![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
Atoms |
The smallest component of an element. |
1. Molecule
2. Life itself is made up of atoms. |
|
|
Molecule |
The smallest unit of an element. |
1. Atom
2. Molecules build up elements. |
|
Element |
Substances that cannot be turned into simpler substances. |
1. Hydrogen
2. The periodic table is built up of elements. |
|
|
Proton |
A positive charged particle in an atoms nucleus. |
1. Positive
2. A proton has the opposite charge of an electron. |
|
|
Electron |
A negative charged particle found outside an atoms shell. |
1. Negative
2. A electron has the opposite charge of a proton. |
|
|
Neutron |
A neutral charged particle found in an atoms nucleus. |
1. Neutral
2. A neutron has no charge. |
|
|
Ion |
An atom formed by the loss or gain of electrons. |
1. Na+
2. An ion doesn't have a normal amount of electrons. |
|
|
Isotope |
An atom formed by the loss or gain of neutrons. |
1. Carbon-12
2. An isotope doesn't have a normal number of neutrons. |
|
|
Ionic bond |
A bond through ions formed by electron transferring. |
1. Ions
2. Two ions can form an ionic bond. |
|
|
Covalent bond |
A bond through atoms formed by electron transferring. |
1. Electron
2. A covalent bond can be caused by electrons. |
|
|
Polar covalent bond |
A covalent bond that the electrons are not shared equally. |
1. Unequal
2. A polar covalent bond doesn't like sharing electrons. |
|

Law of conservation of matter |
A law saying matter can not be created or destroyed, only physically changed. |
1. Matter
2. The law shows that nothing truly is destroyed. |
|
|
Activation energy |
The engel needed to cause a chemical reaction. |
1. Reaction
2. Activation is crucial for a chemical reaction. |
|
|
Hydrogen bond |
A bond to hold together strands of DNA. |
1. Hydrogen
2. DNA relies on a hydrogen bond. |
|
|
pH scale |
A scale showing the strength of a hydrogen bond. |
1. 0 to 14
2. A pH scale helps show the strength of a hydrogen bond. |
|
|
Acid |
Proton donors that yield hydronium ions in water solutions. |
1. Hydronium
2. Acid usually has a very sour taste. |
|
|
Base |
A compound that reacts with acid to form a salt. |
1. Salt
2. A base form a sort of salt with the help of acid. |
|
|
Organic compounds |
Compounds made up of carbon. Hydrogen, and usually oxygen. |
1. CH2O
2. Organic compounds don't always have oxygen. |
|
|
Macromolecules |
Very large molecules. |
1. Plastic
2. Macromolecules are really big. |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
A class of molecules that form supporting tissue in living things. |
1. Fats
2. Carbohydrates are both a nutrients and a polymer. |
|
|
Lipids |
A class of molecules that comprises fats and other things. |
1. Greasy
2. Lipids are only a type of nutrients. |
|
|
Proteins |
A class of molecules that are crucial to the diet of any living thing. |
1.enzymes
2. Proteins are both a nutrients and a polymer. |
|
|
Nucleic acid |
Any group of long linear macromolecules. |
1. DNA
2. Nucleic acids are only a type of polymer. |
|
|
Monosaccharides |
The simplest form of a carbohydrate. |
1. Sugar
2. Monosaccharides are a type of sugar. |
|
|
Fatty acids & glycerol |
The things that make up fats, lipids, and membranes. |
1. C3H8O3
2. Glycerol is a very sweet and syrupy liquid. |
|
|
Amino acids |
Any type of organic compound containing at least one amino group. |
1. -NH2
2. Amino acids are a type of organic compound. |
|
|
Nucleotides |
Any group of molecules that form either DNA or RNA. |
1. Nucleic Acid
2. Nucleotides form DNA or RNA. |
|
|
Disaccharide |
The result of two bonded monosaccharides. |
1. Monosaccharides
2. Disaccharides are meaning 2 instead of 1. |
|
|
Polysaccharide |
The result of many bonded monosaccharides. |
1. Monosaccharide
2. Polysaccharides are a complex carbohydrate. |
|
|
Polypeptide |
A chain of linked amino acids by peptide bonds. |
1. Amino acid
2. Polypeptides have a molecular weight of about 10,000 |
|
|
Peptide bond |
A covalent bond formed by joining one amino acid to another. |
1. Amino acid
2. Peptide bonds are removed of a molecule of water. |
|
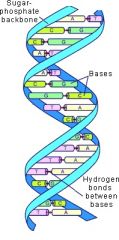
DNA |
Deoxyribonucleic Acid. |
1. Double Helix
2. DNA forms our genes and who we will be. |
|
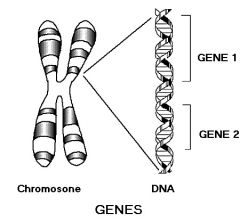
Gene |
The very basic unit of heredity. |
1. DNA
2. Genes are built up of chromosomes. |

