes in, breaks down, and absorbs food; it then excreted waste |
|
|
|
The urinary system |
Excretes waste and regulates body water and dissolved substances |
Kidneys |
|
|
The reproductive system |
Is concerned with the production of offspring |
Ovaries |
|
|
Homeostasis |
The ability of the body to maintain a stable internal environment in response to a changing external environment |
Staying the same |
|
|
Anatomical position |
The body standing erect, arms by the side with palms facing forward |
|
|
|
The anatomical terms |
Describe the body in its anatomical positions |
|
|
|
Anterior (Ventral) |
Toward the front surface Paired with posterior |
Front |
|
|
Posterior (dorsal) |
Toward the back surface Paired with anterior |
Dorsal/back |
|
|
Superior |
Part that is above another part or is closer to the head Ex: the head is closer to the chest Paired with inferior |
Above |
|
|
Inferior |
A part is located below another part Ex: the chest, is inferior to the head Paired with superior |
Below |
|
|
Medial |
Toward Midline of the body A line drawn drawn through the middle of your body Ex: nose is medial to the ears Paired with lateral |
Midline |
|
|
Lateral |
Away from midline of the body Ex: the ears are lateral to the nose Paired with medial |
Away from middle |
|
|
Proximal |
The structure is nearer the point of attachment Ex: the wrist is proximal to the fingers Paired with distal |
Closer |
|
|
Distal |
A part that is further away from the point of attachment of another part Ex: the wrist is distal to the elbow Paired with proximal |
Further away |
|
|
Superficial |
A part located on or near the surface of the body Ex: the skin is superficial to the muscles Paired with deep |
Surface |
|
|
Deep |
The body part is away from the surface of the body Ex: the bones are deep in the skin Ex: Paired with superficial |
Away from surface |
|
|
Central |
The part is located in the center Ex: the heart is located centrally Paired with peripheral |
Centrally |
|
|
Peripheral |
Away from the center Ex: away from the center and extending toward the limbs Central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) /peripheral nervous system (nerves) |
Away from center |
|
|
How many planes are there? |
Three planes: 1) Sagittal 2) Frontal (cornal) 3) Transverse plane |
|
|
|
Sagittal plane |
Divides the body length wise into right and left portions |
|
|
|
The frontal (cornal) |
Divides the body into anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) portions Front part and back part of your body |
Crown |
|
|
Transverse |
Divides the body horizontally creates an upper (superior) and lower (inferior) body |
Cross section |
|
|
Dorsal cavity |
Contains the cranial cavity (brain) The spinal cavity (spinal cord) |
Back |
|
|
Ventral cavity |
Contains the thoracic and adominopelvic cavity |
Larger/front |
|
|
Thoracic cavity |
Above the diaphragm Contains the lungs, and the mediastinum (heart, trachea, esophagus, thymus gland, and the large blood vessels attached to the heart) |
In the Ventral cavity |
|
|
The adominopelvic cavity |
Located below the diaphragm Contains the abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity |
In the Ventral cavity/contains two cavities |
|
|
Abdominal cavity |
The upper part of the adominopelvic cavity (stomach, most of the intestines, the liver, the spleen, and the kidneys) |
Upper/Ventral |
|
|
The pelvic cavity |
Lower part of the adominopelvic cavity (reproductive organs, the urinary system, and the lower part of the intestines) |
Lower/Ventral |
|
|
How is the adominopelvic cavity divided? |
Four quadrants and nine regions |
|
|
|
The 4 quadrants in the adominopelvic cavity |
Right upper quadrant (RUQ) Right lower quadrant (RLQ) Left upper quadrant (LUQ) Left lower quadrant (LLQ) |
|
|
|
The nine regions in the adominopelvic cavity |
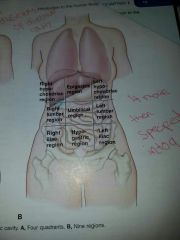
|
|
|
|
What is deep? |
*Opposite of superficial *body part that is away from the surface of the body Ex: bones are deep to skin |
|
|
|
Pedal |
Foot area |
|
|
|
Popliteal |
Refers to the area behind the kneecap |
|
|
|
Gluteal |
Buttocks |
|
|
|
Fermonal |
Thigh area |
|
|
|
Sternal |
Refers to the area in the middle of the anterior chest |
|
|
|
Brachial |
Arm |
|
|
|
Axillary |
Armpit |
|
|
|
Deltoid |
Rounded area of the shoulder close to the upper arm |
|
|
|
Buccal |
Check |
|
|
|
Umbilical |
Navel (belly button) |
|
|
|
Occipital |
Back of the head |
|
|
|
Scapular |
Shoulder blades area |
|
|
|
Pubic |
Genital area |
|
|
|
Abdominal |
Anterior trunk below the ribs |
|
|
|
Patellar |
Kneecap |
|
|
|
Lumbar |
Lower back region |
|
|
|
Cervical |
Neck region |
|
|
|
Inguinal |
Groin area |
|
|
|
Oral |
Pertaining to the mouth |
|
|
|
Digital |
Fingers and toes |
|
|
|
The cavity that is divided into quadrants, such as the right and left upper and lower quadrants |
Adominopelvic cavity |
|
|
|
The lower ventral cavity separated from the thoracic cavity by the diaphragm |
Adominopelvic |
|
|
|
The upper ventral cavity surrounded by the ribs and largely filled with lungs? |
Thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
The part of the ventral cavity that contains the mediastinum |
Thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
A dorsal cavity that extends from the cranial cavity and contains the spinal cord |
Vertebral cavity |
|
|
|
Also called the spinal cord |
Vertebral cavity |
|
|
|
A dorsal cavity that contains the brain |
Cranial cavity |
|
|
|
The location of the adominopelvic cavity |
Ventral cavity |
|
|
|
The location of the thoracic cavity |
Ventral cavity |
|
|
|
The cavity that is divided into regions, such as the epigastric, iliac, and umbilical regions |
Adominopelvic cavity |
|

