![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
extremely important with iron deficiency to always consider _____ ______.
|
underlying cause
|
|
|
in menstruating females, iron deficiency most often results from?
|
inadequate dietary iron intake to replace losses
|
|
|
in male or post-menopausal female pts, what is iron deficiency almost always due to?
what should you do? |
blood loss; all iron deficient pts should be tested for occult blood.
even if neg, these pts whould have GI tract studies (ie. endoscopy) to check for bleeding GI lesion (which 2/3 of pts will have). other causes of bleeding can be GI cancer and hookworms (where endemic) |
|
|
in what situation should you give empiric iron therapy to anemic patients?
|
NEVER!!! always find out what the underlying cause is first!
|
|
|
storage iron is present as ___ and ___.
|
ferritin; hemosiderin
|
|
|
iron is absorbed in the ______.
|
duodenum.
|
|
|
what is the role of hepcidin in iron metabolism?
|
Primary fxn to attach to ferroportin and degrade.
If ferroportin is degraded, Iron that gets absorbed gets locked in the endothelial or macrophages (aka it’s not released into plasma) |
|
|
hepcidin is INCREASED/DECREASED in anemia of chronic inflamation
hepcidin is ______ or ____ _____ in hemochromatosis |
increased; mutated; down regulated
|
|
|
clinical manifestations of iron deficiency anemia (acute)
|
pallor, fatigue, exercise intolerance
cardiomegaly pica impaired psychomotor development spooning of nails/nail palor plummer-vinson syndrome (spoon nails, atrophic glossitis, esophageal web) |
|
|
what would lab tests show for a pt with iron deficiency anemia?
|
-low Hb/hct
-low MCV (microcytosis) - peripheral smear: microcytic , hypochromic anermia, anisocytosis, poikilocytosis, cigar shaped/pencil cells -low retic's (bc it's a hypoproliferative) - low serum iron, low ferritin, high TIBC |
|
|
what are the 3 stages of iron deficiency?
|
1- storage iron deficiency (low plasma ferritin)
2- iron-limited erythropoiesis (dec transferrin saturation, inc erythrocyte protoporhyrin bc no iron to bind to them) 3- iron deficiency anemia (decreased Hb production) |
|
|
what MUST iron deficiency anemia in adult men and post-menopausal women in Western world be attributed to?
|
GI blood loss (unless proven otherwise)
|
|
|
tx for IDA
|
oral ferrous sulfate w/ juice
treat until Hb normalizes and for additional 2-3 months for supplement |
|
|
when would you use blood transfusion to treat IDA?
|
in dire cases....when Hb <5, in the presence of cardiac failure
|
|
|
3 y/o AA female with microcytic anemia. what lab tests do you do next?
nL iron, elevated HbA2. dx? |
test iron panels and gel electrophoresis (to test for thalassemias)
beta thalassemia |
|
|
what are the 3 stages of iron deficiency?
|
1- storage iron deficiency (low plasma ferritin)
2- iron-limited erythropoiesis (dec transferrin saturation, inc erythrocyte protoporhyrin bc no iron to bind to them) 3- iron deficiency anemia (decreased Hb production) |
|
|
what MUST iron deficiency anemia in adult men and post-menopausal women in Western world be attributed to?
|
GI blood loss (unless proven otherwise)
|
|
|
tx for IDA
|
oral ferrous sulfate w/ juice
treat until Hb normalizes and for additional 2-3 months for supplement |
|
|
when would you use blood transfusion to treat IDA?
|
in dire cases....when Hb <5, in the presence of cardiac failure
|
|
|
3 y/o AA female with microcytic anemia. what lab tests do you do next?
nL iron, elevated HbA2. dx? |
test iron panels and gel electrophoresis (to test for thalassemias)
beta thalassemia |
|
|
is anemia of chronic inflammation microcytic, normocytic, or macrocytic
|
normocytic or slightly microcytic
|
|
|
in anemia of chronic inflammation, hepcidin is UP/DOWN regulated.
in hemochromatosis, hepcidin is UP/DOWN regulated. think about why. |
UP
DOWN if hepcidin is up-regulated, like in ACD, then more ferroportin is blocked, leading to less iron being able to enter circulation from GI mucosal cells. |
|
|
should you give iron therapy to someone with ACD?
|
no (just correct underlying disorder)
|
|
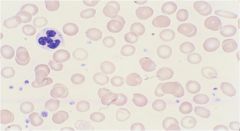
what condition is shown here?
|
iron deficiency anemia (pencil shaped RBCs, increased platelet count, microcytic rbcs)
|
|
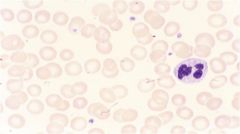
what condition is shown here?
|
anemia of chronic disease (microcytic rbcs)
|
|
|
2 y/o boy with low Hb, low MCV, nL retic count.
low iron, low ferritin, high TIBC, nL gel electrophoresis for Hb |
iron deficiency anemia
|
|
|
8 y/o boy from Africa with TB with low Hb, nL MCV, nL retic count.
low iron, high ferritin, low TIBC, low HbA and high HbS on gel electrophoresis. |
anemia of chronic disease
|
|
|
what's the most prevalent genetic disease in Caucasians
|
hereditary hemochromatosis - from mutation of HFE gene which causes increased iron absorption (normal HFE gene product inhibits DMT-1 which normally allows iron to be absorbed into duodenal cells, leading to inhibition of iron absorption)
|

