![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
POLAR COVALENT BOND |
A covalent bond where one side of the molecule is positive and the other is negative.
|
|
|
|
COVALENT BOND
|
A bond formed when two atoms share their electrons.
|
|
|
|
LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MATTER.
|
Matter cannot be created or destroyed.
|
|
|
|
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
|
Molecules that always have carbon, always have hydrogen, and almost always have oxygen atoms in them.
|
|
|
|
LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MATTER.
|
Matter cannot be created or destroyed.
|
|
|
|
ACTIVATION ENERGY
|
The energy required to get a chemical reaction started.
|
|
|
|
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
|
Molecules that always have carbon, always have hydrogen, and almost always have oxygen atoms in them.
|
|
|
|
MACROMOLECULES
|
Molecules that are very large due to an abundance of carbon atoms in a carbon skeleton.
|
|
|
|
ACID
|
A solution with a greater quantity of hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions.
|
|
|

NUCLEIC ACID |
Macromolecules that control proteins and genetics.
|
|
|
|
COVALENT BOND
|
A bond formed when two atoms share their electrons.
|
|
|
|
POLAR COVALENT BOND
|
A covalent bond where one side of the molecule is positive and the other is negative.
|
|
|
|
POLAR COVALENT BOND
|
A covalent bond where one side of the molecule is positive and the other is negative.
|
|
|
|
COVALENT BOND
|
A bond formed when two atoms share their electrons.
|
|
|
|
COVALENT BOND
|
A bond formed when two atoms share their electrons.
|
|
|
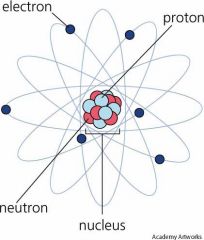
ATOM |
The smallest unit of an element retaining the element's properties.
|
A hydrogen atom, with 1 proton and 1 electron.
The two atoms of hydrogen chemically bonded to the oxygen atom to make a water molecule. |
|
MOLECULE |
A combination of atoms chemically bonded to each other.
|
1. A water molecule: 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 oxygen atom.
|
|
|
ELEMENT
|
A substance with a unique number of protons in its atoms.
|
Potassium is an element with 19 protons in the nucleus of its atoms.
The chemist found a rock consisting of only the element tin. |
|
|
PROTON
|
A subatomic particle with a positive charge, found in the atom's nucleus.
|
|
|
|
ELECTRON
|
A subatomic particle, with almost no mass, having a negative charge, and being in the electron cloud around the nucleus.
|
|
|
|
NEUTRON
|
A subatomic particle, found in an atom's nucleus, that carries no charge.
|
|
|
|
ION
|
A atom of any given element, having an alternative number of electrons.
|
|
|
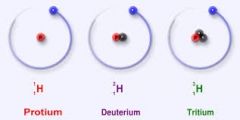
ISOTOPE |
An atom of any given element, having an altered number of neutrons.
|
|
|
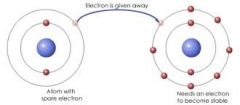
IONIC BOND |
A bond formed when atoms exchange electrons to become ions, and are then attracted to one another by opposite charges.
|
|
|
|
COVALENT BOND
|
A bond formed when two atoms share their electrons.
|
|
|
|
POLAR COVALENT BOND
|
A covalent bond where one side of the molecule is positive and the other is negative.
|
|
|
|
LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MATTER.
|
Matter cannot be created or destroyed.
|
|
|
|
ACTIVATION ENERGY
|
The energy required to get a chemical reaction started.
|
|
|
|
HYDROGEN BOND
|
A weak bond formed between a slightly positive hydrogen atom in a polar molecule and another (at least slightly negative) atom.
|
|
|
|
pH SCALE
|
A logarithmic scale expressing the amount of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions in a solution.
|
|
|
|
ACID
|
A solution with a greater quantity of hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions.
|
|
|
|
BASE
|
A solution with a greater quantity of hydroxide ions than hydrogen ions.
|
|
|
|
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
|
Molecules that always have carbon, always have hydrogen, and almost always have oxygen atoms in them.
|
|
|
|
MACROMOLECULES
|
Molecules that are very large due to an abundance of carbon atoms in a carbon skeleton.
|
|
|
|
CARBOHYDRATES
|
Macromolecules that contain lots of carbon, as well as hydrogen and oxygen in the same ratio as in water.
|
|
|
|
LIPIDS
|
A macromolecule (fat or oil) that is for structure and long-term energy, made from a fatty acid and glycerol, that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, but in no specific ratio.
|
|
|
|
PROTEINS
|
Macromolecules made of amino acids that do and make almost everything in the body/cells.
|
|
|
|
NUCLEIC ACID
|
Macromolecules that control proteins and genetics.
|
|
|
|
MONOSACCHARIDES
|
The monomers of macromolecules in the form of carbohydrates.
|
|
|
|
FATTY ACIDS & GLYCEROL
|
The building blocks of a lipid macromolecule.
|
|
|
|
AMINO ACIDS
|
The monomer of a protein polymer (polypeptide).
|
|
|
|
NUCLEOTIDES
|
The monomer of a nucleic acid chain.
|
|
|
|
DISACCHARIDE
|
A combination of two monosaccharide molecules.
|
|
|
|
POLYSACCHARIDE
|
A complex chain of carbohydrate macromolecules.
|
|
|
|
POLYPEPTIDE
|
A long sequence of amino acids bonded together.
|
|
|
|
PEPTIDE BOND
|
The bond between two amino acids.
|
|
|
|
DNA - Deoxyribonucleic Acid
|
A nucleic acid chain made of nucleotides held together by hydrogen bonds and a backbone of deoxyribose and a phosphate group, containing genetic information.
|
|
|
|
GENE
|
A bit of genetic information that is transferred from parents to offspring through DNA.
|
|

