![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Auscultation of Heart Sounds |
Listening to the intensity and quality of heart sounds can provide useful information about the condition and function of the heart. The diaphragm of the stethoscope is held directly to the pt's skin w/ enough pressure to provide a seal while the pt breathes in through the nose. |
|
|
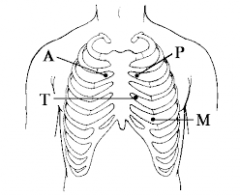
Four areas of auscultation |
Aortic Area: 2nd intercostal space - (R) sternal boarder Pulmonic Area: 2nd intercostal space - (L) sternal boarder Mitral Area: 5th intercostal space - Medial to left midclavicular line Tricuspid Area - 4th intercostal space - (L) sternal boarder |
|
|
Auscultation Areas (Continued) |
|
|
|
Systole Cardiac Cycle |
Ventricles contract pumping blood into arteries. Right ventricle sends blood to lungs. Left ventricle pumps blood to aorta. Summary of events: Ventricles contract, atrioventricular valves close, semilunar valves open, blood flows into pulmonary artery or aorta. |
|
|
Diastole Cardiac Cycle |
Atria and ventricles are relaxed. Blood flows into the right and left atria. The valves between the atria and the ventricles are open. Summary of events: Atrioventricular valves open, SA node activates causing atrial contraction, atria empties blood into ventricles, semilunar valves close. |
|
|
S1 (Lub) |
Mitral and Tricuspid Valve: Atrioventricular valves close at onset of ventricular systole. High frequency with lower longer pitch. |
|
|
S2 (Dub) |
Aortic and pulmonic valve: Semilunar valves close at onset of ventricular diastole. High frequency with higher pitch and shorter duration. |
|
|
S3 |
Ventricular gallop: Vibrations in distended ventricle walls d/t passive flow of blood during rapid filling phase of diastole. Normal in children, abnormal in adults. |
|
|
S4 |
Atrial gallop: Vibrations of ventricular wall with ventricular filling and contraction. Always abnormal |
|
|
Systolic murmur |
Vibrations of longer duration that occur between S1 and S2. |
|
|
Diastolic murmur |
Vibrations of longer duration that occur between S2 and S1 |

