![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Allogeneic Blood Donor
|
Hgb>12.5 g/dL
infx dz screen: -hepB, hepC -HIV -HTLV -Syphilis -W Nile Virus -Chagas |
|
|
pRBC
|
RBC's suspended in: anticoagulant, additive solution (nutrients)
-vol: 250-300 mL -65% RBCs, 35% plasma and AS -contains WBC's, some plt, 200 mg Fe -42 day shelf life |
|
|
pRBC Indications
|
provides O2 carrying capacity
symptomatic anemia: tachy, AMS, ECG shows cardiac ischemia, angina, SOB, dizziness/lightheaded -not based on lab values alone |
|
|
1 unit pRBC provides
|
Hgb increase by 1g/dL
Hct increase by 3% |
|
|
pRBC transfusion
|
-RBCs infuse alone or w/ 0.9% NaCl through 170 um clot-screen filter.
-don't mix w/ Ca, dextrose, meds, hypertonic soln -avoid lactate infused ringers |
|
|
Type & Screen & Cross
|
Type & Screen: determine ABO/Rh type and Ab screen. May need blood w/in 72 hr
Type & Cross: determine ABO/Rh type, Ab screen, and crossmatch w/ donor. Need blood immediately |
|
|
ABO Antigens
|
-IgM>>IgG>IgA
-can bind C' -> intravascular hemolysis |
|
|
Rh Antigens
|
-Rh+ = D+ = more common
-highly immunogenic -important in both RBC and plt transfusion (product may contain some RBC components) |
|
|
Ab Screen
|
see if pt has Ab's to other major blood grp (caused by exposure to others' blood)
-mix pt plasma + 3 other known blood grps -if +rx, then do further testing of RBCs |
|
|
Plasma
|
-5 day shelf life (room temp)
-pooled plt concentrates = multiple donors -platelets, apharesis = one donor |
|
|
Indications for Plasma Transfusion
|
Thrombocytopenia:
-prophylactic: <10k -febrile/unstable: <20k -surgery/trauma: <50k -dramatically dropping plt count Plt dysfx: -uremia (renal) -ASA -post-cardiopulm bypass |
|
|
One therapeutic dose of Plts
|
-apharesis or 6 pooled plt concentrates
-incr plt count by 30-50k |
|
|
Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP)
|
contains:
-all clotting factors -400 mg fibrinogen -citrate |
|
|
FFP Indications
|
multiple factor deficiencies:
-massive transfusion -liver dz -trauma -DIC -unidentified deficiency -wafarin reversal for emergent, invasive procedure -PT/PTT >1.5x nl goal: attain 30% factor level |
|
|
Cryoprecipitate
|
precipitate that forms when FFP is thawed.
contains: -factor 8 -vWF -fibrinogen -fibronectin -factor 13 |
|
|
Cryoprecipitate Indications
|
-FVIII deficiency (better to use factor conc)
-fibrinogen def -FXIII def -improve plt fx in uremia |
|
|
Sx's of Suspected Rx to Transfusion
|
-back pain
-F/C -hypotension -dyspnea blood bank w/u: clerical check, serum color check, DAT, cx, retype pt, u/a (look for hgb) |
|
|
Transfusion Rx's
|
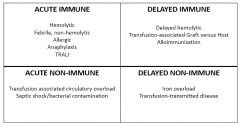
Acute Immune
Delayed Immune Acute non-Immune Delayed non-Immune |
|
|
Hemolytic Rx
|
(acute immune)
-etiology: red cell incompatibility (clerical error) -1/76,000 transfusions -sx's: F/C, hypotension, back pain, DIC/oozing, hemoglobinuria -tx: pressors, fluids, blood products (PRN for DIC) |
|
|
Febrile Non-Hemolytic Transfusion Rx
|
(acute immune)
-etiology: accumulated cytokines in blood products -0.1-1% transfusions -sx's: F/C, HA -tx: acetaminophen |
|
|
Leukocyte Reduction
|
-filter to remove leukocytes
-standard at UNC -indications: reduc CMV transmission, reduc alloimmunization to WBC's in chronic transfusion pt's, reduces febrile non-hemolytic transfusion rx! |
|
|
ALL & Anaphylactic Rx
|
-etiology: Ab to donor plasma proteins
-risk: 1 in 20-50,000 anaphylaxis; 1-3% allergic -sx's: rash, flushing, hypotension, bronchospasm -dx: Anti-IgA for anaphylaxis -tx: antihistamines, epi, steroids, IgA-def or washed blood products |
|
|
Washing
|
remove plasma, by washing RBC/plt w/ saline
-indications: prev ALL, anaphylaxis, IgA def. -time consuming, work, lasts 24 hr |
|
|
TRALI
|
transfusion related acute lung injury
-leading cause of transfusion-related mortality -defn: new lung injury w/in 6 hr of transfusion, hypoxemia, bilateral infiltrates on CXR, no other risk factors for pulmonary edema -usu w/ F/C, hypotension ddx: ARDS, vol. overload |
|
|
TRALI
|
(acute immune)
-etiology: WBC/HLA Ab in DONOR* -risk: unclear -sx's: new lung injury w/in 6hr transfusion -dx: test donor for WBC/HLA Ab, CXR -tx: supportive, defer donor |
|
|
Delayed Hemolytic Transfusion Rx
|
(delayed immune)
-etiology: anamnestic immune response to red cell Ag's -risk: 1 in 2500-11000 -sx's: F, back pain, decr Hgb -Tx: usually none needed |
|
|
Transfusion-associated graft v. host
|
(delayed immune)
-etiology: donor lymphocytes engraft in recipient and attack -rare -sx's: rash, N/V, hepatitis, pancytopenia -Dx work-up: skin biopsy, analysis for donor DNA -tx: no effective tx |
|
|
Irradiation
|
prevents TA-GVHD
-indicated in severe immunodeficient settings (lymphopenia) -cons: 28 day expiration, increased K in RBC product |
|
|
Alloimmunization
|
etiology: immune response to transfused allogeneic RBCs
-risk: 1/100 -sx's: none -tx: none needed, avoid unnecessary transfusions |
|
|
Transfusion associated Circulatory Overload (TACO)
|
(acute non-immune)
-etiology: vol. overload -risk: <1% -sx's: dyspnea, htn, cough -dx: CXR tx: diuretic, upright posture, oxygen |
|
|
Transfusion-related sepsis
|
-etiology: bacterial contamination
-risk: 1/75000 in plt, 1/500000 in pRBC -sx's: F/C, hypotension -supportive care, abx |

