![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
PRIMARY HEMOSTASIS Step 1 transient vasoconstriction |
Neural reflex Endothelin |
|
|
PRIMARY HEMOSTASIS Step 2 platelet adhesion |
vWF binds exposed collagen Platelets binds vwf via Gp1b |
|
|
VWF |
From weibel palade bodies (of endothelial cells) and alpha granules (of platelets) |
|
|
PRIMARY HEMOSTASIS Step 3 platelet degranulation |
Adhesion induces shape change and release of multiple mediators ADP is released from platelet granules; promotes exposure of gPIIb/IIIa receptor on platelet TXA2 synthesized by platelet cox and promotes platelet aggregation |
|
|
PRIMARY HEMOSTASIS Step 4 platelet aggregation |
Platelets aggregate via gp2b/3a using fibrinogen (from plasma) as linking molecule |
|
|
Petechiae, purpura, ecchymoses |
Seen in QUANTITATIVE DISORDERS |
|
|
Labs |
Normal to ⬇️ platelet Normal (2-7mins) to prolonged bleeding test Blood smear - assess # and size of platelets BM biopsy - assess megakaryocytes |
|
|
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (Quanti) |
Autoimmune prodn of IgG against platelets (GPIIb/3a) |
|
|
ITP (Quanti) |
Autoimmune; IgG (from plasma cells in spleen) attach to platelets and are eaten up by splenic macrophages In children - after viral infection and self limited/immunization In adults - primary or secondary (autoimmune dx like SLE)
Labs: thrombocytopenia Normal PT/TT Inc megakaryocytes on BM biopsy
Tx: IVIG - "throwing a stick at the dog," short lived Splenectomy - for refractory cases |
|
|
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (Quanti) |
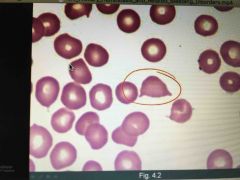
Formation of microthrombi in small vessels ➡️ shears the rbc that pass by (schistocytes) Seen in: HUS and TTP Tx: Plasmapheresis and corticosteroids (particularly in TTP) |
|
|
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic purpura (Quanti) |
TTP - ⬇️ ADAMST13 (degrades or chops up vWF into monomers) usually due to an autoimmune process which eats it up, lead to abnormal platelet adhesion |
|
|
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (Quanti) |
Endothelial damage from drugs and infection Ex: Dysentery - infection with E. coli O157:H7 verotoxin, causing endothelial damage
|
|
|
Bernard-Soulier Syndrome (Quali) |
Qualitative GP1b deficiency (impared platelet adhesion) Blood smear: mild thrombocytopenia with enlarged platelets (immature platelets that die easy) |
|
|
Glanzmann thrombasthenia (Quali) |
Deficiency GIIb/IIIa; impaired platelet aggregation |
|
|
Aspirin intake (quali) |
Irreversibly inactivates cyclooxygenase -> lack TXA2, impaired platelet aggregation |
|
|
Uremia (Quali) |
Platelet fxn is disrupted Both adhesion and aggregation is impaired |

