![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Population Genetics |
Biological field that deals with change within species |
1. The field of a scientist studying polymorphic traits in turtle 2. Population genetics attempts to answer the question of why are species different |
|
|
Gene Pool |
Compendium of all the genes and alleles of a specific population of a species |
1. All the genes of alligators in the Florida Everglades 2. Gene pools do not refer to all the organisms in a species, just in a local population |
|
|
Population |
All the members of a species in a specific geographic location |

2.Populations of organisms are often very inbred |
|
|
Evolution |
The difference in populations of species throughout time |

2. Charles Darwin developed the theory of evolution |
|
|
Polymorphic |
A population that has a gene pool with multiple alleles for a trait |

2. Populations can be polymorphic for many traits |
|
|
Genetic Variation |
The differences among individuals in the same species |

2. Genetic variation is why apples don't taste exactly alike |
|
|
Mutation |
Error in the sequence of a cell's DNA that can be silent, harmful, or helpful |
1. If an A base is paired with a C base 2. Although mutations can kill us they are responsible for evolution |
|
|
Genetic Recombination |
The process of creating new genetic combinations during crossing over in meiosis |
1. A chromosome replacing it's A allele with an a allele during crossing over 2. Genetic recombination is the second highest cause for genetic variation |
|
|
Hardy-Weinberg Model/Equation |
Mathematical model that calculates allele frequencies under ideal conditions |
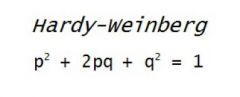
2. The Hardy-Weinberg Model shows the stability of allele frequencies over time |
|
|
p |
Variable in the Hardy-Weinberg equation standing for the frequency of the A allele |
1. The frequency of purple flowers in a population 2. P can stand for a dominant and recessive allele |
|
|
q |
Variable in the Hardy-Weinberg equation standing for the frequency of the B allele |
1. The frequency of white flowers in a population 2. The Hardy-Weinberg equation would be unchanged if written q+p=1 |
|
|
p^2 |
Variable in the Hardy-Weinberg equation standing for the frequency of homozygous plants of the A variable in the next generation |
1. Frequency of PP flowers in the 2nd generation of a population 2. The frequency of purple flowers in the 3rd generation will be (p^2)^2 |
|
|
2pq |
Variable in the Hardy-Weinberg equation standing for the frequency of heteorzygous plants in the next generation |
1. Frequency of Pp plants in the 2nd generation of the population 2. The 2pq number will be larger than the p^2 or q^2 number |
|
|
q^2 |
Variable in the Hardy-Weinberg equation standing for the frequency of homozygous plants of variable B in the next generation |
1. Frequency of pp plants in the 2nd generation of a population 2. Even though q^2 may be a recessive trait its frequency will stay stable through generations |
|
|
Microevolution |
The branch of evolution focusing on the differences in species over many generations |
1. Differences in horses since the 1300's 2. Macroevolution looks at a much longer period of time than microevolution |
|
|
Natural Selection |
Process of changing the gene pool by having only the members of a population with the best traits reproduce |
2. Natural selection is how organisms develop such specific defense mechanisms |
|
|
Gene Flow |
Change in the gene pool due to distant organisms entering the population |
1. A Siberian bear entering the population of Grizzly Bears 2. When European discovered Americas there was a major gene flow |
|
|
Genetic Drift |
Arbitrary differences in the frequencies of alleles |
1. A generation of Chickadees who have a random red streak 2. Genetic drift is not a factor in large populations |
|
|
Founder Effect |
A type of genetic drift that deals with the starters of new populations |
1. Two parrots who fly to a new island who just happen to have slightly less yellow feet than the normal population 2. The founder effect means that it may be hard to tell where different species of animal evolved from |
|
|
Inbreeding |
Steady increase of homozygous alleles due to loss of genetic variation |
1. Why male cheetahs have misshaped sperm 2. Because of the harmful effects of inbreeding incest is not approved of |
|
|
Population Bottleneck |
A period of time where a population of a species was substantially lowered and inbreeding occurred |
1. 3 generations where only 27 Rhinos were left alive in a Savannah 2. Population bottlenecks can have negative effects on a population for the duration of their existence |
|
|
Inbreeding Depression |
Negative effects of inbreeding due to increased homozygousity |
1. An inbred population of flamingos being less fertile 2. After about 20 generations of inbreeding the inbreeding depression will become so bad the organisms may die |
|
|
Quantitative Traits |
Traits that are affected by multiple traits and environmental factors |
1. Eye color 2. Because most traits are quantitative they cannot be studied just from examining the genome |
|
|
Quantative Trait Loci (QTLs) |
The places on the chromosome where genes that affect the quantitative traits are found |
1. The location of the gene for blue eyes being found near marker 4 on chromosome 5 2. Mapping of QTLs can be used to find the genes that cause obesity |
|
|
Artificial Selection |
Changing the genetic pool by human interaction |
1. Humans only planting the seeds of the tastiest tomatoes 2. Artificial selection is how we domesticated farm animals |

