![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Factors controlling ring synthesis through cyclization |
Thermodynamics 5,6 favoured Kinetics eyring equation - delta h and s |
|

For different ring sizes |
3: fast, S= favourable little preorganisation outweighs H ring strain 4: slower, S = less favourable as more ordered, H similar, harder to form 5: fastest gets smaller as well increasing across normal and medium S increases with increasing ring size 5-7 H constant 5-7 as relatively unstrained S increasing proportionately less as ring size increases medium H dominant as large transannular strain Large: S unfavourable - oligomerisation H no ring strain so unimportant Form large rings under high dilution Substrate dependent |
|

Ring size 3,4,5 |
3 favourable entropy dominates 4 unfavorable 5 enthalpy dominates |
|

3,4,5,6 |
3 unfavourable sp2 strain 5 favourable entropy and enthalpy |
|
|
Baldwin's rules |
Approach at 180 for Max homo-lumo overlap - need correct orbital alignment Baldwin's original rules and changes Table Exo tet and trig all allowed Endo tet and trig disallowed (except 6 endo-trig) All exo allowed by new rules |
|

Cyclization |
Attack at oxygen because poor orbital overlap for carbon attack 5-enolendo-exo-tet disfavoured 5-exo-tet favoured |
|

Cyclization |
Attack from carbon |
|
|
Baldwin's rules for enolates |

|
|

What happens |
6 endo tet disafvoured |
|

What happens |
6 exo tet favoured |
|
|
5 factors controlling ring synthesis through cyclization |
Thermodynamics Kinetics Stereoeletronic effects Thorpe Ingold effect Macrocyclic conformational control: templating/preorganization effects |
|

What happens |

Radical cyclizations |
|

Reaction and reactants |
Bu3sn and trace AIBN |
|

|
5 endo trig disfavoured 6 endo trig favoured |
|

What happened |
Nah naome no reaction since 5 endo trig disfavoured Cat tsoh c6h6 heat yes 5-exo trig favoured |
|
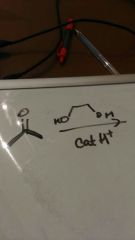
Acetal formation |

5 endo trig favoured as p orbital being attacked |
|

Explain x4 |
Thorpe-Ingold effect (A) lower H due to ground state bond angle compression (B) lower H due to ground state relief on commission (less sterics between Me groups) (C) lower S - reduced population of non reactive conformations (D) lower S - poor solvation of tertiary alcohols |
|

Cyclization order |

|
|

Make this |

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
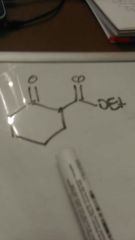
Make this |
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

Synthesise this |

|
|

|

|
|

Make this |

|
|

|

|
|

|

Dieckmann don't forget h+ workup |
|

|

Use reversibility of dieckmann |
|
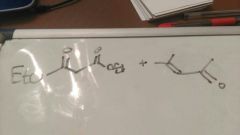
|

Robinson annelation = Michael and aldol |
|

Synthesise this |

Robinson annelation |
|

Synthesise |

Robinson ring annelation |
|

|

|
|

Synthesize |

|
|

|

|
|

|

5 exo trig |
|

|
25 |
|

What happens |
26 |
|

|
27 |
|

|
27 |
|
|
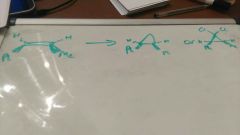
Carbene and carbenoid |
|

|
30 |
|

|
30 |
|

|
Ozonolysis 31 |
|

|
Go on do it P32 |
|

|
P32 |
|

|
P32 |
|

Make this |
P32 |
|
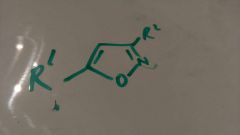
Make |
Nitrite oxide and alkyne |
|

|
P35 |
|

|
P36 |
|

|
P36 |
|

|
P36 |
|

|
36 |
|

|
37 |
|

|
37 |
|

|
37 |
|

|
37 |
|

|
38 |
|

|
38 |
|

|
Favorskii naoh |
|

|
39 |
|

|
39 |
|

Ruzicka |
Notes p3 grossel |
|

|
Make that |
|

|
P3 grossel notes |
|

|
P3 grossel |
|

|
P3 grossel |
|

|
Thorpe Ziegler then hydrolysis then decarboxylation p3/4 notes grossel |
|

|
Thorpe Ziegler |
|

|
Robinson ring annelation p4 grossel |
|
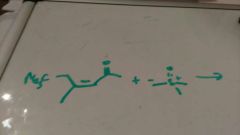
|
P4 grossel |
|

|
P4 grossel |
|

|
P4 grossel |
|

|
P4 grossel |

