![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
94 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
50 y.o. M came with complaint of weakness, exertional SOB, denies CP, on examination BP 130/70, P=100, pallor present, soft systolic murmur is present, lungs are clear, no lower extremity edema. What do you do next?
|
Order CBC. this patient likely has anemia.
|
|
|
70 y.o. M found to have hemoglobin 10, hct 32, MCV of 70, reticulocyte index of 2, what do you do next?
|
Order iron studies
|
|
|
70 y.o. M found to have hemoglobin 10, hct 32, MCV of 70, reticulocyte index of 2, iron is low, iron capacity is high, ferritin is low. what do you do next?
|
colonoscopy because GI blood lost
|
|
|
Once CBC suggests microcytic anemia, what is the following step?
|
Iron studies
|
|
|
Once CBC suggests microcytic anemia. if Iron studies are normal what to do you do next?
|
hemaglobin electrophoresis, to r/o thala
|
|
|
Once CBC suggests microcytic anemia. if Iron studies are normal and hemoglobin electrophoresis is normal what is the likely diagnosis?
|
alpha thalassemia trait
|
|
|
26 y.o. F came with complete of fatigue, heavy menstrual bleeding, CBC has low MCV of 70, Hct 30, iron is low, TIBC is high, what do you do next?
|
supplement oral iron
|
|
|
26 y.o. F came with complete of fatigue, heavy menstrual bleeding, CBC has low MCV of 70, Hct 30, iron is low, TIBC is high. you started supplementing iron. after two months anemia was corrected. what do you do next?
|
continue iron for another 3-4 months, to build iron storage
|
|
|
18 y.o. patient started on iron for iron deficiency anemia, after two weeks of starting therapy, which of the following tests would you like to order, to determine if patient is responding. iron level, TIBC, reticulocyte count, ferritin level
|
reticulocyte count
|
|
|
A patient on iron tablets c/o having abdominal cramps, what should you do?
|
tell them to keep taking the tablets as cramps are a common side effect along with constipation. treat with colace
|
|
|
A patient on iron tablets c/o having abdominal cramps, and they absolutely cannot tolerate it, what should you do?
|
change ferrous sulfate to ferrous gluconate, with low elemental iron which some patients tolerate better
|
|
|
Mother of a young child, between 1-3 years of age complains that her baby is pale and easily tired, workup suggests iron deficiency anemia, which of the following most important thing would you like to ask in the history?
|
ask about food habits, may not have enough iron. suggest that she eats solid foods.
|
|
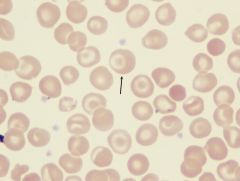
In what diseases will you see these types of cells.
|
these are target cells seen in liver disorder, sickle cell anemia, SC disease, and thalassemia
|
|
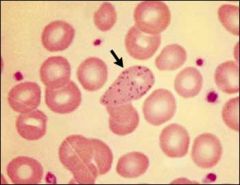
In what conditions will you see this type of RBC morphology?
|
basophilic stippling seen in lead poisoning, thalassemia, and alcohol abuse
|
|
This cell was seen on a peripheral blood smear of a patient. what's the next step?
|
check B12 and folate levels
|
|
|
a patient with pernicious anemia on B12 supplement, the next visit which test would you order.
|
check serum potassium, erythropoiesis increases and patient can develop hyperkalemia.
|
|
|
etoh abuser with h/o seizure disorder, is taking phenytoin, c/o weakness, hct of 35, MCV 110, reticulocyte index 0.5, cause of anemia?
|
Folate deficiency, due to alcohol and phenytoin.
|
|
|
child presents with anemia, on examination has icterus present, splenomegaly present, the lab shows increase reticulocyte count, increased MCHC w/ spherocytes present. what's the diagnosis?
|
hereditary spherocytosis.
|
|
|
16 y.o. patient c/o exertional sob, easy fatiguability, on exam pallor is present, hgb is low, increased retic count, increased LDH, low haptoglobin, spherocytes present in peripheral blood smear. Coomb's test is positive for immunoglobulin G. what's the diagnosis?
|
Warm antibody hemolytic anemia.
|
|
|
30 y.o. pregnant patient,came with c/o symptoms of anemia, patient is on medication for hypertension and a recent infection. on examination pallor is present, hemoglobin low, increase retic count, increased ldh, spherocytes are present, coombs positive for IgG, indirect coombs positive only when drug is added? what cause her anemia.
|
penicillin-type drug induced hemolytic anemia
|
|
|
patient with anemia, thrombocytopenia, PT& PTT are normal, patient had change in mental status
|
TTP
|
|
|
Patient has anemia, thrombocytopenia, increased BUN, what's the diagnosis?
|
HUS
|
|
|
Patient has h/o prosthetic valve, w/ anemia, schistocytes present, what's the diagnosis?
|
prosthestic valvue hemolytic anemia
|
|
|
patient w/ DM, HTN, admitted w/ PNA go intubated due respiratory failure, developed anemia, thrombocytopenia, schistocytes present, PT&PTT are elevated. what's the diagnosis?
|
DIC
|
|
|
American black man, came w/ complete of since, increased pallor, ldh, reticu count, bilirubin, suspect g6pd deficiency. the G6pd level is normal. what do you do?
|
repeat in a few weeks, because these cells may not have low levels (?)
|
|
|
what determines prognosis of sickle cell patient?
|
hbF levels
|
|
|
if a patient is having recurrent sickle cell crisis, which medication will be helpful.
|
hydroxyurea
|
|
|
sickle cell w/ beta thalassemia will they have a better or worse disease
|
better b/c those w/ beta thalassemmia have increase hemaglobin F.
|
|
|
Patient w/ sickle cell presents w/ SOB, weakness, has hgb of 5, what do you do next
|
reticulocyte b/c patient may have an aplastic crisis or hemolytic crisis
|
|
|
Patient w/ sickle cell comes w/ weakness hct 30, reticulocyte index of 0.8, h/o febrile illness, w/ skin rash one week ago. what's the diagnosis?
|
aplastic crisis secondary to parvovirus infection.
|
|
|
sickle cell pt, comes w/ weakness, hct of 20, spleen is palpable, retic is 5%. what's the diagnosis?
|
splenic sequestration crisis
|
|
|
patient w/ sickle cell comes w/ fever, UR tract infection symptoms.
|
Admit the patient b/c they can develop sepsis quickly.
|
|
|
pt w/ sickle cell comes w/ cough, CP, fever, CXR shows lung infiltrate, patient started on IV fluid and Abx. after 24 hours, no improvement. what's the diagnosis and treatment?
|
acute chest pain syndrome and treat w/ exchange transfusion
|
|
|
patient w/ SC disease came w/ acute hip pain, hip XR is negative, what's the diagnosis?
|
Avascular necrosis of femoral head
|
|
|
young newborn deilvered by CS presents in fetal distress at 38 weeks, during delivery amniotic fluid was bloody. newborn appears normal, hct 25%, which of following test would you do to work up anemia
|
apt test looks at fetal hemoglobin and hemoglobin
|
|
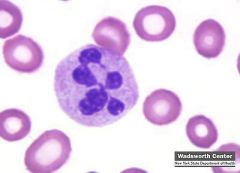
Name this type of cell and what is it pathognomonic for?
|
A pelger-huet cell that is pathognomonic for myelodysplastic syndrome
|
|
|
65 y.o. c/o weakness, has pancytopenia, peripheral smear has neutrophils w/ bi-lobed nucleus. what is the diagnosis?
|
myelodysplastic syndrome
|
|
|
pt w/ ITP and a platelet count of 8,000 is started on prednisone 40 mg, after four weeks platelet count is 150,000. Prednisone was tapered to 20 mg, the platelet count became 20,000. what do you do next?
|
Arrange for a splenectomy
|
|
|
A patient is admitted in a-fib and started on IV heparin. the next day the platelet count is decreased from 150,000 to 110,000. what is the most likely cause?
|
Heparin induced thrombocytopenia type I (non-immune).
|
|
|
A patient is admitted in a-fib and started on IV heparin. the next day the platelet count is decreased from 150,000 to 110,000. what is the most likely cause? Do you stop the heparin?
|
Heparin induced thrombocytopenia type I (non-immune). Don't stop heparin.
|
|
|
Why can't coumadin be started right away for a patient at risk for hypercoagulation?
|
coumadin works on vitamin k factors proteins C and S, and factors II, IX, and X. protein C has the shortest halflife so when you start coumadin protein C, a thrombin inhibitor, goes down first, leading to hypercoagulable state leading to blood clots especially in the tiny vessels of the skin, leading to skin necrosis.
|
|
|
20 y.o. c/o significant bleeding after a dental extraction. The platelet count is normal. PT and PTT are normal. bleeding time is high. what is the most likely diagnosis?
|
von willebrand's disease
|
|
|
A patient w/ hemolytic anemia, matching blood is not available. what do you do?
|
transfuse O negative blood.
|
|
|
A patient w/ anemia getting a blood transfusion, develops, fever, chills, chest pain, flank pain, tachycardia, hypotension. what is the diagnosis? and what is the treatment?
|
ABO incompatibility. stop transfusion and send blood to blood bank again. start IV fluids to prevent acute tubular necrosis.
|
|
|
four hours after blood transfusion, a patient develops fever, chills. what is the diagnosis? how do you treat?
|
leukoagglutination reaction. due to antigen sensitization. give them acetaminophen and diphenhydramine (benadryl).
|
|
|
after 8 days of blood transfusion. a patient c/o mild fever, decreased hemoglobin, and findings of hemolysis. what's the diagnosis? what's the treatment?
|
delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction secondary to minor incompatibility. no treatment.
|
|
|
h/o of febrile reaction w/ blood transfusion needs to be transfused again. what do you do?
|
Use a leukocyte depletion filter, also use for someone who needs recurrent transfusions.
|
|
|
A pt w/ lymphoma needs a blood transfusion, what do you do?
|
Transfuse gamma irradiated blood to prevent graft versus host disease?
|
|
|
a pt w/ h/o of blood transfusions causing hives or bronchospasm due to plasma proteins needs a transfusion. what do you do?
|
transfuse w/ washed packed red blood cells.
|
|
|
anaphylaxis after blood transfusion due to IgA deficiency. what do you do?
|
Give them IgA negative blood
|
|
|
after blood transfusion a pt develops SOB w/ bilateral crackles in the lungs, CXR shows diffuse infiltrate, pt was intubated. 24 hours later the patient feels better, gets extubated, what's the diagnosis?
|
Donor anti-HLA antibody causing agglutination reaction ie. transfusion related acute lung injury
|
|
|
18 y.o. black male has wbc of 2,000, PMNs of 30%, the patient is asymptomatic. what do you do?
|
The patient has neutropenia, repeat the CBC in 2-4 weeks. Benign neutropenia.
|
|
|
18 y.o. black male has wbc of 2,000, PMNs of 30%, the patient is asymptomatic. what do you do? if after 3-4 weeks the WBC increases, then what do you do? are they at increased risk of infection?
|
Repeat in 3-4 weeks. If the count decreases again then it is cyclic neutropenia.
|
|
|
A patient has cyclic neutropenia, how do you treat him?
|
Granulocyte Macrophage -Colony Stimulating Factor
|
|
|
A patient w/ chronic kidney disease, went for placement of double lumen dialysis catheter. The patient has oozing of blood from the exit site. in the lab the platelet count is normal. PT and PTT is normal. the bleeding time is elevated. what's the diagnosis? what is the treatment
|
abnormal platelet function secondary to uremia. The treatment is desmopressin. the symptoms will improve once dialysis commences.
|
|
|
pt comes w/ bleeding, has normal platelets, increased PTT, PT is normal, bleeding time is normal. what do you do next?
|
perform a mixing study w/ normal plasma to find it the patient has clotting factor deficiency OR if an antibody to the clotting factor is present.
|
|
|
pt comes w/ bleeding, has normal platelets, increased PTT, PT is normal, bleeding time is normal. after performing a mixing study, PTT becomes normal. what does this mean?
|
pt has a clotting factor deficiency. check factor VIII, IX, or XI levels.
|
|
|
pt comes w/ bleeding, has normal platelets, increased PTT, PT is normal, bleeding time is normal. after performing a mixing study, PTT still abnormal. what does this mean? and what do you order next?
|
patient does not have a factor deficiency, instead an antibody to one of the factors is there. order factor VIII or factor IX antibody levels.
|
|
|
pt w/ increased PTT presents w/ hypercoagulable state like a stroke, DVT, PE. a mixing study does not correct the PTT. what test you'd like to order?
|
lupus anticoagulant test
|
|
|
A pt is planned for colecystectomy, found to have increase PTT. the pt says that he knows about it, his doctor has done an extensive workup about it and told him not to worry. what's the likely diagnosis?
|
factor XII deficiency, don't worry because they don't bleed.
|
|
|
After a dental extraction a patient has severe bleeding, his platelets are normal. his bleeding time, PT, and PTT are normal. what's the diagnosis? what's the confirmatory test to perform?
|
factor XIII deficiency. confirm w/ clot solubility test in 5M urea.
|
|
|
90 y.o. man c/o multiple ecchymosis over dorsum of the hand. his platelets are normal, bleeding time is normal, PT/PTT normal.
|
benign senile purpura, secondary to increased fragility of superficial vessels due to aging.
|
|
|
causes of Vitamin K deficiency
|
broad spectrum antibiotics (bacteria that produce Vitamin K) and dietary deficiency.
|
|
|
a post-op patient is not eating and taking broad spectrum antibiotics, the patient is bleeding easily. has increased PT and PTT. what's the diagnosis and how do you treat?
|
Vitamin K deficiency, supplement w/ Vitamin K.
|
|
|
18 y.o. female on OCP, came w/ complete of pain and swelling of R lower extremity for two days, in the lab WBCs are normal, hemoglobin normal, PT/PTT normal. what's the diagnosis? How do you confirm? How do you treat?
|
DVT secondary to oral contraceptives. confirm w/ doppler U/S. start the patient on heparin.
|
|
|
advantages of low molecular weight heparin
|
less likely to cause thrombocytopenia, no need to monitor PT INR (ratio of PT to normal control), causes less osteoperosis than unfractionated heparin.
|
|
|
what is the disadvantage of low molecular weight heparin.
|
needs dose adjustment in patients w/ chronic kidney disease, it is expensive, does not have a specific antibody so there's no antidote.
|
|
|
20 y.o. man came w/ pain and swelling in right lower extremity. he doesn't have any significant past medical history. his routine labs are normal. what is the most likely cause?
|
DVT caused by factor V Leiden deficiency.
|
|
|
a patient is on coumadin. his INR is 8. the patient is asymptomatic. what do you do?
|
Hold the coumadin for 1-2 days and repeat the INR.
|
|
|
a patient is on coumadin. his INR is 8. the patient is asymptomatic. what do you do? if patient develops ecchymosis what do you do?
|
Give vitamin K.
|
|
|
a patient is on coumadin. his INR is 8. the patient is bleeding severely. what do you do?
|
Give FFP
|
|
|
A patient w/ DVT is at risk of PE. if anticoagulation is contraindicated or patient is non-compliant, what can you do?
|
Place an inferior vena cava filter to prevent a PE.
|
|
|
a patient w/ a hct of 60, what physical exam finding will suggest polycythemia vera?
|
splenomegaly
|
|
|
An athletic patient taking testosterone has a hematocrit of 60. what is the cause of polycythemia?
|
androgen-stimulated polycythemia
|
|
|
COPD patient w/ a hct of 60, w/ normal wbc and platelet, increased erythropoietin, O2 saturation is 98% on RA, what is the most likely cause of increased hct. COPD, polycythemia vera, renal cell carcinoma, hemochromatosis?
|
renal cell carcinoma, producing erythropoietin.
|
|
|
polycythemia patient's are at increased risk of what state?
|
hypercoagulable state ie stroke.
|
|
|
a polcythemia pt c/o pain and redness of hands and feet. what's the diagnosis and how do you treat?
|
erythromelalgia. treat w/ aspirn and phlebotomy.
|
|
|
patient w/ hgb 8, MCV 70, has platelet count of 800,000. what's the most liely cause of increased platelet?
|
reactive thrombocytosis secondary to iron deficiency anemia.
|
|
|
8 y.o. boy comes w/ complaint of abdominal pain of two days. has multiple raised erythematous lesion on lower extremities and buttocks which don't blanch w/ pressure. has recent h/o URI. hgb is normal, wbc normal, platelets normal, PT/PTT normal. UA has 5-6 RBC.
|
Henoch-Schlonlein Purpura
|
|
|
5 y.o. boy comes w/ recurrent epistaxis and gum bleeding. he is lethargic, irritable, on examination has hepatosplenomegaly, lab shows no platelets, low hgb, wbc 100,00, 90% blast cells.
|
ALL
|
|
|
patient w/ hgb 8, MCV 70, has platelet count of 800,000. what's the most liely cause of increased platelet?
|
reactive thrombocytosis secondary to iron deficiency anemia.
|
|
|
8 y.o. boy comes w/ complaint of abdominal pain of two days. has multiple raised erythematous lesion on lower extremities and buttocks which don't blanch w/ pressure. has recent h/o URI. hgb is normal, wbc normal, platelets normal, PT/PTT normal. UA has 5-6 RBC.
|
Henoch-Schlonlein Purpura
|
|
|
5 y.o. boy comes w/ recurrent epistaxis and gum bleeding. he is lethargic, irritable, on examination has hepatosplenomegaly, lab shows no platelets, low hgb, wbc 100,00, 90% blast cells.
|
ALL
|
|
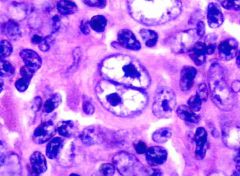
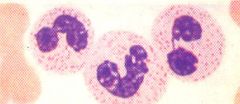
what disease is this cell pathognomonic for?
|
Hodgkin's Lymphoma
|
|
|
15 y.o. boy comes w/ swelling in the neck that is slowly growing. he denies pain, cough, fever. on examination cervical lymph nodes are enlarged. what's the diagnosis? What's the next logical step?
|
Hodgkin's disease type A. perform lymph node biopsy.
|
|
|
An 18 y.o. c/o abdominal pain and a low grade fever. intaabdominal mass is suspected. CT of abdomen suggests retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy. what's the diagnosis?
|
Burkhitt's Lymphoma.
|
|
|
What anti-seizure medication can cause lymphadenopathy.
|
phenytoin can cause reactive lymphadenopathy
|
|
|
70 y.o. male came w/ complain of low back pain, has anemia, increase BUN/Cr, increased calcium. what's the next test?
|
serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP) or urine protein electrophoresis (UPEP)
|
|
|
65 y.o. w/ diabetes, renal failure, anemia, found to have monoclonal immunologlobulin G spike 2 g/dL. Bone marrow exam is normal.
|
Monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance. multiple myeloma has bone marrow filled w/ plasma cells.
|
|
|
65 y.o. man c/o dizziness, visual disturbance, found to have anemia, protein electrophoresis shows monoclonal immunoglobulin M spike, no renal failure, bone xray is normal. the most likely diagnosis is? what is the treatment?
|
waldenstrom's immunoglobulinemia. they have hyperviscosity symptoms. treatment is emergency plasmaphoresis?
|
|

what is the radiographic finding and what is it pathognomonic of?
|
Hair on end of skull appearance. suggests thalassemia or another type of anemia. caused by bone marrow hyperplasia.
|
|
|
C/F of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
|
lymphocytosis (>20,000) in a person over 65 w/ LAD and hepatosplenomegaly,
|
|
|
T/t of CLL
|
if no anemia or thrombocytopenia, no treatment, if there's anemia or thrombocytopenia then use fludrabine
|
|
|
poor prognostic factors in CLL
|
presence of anemia or thrombocytopenia
|

