![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an increase in neutrophils called? What does this suggest? |
Neutrophilia: suggests bacterial infection
|
|
|
What is an increase in lymphocytes called? What does this suggest?
|
Lymphocytosis: suggests viral infection
|
|
|
What is an increase in eosinophils called? What does this suggest?
|
Eosinophilia: suggests allergy or parasitic infection
|
|
|
What change in WBC count would suggest a bacterial infection?
|
Neutrophilia (increased number of neutrophils)
|
|
|
What change in WBC count would suggest a viral infection?
|
Lymphocytosis (increased number of lymphocytes)
|
|
|
What change in WBC count would suggest a parasitic infection?
|
Eosinophilia (increased number of eosinophils)
|
|
|
What change in WBC count would suggest an allergic reaction?
|
Eosinophilia (increased number of eosinophils)
|
|
|
How do you determine the WBC count?
|
Component of CBC, determined by a hematology analyzer through various methods
|
|
|
What does a WBC differential give you?
|
Percentages of each WBC type
|
|
|
How do you perform a manual WBC differential?
|
- Scan slide at 40x
- Tally number of each type of WBC until you reach 100 cells counted - Preferred method is bottom to top, L to R, top to bottom, R to L, etc |
|
|
What is the mnemonic for remembering the relative abundance of WBCs from most to least?
|
Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas:
- Neutrophils (34-71%) - Lymphocytes (19-53%) - Monocytes (5-12%) - Eosinophils (0-7%) - Basophils (0-1%) - Band Neutrophils (0-3%) |
|
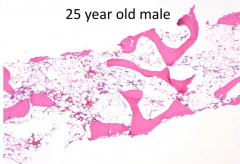
How would you describe the core biopsy?
|
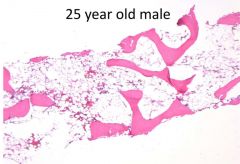
Hypocellular marrow for age
|
|
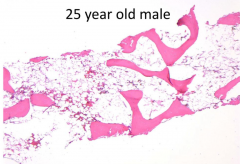
What are the expected CBC results?
|
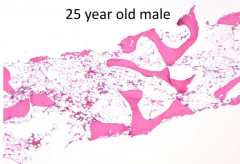
Cytopenias
|
|
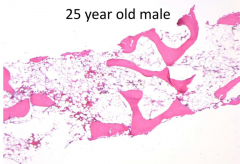
What are the clinical consequences of this marrow abnormality?
|
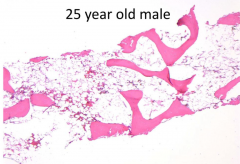
- Shortness of breath
- Infections - Bleeding - Petechiae |
|
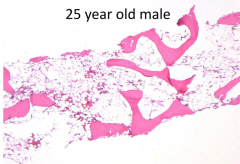
What are the potential causes of this abnormality?
|
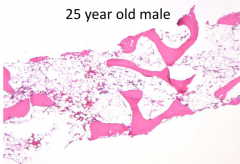
- Radiation
- Chemotherapy - Lupus - Malignancy - Viral infection - Immunosuppressant agents or conditions |
|
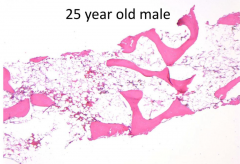
In attempts to treat this bone marrow abnormality, which cell type should be transplanted?
|
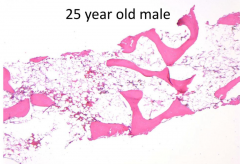
Progenitor Cells
|
|
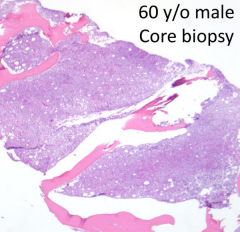
How do you describe the core biopsy?
|
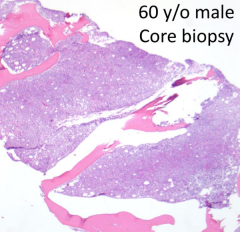
Hypercellular marrow for age
|
|
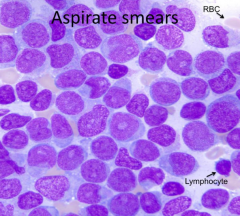
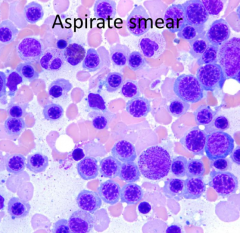
How do you describe the aspirate smear?
|
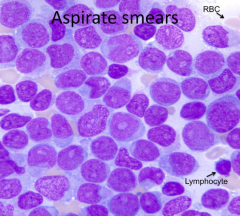
Monotonous and without maturation
|
|
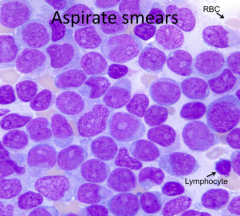
What cell type is predominating, immature or mature cells?
|
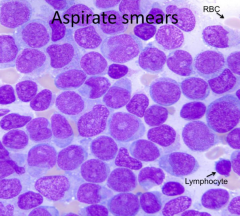
Immature cells
|
|
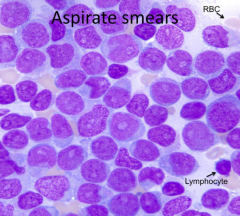
What are the clinical consequences of this marrow abnormality?
|
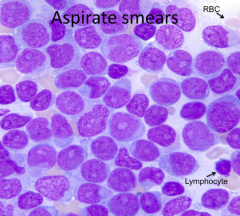
- Shortness of breath
- Infections - Bleeding - Petechiae |
|
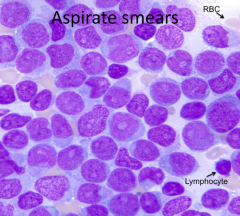
What are the expected CBC results?
|
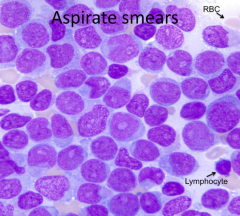
- Low WBC Count
- Low Platelet Count - Neutropenia - Low RBC Count - Myeloid Leukemia (high myeloid progenitor cells) |
|
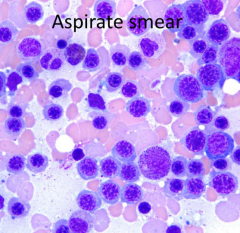
What is the predominant cell lineage in this aspirate smear?
|
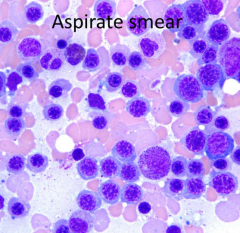
Erythroid
|
|
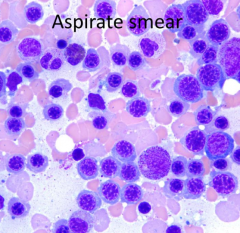
What is the myeloid/erythroid (M/E) ratio compared to a normal M/E (1.5-4)?
|
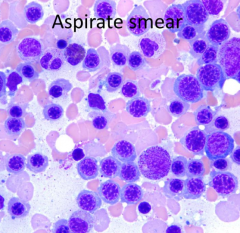
Lower than normal because more Erythroid cells
|
|
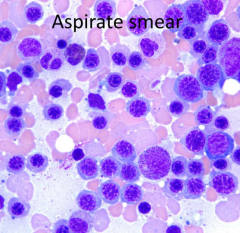
What are the expected CBC results?
|
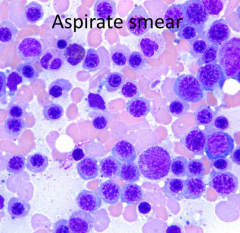
Elevated MCV d/t increased reticulocytes
|
|
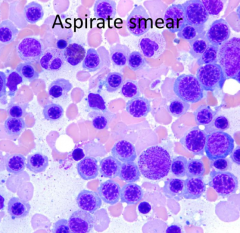
What growth factor would cause this marrow finding?
|
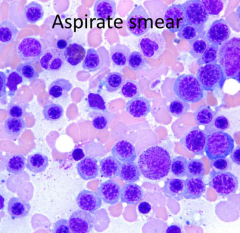
Erythropoietin
|
|
What clinical scenarios may produce this marrow finding?
|
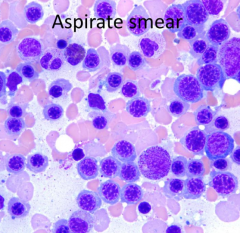
- High altitude
- Anemia - Hemorrhage |

