![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
118 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
BAND/STAB FORM |
Cell without complete formation of nuclear nuclear lobes |
Sausage shaped nucleus |
|
|
HYPERSEGMENTED NEUTROPHIL |
Presence of even a single neutrophil with six or more lobes or the presence of more than 5% of neutrophils with five lobes |
|
|
|
EOSINOPHILS |
2 nuclear lobes are present giving the nucleus a spectacle shape |
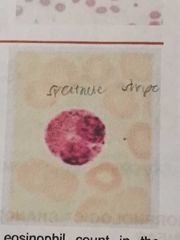
They are slightly larger than segmented neutrophil The cytoplasm has a pale hue and has numerous dense orange red |
|
|
BASOPHILS |
Its granules are rich in histamine, serotonin and heparin |
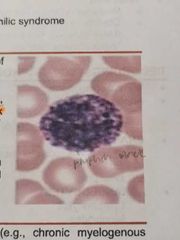
Has lobulated nucleus, distinguished by their large, coarse, purplish black granules |
|
|
MONOCYTE |
The granules resemble fine dust and give the bluish cytoplasm a ground glass appearance |
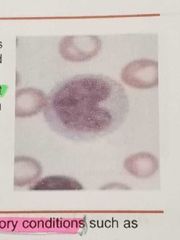
The cytoplasm is abundant, is gray or light blue gray and contains numerous vacuoles |
|
|
DOWNEY CELLS / LARGE LYMPHOCYTE |
Have abundant cytoplasm that may be irregular (SCALLOPING/SKIRTING RBC) |
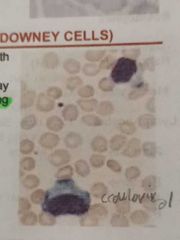
Have slightly larger nuclei with more open chromatin |
|
|
DOHLE BODIES |
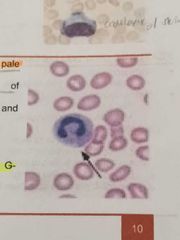
Small, round or oval, pale blue grey structure that contains ribosomes and endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|

ALDER-REILLY ANOMALY |
This abnormality is commonly seen in mucopolysaccharidoses such as in hurfers and hunters syndrome. Granules are large, discrete, stain deep red and may obscure the nucleus |
|
|

MAY-HEGGLIN ANOMALY |
Is an autosomal dominant inheritance that is a triad of giant platelets, thrombocytopenia, dohle body |
MYH-9 gene |
|
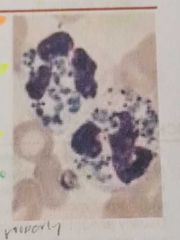
CHEDIAK-HIGASHI SYNDROME |
Is a rare autosomal recessive disease that have a giant peroxidase positive lysosomal granules in granulocytes |
|
|

PELGER-HUET CELLS/ANOMALY |
Is a benign inherited condition wherein nuetrophil nuclei fail to segment properly. Majority of circulating neutrophils have only two discrete equal sized lobes connected by a thin chromatin bridge |
|
|
|
PSEUDO-PELGER CELLS |
Is an acquired condition that morphologically similar to pelger huet anomaly |
AKA acquired pelger-huet anomaly |
|

HYPOCHROMIA |
Decrease in hemoglobin content of RBC Increase in central pallor (>1/3) Decrease in MCH and MCHC |
|
|
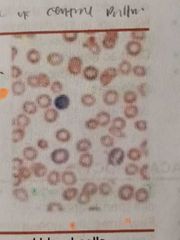
POLYCHROMATOPHILIA |
Blue gray tint of red cells due to the presence of residual RNA in young cells. It is larger than normal and may lack central pallor Implies reticulocytosis |
|
|

MICROCYTES |
Size of RBC is reduced (<80fl). It is seen when hemoglobin synthesis is defective |
|
|
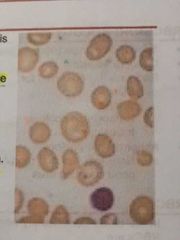
MACROCYTES |
Seen when MCV of RBC is increase (>100fl). It is seen particularly in Vitamin B12 and folate deficiency |
|
|
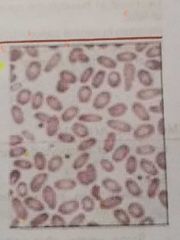
ELLIPTOCYTES |
Elliptical in shapes. Most abundant in hereditary elliptocytosis |
|
|

SCHISTOCYTES |
These are fragmented erythrocytes; Smaller than normal red cells and of varying shape and is hallmark in the diagnosis of HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA |
|
|

ACANTHOCYTES/SPURR CELLS |
Thorny projections on red cell membrane. Has few, irregular non-uniform spicule |
|
|
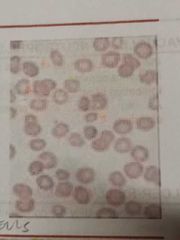
ECHINOCYTES/BURR CELLS |
Numerous, short, regular projection and is commonly occur as an artifact during preparation of film |
|
|
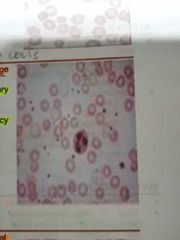
LEPTOCYTES |
Thin red cells with large unstained central area. It is also known as pessary cell |
|
|
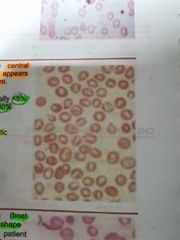
STOMATOCYTES |
Red cells with central biconcave area appears slit like in dried film |
|
|
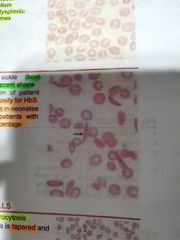
SICKLE CELL |
Boat shape or crescent shape. It is present in film of patient with homozygosity for HbS. Usually absent in neonates and rare with patients with high Hb F percentage |
|
|
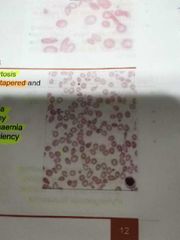
TEAR DROP CELLS / DACROCYTES |
One side of cell is tapered and the other is blunt |
|
|
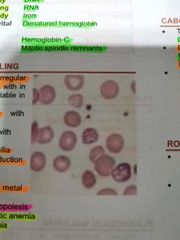
BASOPHILIC STIPPLING |
Presence of irregular basophilic granules within RBC which are variable in size Stain deep blue with wright's stain |
|
|
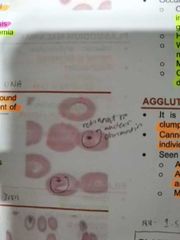
HOWELL-JOLLY BODIES |
Smooth single large round inclusions which are remnant of nuclear chromatin |
|
|
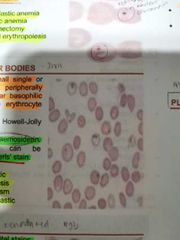
PAPPENHEIMER BODIES |
These are small single or multiple peripherally situated angular basophilic (almost black) erythrocyte inclusions. Composed of hemosiderin |
|
|
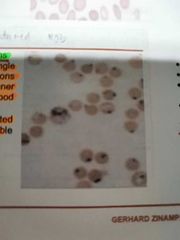
HEINZ BODIES |
Seen on supravital stains and represent precipitated normal or unstable hemoglobins |
|
|
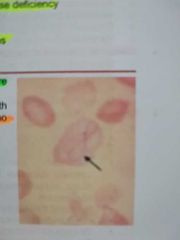
CABOT RINGS |
These are ring shaped, figure of eight or loop shaped. |
|
|
|
ROULEAUX FORMATION |
Alignment of red cells one upon another so that they resemble stock of coins |
|
|
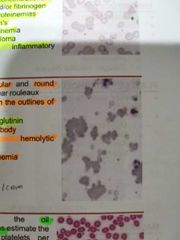
AGGLUTINATION |
It is more irregular and round clumping then linear rouleaux. Cannot distinguish the outlines of individual RBCs. It is seen with cold agglutinins |
|
|
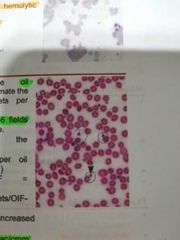
PLATELETS |
Non nucleated derived from cytoplasmic fragments of megakaryocyte |
|
|
|
THROMBOCYTOPENIA (ARTIFACTUAL) |
Platelet clumping caused by anticoagulant-dependent immunoglobulin |
|
|
|
THROMBOCYTOSIS |
Essential thrombocytopenia |
|
|
|
P. falciparum |
Infected RBCs are normal size |
|
|
|
P. vivax |
Infected RBCs are enlarged and deform |
|
|
|
P. ovale |
Infected RBCs are moderately enlarged fimbriated and oval |
|
|
|
P. malariae |
Infected RBCs are normal to decreased size. Schizont: 6-12 merozoites |
|
|
|
ANISOCHROMIA |
Variation in color and hgb content |
|
|
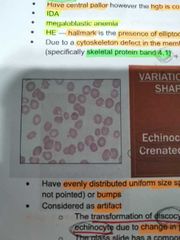
ECHINOCYTE / CRENATED CELLS |
Have evenly distributed unifrom size spicules (blunt but not pinted) or bumps. Considered as artifact |
|
|
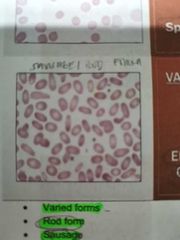
ELLIPTOCYTES / OVALOCYTES |
Rod form, sausage form, pencil form and eggshape. Have central pallor however, the hgb is concentrated |
|
|

BURR CELLS |
Uneven spicules and uneven space |
|
|
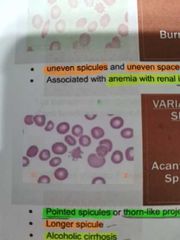
ACANTHOCYTES |
Pointed spicules or thorn-like projections |
|
|
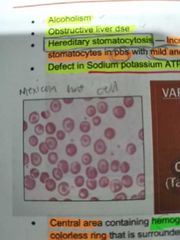
CODOCYTES / TARGET CELL |
Central area containing hemoglobin surrounded by colorless ring. Bell shaped or Tall hat shaped, mexican hat cell |
|
|
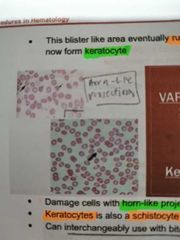
KERATOCYTES |
Damage cells with horn-like projection. Can interchangeably use with bite cells |
|
|
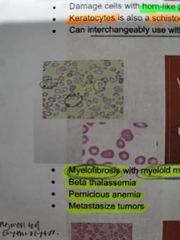
DACROCYTES / TEARDROPS |
Myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia |
|
|
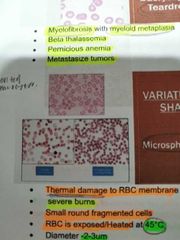
MICROSPHEROCYTES |
Thermal damage to RBC membrane. Small round fragmented cells |
|
|
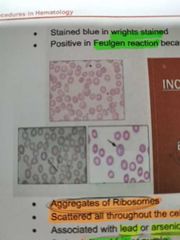
BASOPHILIC STIPPLING |
Aggregates of ribosomes. Scattered all throughout the cell. Associated with Lead or arsenic poisoning |
|
|
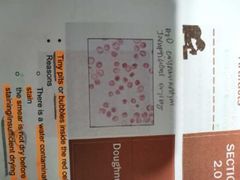
DOUGHNUT CELLS |
Tiny pits or bubbles inside the red cell due to: there is a water contamination of the wright stain, the smear is not dry before staining/insufficient drying |
|
|
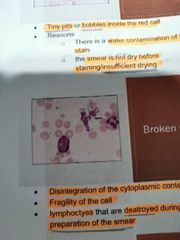
BROKEN CELLS |
Disintegration of the cytoplasmic content of the cell; Fragility of the cell; Lymphocytes that are destroyed during improper preparation of the smear |
|
|
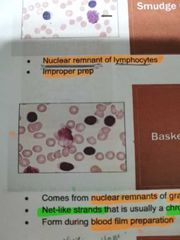
BASKET CELL |
Comes from nuclear remnants or granulocytic cells; Net like strands that is usually a chromatin strand. It is form during blood film preparation |
|
|
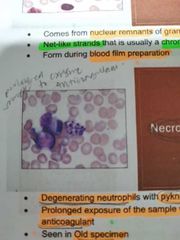
NECROTIC CELL |
Degenerating neutrophils with pyknotic nuclei; Prolonged exposure of the sample with the anticoagulant . Seen in old specimen |
|
|
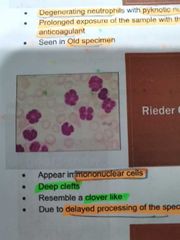
REIDER CELLS |
Appear in mononuclear cells; deep cleft and resemble a clover like due to delayed processing of the specimen |
|
|
|
TOXIC GRANULATION |
Happens in cases of inflammation or infection and in lead poisoning. Occurs also in normal phenomenon usually in cases of preganancy Caused by alteration in the non-specific granules of the cytoplasm of neutrophils |
|
|

PELGER-HUET ANOMALY |
Peanut shaped nucleus nad occurs in congenital anomaly Hyposegmentation: Decreased lobulation (LEFT SHIFT) |
|
|
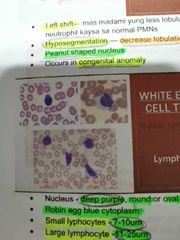
LYMPHOCYTE |
Robin egg blue cytoplasm. Increased in atypical lymphocyte |
|
|
HAIRY CELL |
Peanut shell or dumb bell shape Small lymphocytes that have minimal cytoplasmic projections that look like hairs TRAP positive |
|
|
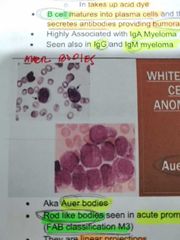
AUER RODS |
Rod like bodies seen in acute promyelocytic leukemia. They are linear projections
AKA Auer bodies |
|
|
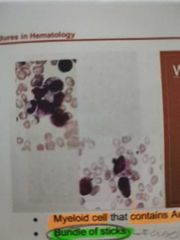
FAGGOT CELL |
Myeloid cell that containes Auer rods Bundle of sticks |
|
|
|
Acute Blood Loss Hemolytic Anemia Aplastic Anemia |
Associated conditions in the presence of normocytic, normochromic RBC |
|
|
|
Iron Deficiency Anemia Thalassemia Anemia of Chronic Inflammation Sideroblastic Anemia (occasional) |
Conditions associated with the presence of microcytic, hypochromic RBC |
|
|
|
Megaloblastic Anemia Myledysplastic Syndrome Mycoplasma pnemuniae infection Chronic Liver Disease Bone marrow failure Reticulocytosis Sideroblastic Anemia |
Conditions associated with the presence of Macrocytic RBC |
|
|
|
Multiple Myeloma Macroglobulinenemia Hyperproteinemia |
Conditions associated with the presence of rouleaux formation |
|
|
|
Cold Agglutinin Disease Primary Atypical Pneumonia |
Conditions associated with the presence of agglutination |
|
|
|
Mcleoid Phenotype Alcoholic Cirrhosis PK Deficiency Abetalipoproteinemia Neuroacanthocytes Severe Liver Disease |
Conditions associated with the presence of Acanthocytes/Spurr Cells |
|
|
|
Acanthocytes |
Its presence is due to increase sphingomyelin over than lecithin |
|
|
|
Oval macrocytes/Megalocytes/Macroovalocytes |
Its presence is due to nuclear maturation defect |
|
|
|
Oval Macrocytes |
Oval or egg like apperance |
|
|
|
Megaloblastic anemia |
Conditions associated with the presence of oval macrocytes |
|
|
|
Echinocytes |
Also known as crenated or sea urchin |
|
|
|
Echinocytes |
Its crenation is due to osmotic imbalance |
|
|
|
Drying (Increased pH) Stored blood (Decreased ATP) |
Reasons for the presence of echinocytes (just an artifact) |
|
|
|
Burr cells |
An RBC with irregular sized and uneven spaced spicules |
|
|
|
Burr cell |
Its presence is due to increased BUN and increased Burr cells |
|
|
|
Renal Insufficinecy Uremia |
Conditions associated with the presence of Burr Cell |
|
|
|
Hemoglobinopathies Obstructive Liver Disease Thalassemia IDA Post-splenectomy |
Conditions associated with the presence of Codocytes/Target cells |
|
|
|
Codocyte/Target Cell |
Also known as Mexican Hat |
|
|
|
Codocyte/Target Cell |
Its presence in the blood film is due to increased cholesterol and phospholipid |
|
|
|
Leptocyte |
It resembles codocyte but not detached from outer membrane |
|
|
|
Leptocyte |
Also known as "Pessary Cell" |
|
|
|
Leptocytes |
RBC which thinner than normal with colorless center and increased surface area |
|
|
|
Thalassemia Hemiglobinopathies Cirrhosis Steatorrhea Sideroblastic Anemia Bile Duct Obstruction |
Conditions associated with the presence of Leptocytes |
|
|
|
Spherocytes |
RBC with a ball or biconcave shape |
|
|
|
Spherocytes |
Its presence in the blood film is due to a decreased spectrin |
|
|
|
Hereditary Spherocytosis (DAT +) Immune Hemolytic Anemia (DAT -) Prolonged blood storage Extensive Burns |
Conditions associated with the presence of spherocytes |
|
|
|
Spherocyte |
Also known as Bronze Cell |
|
|
|
Stomatocyte |
Mouth shaped central pallor |
|
|
|
Stomatocytes |
Bowl shaped cells |
|
|
|
Stomatocytes |
Its presence in the blood film is due to cationic imbalance: Increased permeability to sodium |
|
|
|
Hereditary stomatocytosis Alcoholism Artifact Cirrhosis Obstructive Liver Disease RH null disease |
Conditions associated with the presence of stomatocytes |
|
|
|
Elliptocytes |
Cigar shaped RBC |
|
|
|
Eliptocytes |
Hb appears to be concentrated at the two ends of the cell |
|
|
|
Elliptocytes |
Its presence in the blood is due to the presence of decreased protein band 4.1 (defect in cytoskeleton) |
|
|
|
Hereditary elliptocytosis IDA Megaloblastic anemia Myelopthisic Anemia |
Conditions associated with the presence of Elliptocytes |
|
|
|
Ovalocytes |
Egg-shaped RBC that is wider than elliptocytes |
|
|
|
Ovalocytes |
Its presence in the blood film is due to decreased cholesterol |
|
|
|
Megaloblastic anemia Myelopthisic anemia |
Conditions associated with the presence of ovalocytes |
|
|
|
Pencil or Oat cell |
It is a thinner variant of elliptocytes |
|
|
|
IDA |
Conditions associated with the presence of pencil or oat cell |
|
|
|
Schistocyte |
Fragmented RBC due to membrane damage |
|
|
|
Schistocyte |
It is associated with the presence of deposited fibrin strand (MAHA) |
|
|
|
Schistocyte |
Also known as "Fragmentocyte" |
|
|
|
Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia (MAHA) Traumatic Hemolytic Anemia Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Extensive Burns Diffuse Intravascular Coagulation |
Conditions associated with the presence of schistocytes |
|
|
|
Blister cell or pre-keratocyte |
RBC with vacuole-like area |
|
|
|
Keratocyte/ Helmet cell |
Helmet shaped RBC |
|
|
|
Keratocytes |
RBC with a horn-like projections |
|
|
|
Knizocyte |
Resembkes a pinched bottle |
|
|
|
Knizocytes |
Triangular RBC with 2 pallor areas |
|
|
|
Dacrocyte / Tear Drop Cell |
Pear shaped cell |
|
|
|
Dacrocyte |
Squeezing / fragmentation during splenic passage |
|
|
|
Myelofibrosis with Myeloid Metaplasia Myelopthisic anemia B-thalassemia Pernicious Anemia |
Conditions associated with the presence of Dacrocyte |
|
|
|
Microshperocytes / Pyropoikilocytes |
Its appearance in the blood film is due to thermal damage to the cell membrane |
|
|
|
Microshperocyes / Pyropoikilocytes |
It fragments at 45-46 Degree Celcius instead of 49 |
|
|
|
Hereditary pyropoikilocytosis Severe Burns |
Conditions associated with the presence of microshperocytes / pyropoikilocytes |
|
|
|
Semilunar bodies |
Large, pale pink staining ghost of the RBC |
|
|
|
Semilunar Bodies |
Also known as Crescent shaped or half moon shaped RBC |
|
|
|
Semilunar Bodies |
Red cell membrane remaining after the contents have been released |
|
|
|
Malaria Overt hemolysis |
Conditions associated with the presence of Semilunar Bodies |
|

