![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

DNA |
A material present in almost all organisms, makes up chromosomes, genetic info carrier |
People DNA is in us |
|
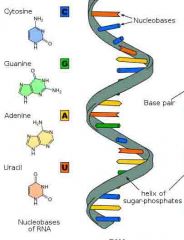
RNA |
A material in all living cells carries instructions for DNA |
People RNA is in all cells |
|
Gene expression |
The appearance in a phenotype it is a characteristic or the gene |
People Gene expression is in humans |
|
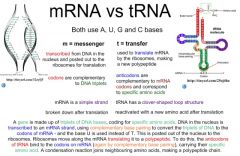
mRNA |
Large association of messenger RNA give genetic material from DNA to ribosomes |
People mRNA is messenger RNA |
|
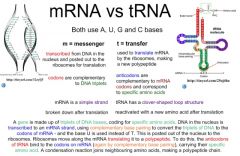
tRNA |
Very small molecules of RNA that are carriers of amino acids to ribosomes |
People tRNA carriers amino acids |
|
|
Genetic code |
Nucleotide triplets of DNA and RNA molecules, they carry genetic material in living cells |
People Genetic code involves both RNA and DNA |
|
|
Codon |
Sequence of three nucleotides that when together form a group of genetic code in either DNA or RNA |
People Codon involves three nucleotides |
|
|
Anticodon |
Sequence of three nucleotides that form a unit of genetic code through a transfer of in an RNA molecule |
People Anticodons involve RNA |
|
|
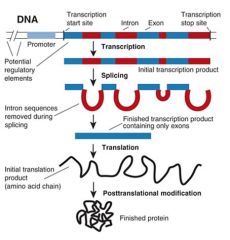
Transcription |
The first step in genetic expression, it where a segment of DNA into RNA |
Genes Transcription involves genetic expression |
|
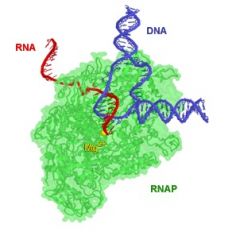
RNA polymerase |
Enzyme that makes primary transcript RNA. It is necessary for making RNA with DNA |
People RNA polymerase is an enzyme |
|
|
Transcription |
The enzyme-catalyzes assembly of an RNA molecule |
Complementary to a strand of DNA Product may be messenger of RNA, transfer RNA, or ribosomal RNA |
|
|
RNA polymerase |
An enzyme that catalyzes the assembly of an RNA molecule |
Joins RNA nucleotides according to the base sequence in DNA Prokaryotes have one type of RNA polymerase. RNA processing |
|
|
RNA processing |
When the RNA copy of a protein encoding gene is modified |
It has to be modified in many different ways before moving out of the nucleus |
|
|
Intron |
A segment of DNA that is transcribed into precursor messenger DNA |
Removed before the mRNA left the nucleus Do not code for proteins |
|
|
Exon |
A segment of DNA that is transcribed into RNA and translated into protein |
Specifies the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide. Remain in the nucleus after introns are removed |
|
|
Exon |
A segment of DNA that is transcribed into RNA and translated into protein |
Specifies the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide. Remain in the nucleus after introns are removed |
|
|
Splicing |
The process that joins exons after introns are removed |
The joining of two pieces of DNA Requires precise recognition of the site to be cut |
|
|
Translation |
The assembly of a protein on ribosomes |
Uses messenger RNA to direct the order of amino acids Happens with protein synthesis |
|
|
Translation |
The assembly of a protein on ribosomes |
Uses messenger RNA to direct the order of amino acids Happens with protein synthesis |
|
|
Tertiary structure |
The 3 D folded structure of a polypeptide or protein molecule |
Complex folding Not the first level of organization |
|
|
Translation |
The assembly of a protein on ribosomes |
Uses messenger RNA to direct the order of amino acids Happens with protein synthesis |
|
|
Tertiary structure |
The 3 D folded structure of a polypeptide or protein molecule |
Complex folding Not the first level of organization |
|
|
Translational error |
An error in the translation of RNA |
Most errors are caught and connected. Usually result from misreading the nucleotide sequence |
|
|
Frame shift mutation |
The insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a gene |
Causes disruption of the reading frame Change every subsequent codon |

