![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Cell Theory |
A biological theory formed in the 1800's that calls cells the basic units of life |
1. The theory put forth by Robert Hook 2. The second part of cell theory says that all cells come from cells |
|
|
Prokaryotes |
The simple type of unicellular organism that has no cell organelles |

2. The prokaryote had a corkscrew shape |
|
|
Eukaryotes |
A complex type of organism that can be mulitcellular and cell's have many organelles |

2. The cells of the eukaryote all did specific functions |
|
|
Nucleus |
The cell organelle that contains its protein synthesizing genetic code |
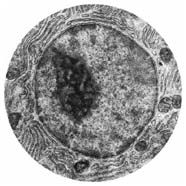
2. Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus |
|
|
Chromosome |
A large strand of DNA by itself or wrapped around proteins |
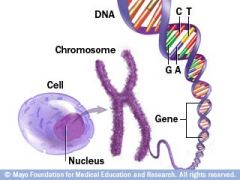
2. Chromosones contain RNA as well as DNA and proteins
|
|
|
Nucleoid
|
The area of a prokaryotic cell which contains its protein synthesizing genetic code |
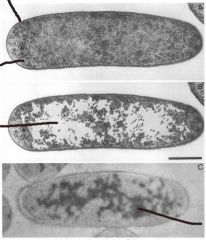
2. The nucleoid only has one chromosome while the the nucleus has many |
|
|
Plasmids |
Small circular DNA molecules found in the prokaryote |
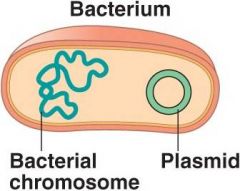
2. Plasmids and Chromosones do some of the same things but are found in different places |
|
|
Flagella |
Tail like proteins found on cells that allow them to move through liquids |
2. The flagella of eukaryotes are found inside the cell |
|
|
Cell/Plasma Membrane |
A phosopholipid barrier that regulates material passage |

2. Eukaryotic cell organelles have their own plasma membranes |
|
|
Cell Wall |
Rigid structures made of macromolecules that are found in prokaryotes, fungi, algae, and plants |
2. The cell wall prevents plants cells from exploding in osmosis |
|
|
Ribosomes |
Structures made of RNA and proteins that build proteins |
2. The ribosomes are part of the ER in eukaryotes |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
Portion of a cell where the organelles that are not the nucleus are located |

2. The organelles of the cytoplasm are bathed in the cytosol |
|
|
Cytosol |
Solution containing salts, organic compounds, and protein system called the cytoskeleton |
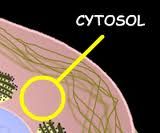
2. The cytosol is more complex than originally thought |
|
|
Organelles |
Parts of cells that had specific functions |
1. Mitochondria 2. Only eukaryotic cells have organelles |
|
|
Nucleolus |
Part of cell where RNA is built |
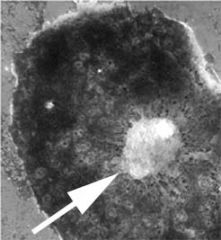
2. It is odd to think the nucleolus synthezises RNA which will synthesize something else |
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
Protein network found in the cytoplasm that lets the cell change shape |
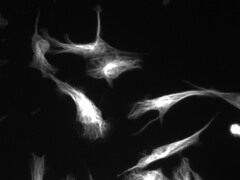
2. The cytoskeleton is in charge of moving organelles |
|
|
ER |
Part of cell that transports proteins to where they are needed in the cell |
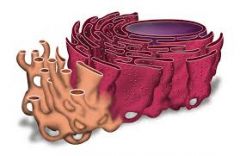
2. The part of the ER that contains ribosomes is called the rough ER |
|
|
Golgi |
Cell organelle modifies proteins that come from ER |

2. The golgi is connected the ER and the vesicles |
|
|
Vesicles |
Cell structure connected to golgi and that releases proteins outside the cell |
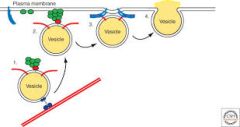
2. The vesicles participate in exocytosis |
|
|
Lysosomes |
Type of vesicle that decomposes macromolecules |
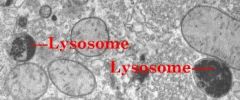
2. Lysosomes are used in breaking down foreign particles |
|
|
Vacuoles |
Large plant vesicles that contain organic compounds |
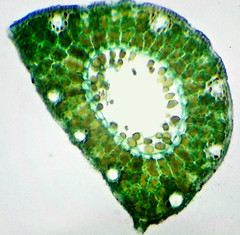
2. Vacuoles make up the majority of plant cells |
|
|
Centrioles |
Plant and Fungi organelles that help cells reproduce |

2. Centrioles participate in the type of reproduction called mitiosis |
|
|
Cilia |
Eukaryotic flagella that move the cell |
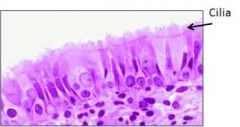
2. Eukaryotic cells have many cillia, unlike prokaryotic cells |
|
|
Colony |
Groups that unicellular organisms associate in |
1. Volvax 2. Cells in colonies are still their own seperate organisms |
|
|
Mutlicellular |
Organisms made of more than one cell |

2. The cells of multicellular organisms have different purposes |
|
|
Cell differentiation |
The process of cells becoming more complex and specialized |
1. A red blood cell 2. Cell differentation is how mutlicellular organisms function |
|
|
Tissue |
A mass of cells with the same function in multicellular organisms |
1. Muscle 2. Tissues are all made of the same type of cell |
|
|
Organ |
The arrangement of different tissues |
1. Lungs 2. Organs are the part of biology most humans first learn about |
|
|
Organ System |
The arrangement of different organs |
1. Nervous System 2. Animals have a variety of organ systems |
|
|
Organism |
The arrangement of different organ systems |
1. Rabbit 2. Organisms have extremely complex levels of organization |

