![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the histologic features of Small Lymphocitic Lymphoma?
|
Small and well-differentiated B lymphocytes, with diffuse effacement of nodal architecture and no follicles |
|
|
What is the immunophenotype of SLL?
|
CD19, 5; Bcl-2 and Bcl-6 expression
|
|
|
What are the histological features of follicular lymphoma?
|
Nodal architecture is effaced by monotonous, crowded follicles composed of monomorphous small cleaved B-lymphocytes
|
|
|
What is the immunophenotype and genetics of follicular lymphoma?
|
CD19, 20, 79a; t(14:18); Bcl-2 expression
|
|
|
What are the histologic features
of DLBCL? |
Cells are large, with prominent nucleoli and abundant cytoplasm and many mitoses. Most are B-cell, but 20% are T-cell phenotype |
|
|
What is the immunophenotype and genetics of DLBCL?
|
CD19, 20, 79a; some have t(14;18); some have Bcl-2 and Bcl-6 expression; linked to EBV infection; negative TdT
|
|
|
What are the histologic features of Burkitt Lymphoma?
|
Very very high mitotic rate (99% Ki-67) |
|
|
What is the immunophenotype and genetics of Burkitt Lymphoma?
|
CD10, 19, 20, 79a; t(8:14) is characteristic; African form linked to EBV infection; negative TdT |
|
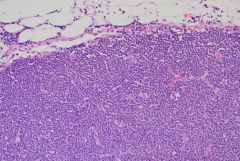
Describe architecture
|
This pattern of malignant lymphoma is diffuse and no lymphoid follicles are identified in this lymph node. Note that the normal architecture of the lymph node is obliterated. The lymph node is replaced by an infiltrate of small (mature-appearing) neoplastic lymphocytes, and the infiltrate extends through the capsule of the lymph node and into the surrounding fat. SLL |
|
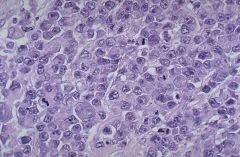
Describe and diagnose
|
The malignant lymphocytes here are very large with a moderately abundant cytoplasm, and the nuclei are round to ovoid with prominent nucleoli and occasional mitoses. The diagnosis is diffuse large B cell lymphoma (also known as immunoblastic lymphoma). The major differential diagnosis in this case would be a metastatic carcinoma.
|
|
|
How is hemoglobin measured?
|
|
|
|
What is hematocrit? |
Centrifuged whole blood, ratio of pRBCs to total height |
|
|
How do you calculate MCV (mean corpuscular volume)?
|
Hct X 100/ RBCs |
|
|
How do you calculate MCHC?
|
|
|
|
|
|

