![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
137 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Frank breech? |
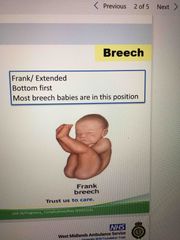
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Definition of gynaecology |
Medical practice dealing with female reproductive system, vagina,uterus, ovaries and the breast. |
|
|
The first trimester is how many weeks? |
1-12 weeks |
|
|
2nd trimester is? |
13-23 weeks |
|
|
3rd trimester is? |
24 plus weeks |
|
|
EDD |
Estimated date of delivery |
|
|
Gravid |
Pregnant uterus |
|
|
Parity |
Number of live children born |
|
|
G1P0 |
Shortened in notes to G and P this woman would be on her first pregnancy and has no live children |
|
|
G2P1 |
Second pregnancy, having one child already |
|
|
Fundus |
Top portion of uterus that forms the landmark for assessing gestation |
|
|
Ceph. / cephalic |
Baby is head down position for birth |
|
|
Br./breech |
Baby is in the bottom or feet first presentation |
|
|
SROM |
Spontaneous rupture of membranes |
|
|
USS |
Ultra sound scan |
|
|
LSCS |
Lower segment Caesarian section |
|
|
VBAC |
Vaginal birth after C section |
|
|
Vent |
Ventous delivery |
|
|
NBFD |
Neville Barnes forcep delivery |
|
|
APH |
Ante partum haemorrhage |
|
|
PPH |
Post partum haemorrhage |
|
|
EBL |
Estimated blood loss |
|
|
AN/ANC |
Antenatal/antenatal clinic |
|
|
Cx |
Cervix; for example if a woman has been examined vaginally it may be written in her notes Cx=2-3 , so her cervix is dilated 2-3cm |
|
|
NAD |
Nothing abnormal detected |
|
|
MLU |
Midwife led unit (low risk) |
|
|
CLU |
Consultant led unit |
|
|
Airway changes in pregnancy? |
Capillary engorgement due to hormones can cause swelling in the airway . Oedema in hypertensive conditions I.e. pre-eclampsia |
|
|
Airway changes in pregnancy? |
Capillary engorgement due to hormones can cause swelling in the airway . Oedema in hypertensive conditions I.e. pre-eclampsia |
|
|
Pregnant women are likely to have ? |
Short obese neck Engorged breast tissue Full dentition Can make airway maintenance difficult, intubation, fitting a collar, increased risk of aspiration |
|
|
Airway changes in pregnancy? |
Capillary engorgement due to hormones can cause swelling in the airway . Oedema in hypertensive conditions I.e. pre-eclampsia |
|
|
Pregnant women are likely to have ? |
Short obese neck Engorged breast tissue Full dentition Can make airway maintenance difficult, intubation, fitting a collar, increased risk of aspiration |
|
|
Thorax alterations during pregnancy? |
Diaphragm rises Intercostal angle increases 68-103 degrees in late pregnancy , known as splayed ribs Splayed ribs lead to decreased thoracic compliance due to raised diaphragm and splayed ribs Breathing is diaphragmatic Tidal volume will increase by up to 700ml 20% by week 12 40% by week 40 Residual capacity is reduced |
|
|
Cardiovascular changes |
Plasma volume increases until week 34 Blood volume increases by 48-50% Increased blood volume reduces impact of loss at birth 300-500ml normal birth 750-1000ml c-section Increase in RBC and wbc production Increase in plasma and blood cell production not in proportion , leads to relative haemodilution: anaemia
|
|
|
Cardiovascular changes |
Plasma volume increases until week 34 Blood volume increases by 48-50% Increased blood volume reduces impact of loss at birth 300-500ml normal birth 750-1000ml c-section Increase in RBC and wbc production Increase in plasma and blood cell production not in proportion , leads to relative haemodilution: anaemia
|
|
|
Hormonal changes |
Increase in HCG causes vasodilation HR increases by 10-15bpm Stroke volume increases to assist in raising cardiac output 64-71 ml Ectopics are present and usually harmless Heart enlarges by 70-80ml resulting from diastolic filling and hyper trophy Can lose 35% of circulating blood volume before hypotension Fewer reserves of blood left Foetal distress after 10-20% of maternal blood loss |
|
|
Cardiovascular changes |
Plasma volume increases until week 34 Blood volume increases by 48-50% Increased blood volume reduces impact of loss at birth 300-500ml normal birth 750-1000ml c-section Increase in RBC and wbc production Increase in plasma and blood cell production not in proportion , leads to relative haemodilution: anaemia
|
|
|
Hormonal changes |
Increase in HCG causes vasodilation HR increases by 10-15bpm Stroke volume increases to assist in raising cardiac output 64-71 ml Ectopics are present and usually harmless Heart enlarges by 70-80ml resulting from diastolic filling and hyper trophy Can lose 35% of circulating blood volume before hypotension Fewer reserves of blood left Foetal distress after 10-20% of maternal blood loss |
|
|
Metabolic changes |
Extra workload on heart limited due to viscosity of blood Growing foetus will increase organ activity |
|
|
Cardiovascular changes |
Plasma volume increases until week 34 Blood volume increases by 48-50% Increased blood volume reduces impact of loss at birth 300-500ml normal birth 750-1000ml c-section Increase in RBC and wbc production Increase in plasma and blood cell production not in proportion , leads to relative haemodilution: anaemia
|
|
|
Hormonal changes |
Increase in HCG causes vasodilation HR increases by 10-15bpm Stroke volume increases to assist in raising cardiac output 64-71 ml Ectopics are present and usually harmless Heart enlarges by 70-80ml resulting from diastolic filling and hyper trophy Can lose 35% of circulating blood volume before hypotension Fewer reserves of blood left Foetal distress after 10-20% of maternal blood loss |
|
|
Metabolic changes |
Extra workload on heart limited due to viscosity of blood Growing foetus will increase organ activity |
|
|
Vascular changes |
Placental bed acts as shunt between arterial and venous systems - no capillary circulation Heart fibres enlarge - myocardial fibres -(hypertrophy 70-80mls) Cardiac output increases 40% BP will drop in 2nd trimester by 5-15mmHg Profine falls in BP may occur after 20wks when woman is laid supine |
|
|
Gastrointestinal conditions |
Raised intra abdo pressure Displaced and relaxing of cardiac sphincter lead to reflux Gastric motility is slowed Intestines are relocated to upper abdo Risk of gastric aspiration Always assume patient has full stomach |
|
|
Gastrointestinal conditions |
Raised intra abdo pressure Displaced and relaxing of cardiac sphincter lead to reflux Gastric motility is slowed Intestines are relocated to upper abdo Risk of gastric aspiration Always assume patient has full stomach |
|
|
Orthopaedic changes |
Production of progesterone alters centre of gravity leading to increased risk of orthopaedic injury Other changes occur from smell |
|
|
3 layers of uterus? |
Endometrium Myometrium Perimetrium |
|
|
3 layers of uterus? |
Endometrium Myometrium Perimetrium |
|
|
Uterus stays within the pelvis for? |
12 weeks |
|
|
3 layers of uterus? |
Endometrium Myometrium Perimetrium |
|
|
Uterus stays within the pelvis for? |
12 weeks |
|
|
Foetus moves to umbilical region by? |
Week 20 |
|
|
3 layers of uterus? |
Endometrium Myometrium Perimetrium |
|
|
Uterus stays within the pelvis for? |
12 weeks |
|
|
Foetus moves to umbilical region by? |
Week 20 |
|
|
Foetus moves to costal region by? |
34-36 weeks |
|
|
Foetus descends week? |
38 weeks Head engages pelvis ; cephalic presentation |
|
|
Foetus descends week? |
38 weeks Head engages pelvis ; cephalic presentation |
|
|
Thickness of uterus |
Thick walled in trimester 1 well protected by pelvis Thin walled in trimester 3 less protected Bowel and stomach are compressed Bowel is protected to a degree from penetrating trauma |
|
|
When does placenta develop? |
14 days after ovulation |
|
|
When does placenta develop? |
14 days after ovulation |
|
|
Functions of placenta ? |
Respiratory gas exchange Transport nutrients Excrete waste Heat transfer Hormone production Barrier |
|
|
Structure of umbilical cord |
Connects foetus and placenta 2 arteries and 1 vein, vein carries oxygenated blood to foetus Foetal circulation bypasses lungs via the foreman ovale Cord length: 30-90cm, short cord less than 40cm |
|
|
Structure of umbilical cord |
Connects foetus and placenta 2 arteries and 1 vein, vein carries oxygenated blood to foetus Foetal circulation bypasses lungs via the foreman ovale Cord length: 30-90cm, short cord less than 40cm |
|
|
Function of amniotic sac? |
Membranous bag Encloses foetus and contains amniotic fluid Fluid allows weightless environment to enable development of baby Assists in removal of waste products Foetus swallows fluid and urinates |
|
|
Is pregnancy an illness? |
No, massive physiological event, causing immense changes to maternal body |
|
|
Is pregnancy an illness? |
No, massive physiological event, causing immense changes to maternal body |
|
|
What is gestational period? |
40 weeks from first day of last period This is 2 weeks before conception |
|
|
Is pregnancy an illness? |
No, massive physiological event, causing immense changes to maternal body |
|
|
What is gestational period? |
40 weeks from first day of last period This is 2 weeks before conception |
|
|
How many weeks passed as term? |
37 |
|
|
Fundal height assessment |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
After 20 weeks fundal height often matches weeks of pregnancy |
True |
|
|
After 20 weeks fundal height often matches weeks of pregnancy |
True |
|
|
Assessment |
Smart Go cat Avpu ABCD |
|
|
Exposure |
Consent for examination Consider environment is fit for delivery Any bleeding? Pads, how saturated Aim is to identify time critical problems to allow for rapid management and transport |
|
|
Exposure |
Consent for examination Consider environment is fit for delivery Any bleeding? Pads, how saturated Aim is to identify time critical problems to allow for rapid management and transport |
|
|
Clinical assessment |
RR HR Temp BP Frequency of contractions Blood loss Blood loss at each stage Consider BM if history of gestational diabetes |
|
|
Exposure |
Consent for examination Consider environment is fit for delivery Any bleeding? Pads, how saturated Aim is to identify time critical problems to allow for rapid management and transport |
|
|
Clinical assessment |
RR HR Temp BP Frequency of contractions Blood loss Blood loss at each stage Consider BM if history of gestational diabetes |
|
|
Obstetric history |
EDD Any bleeding presenting part of baby cord prolapse Previous birth history Previous complications Safeguarding? Obstetric unit booked ? Planned home birth Midwife contacted Recent trauma ? Onset of symptoms Perineum bulge present Has baby been born? Check area/toilet |
|
|
Assessment |
Discharge/ membranes ruptured? Colour- clear and odourless , clear and smells of urine, green, yellow, pink or red Smell Consistency - watery, thick jelly like, frothy Quantity - gush, trickle, still draining |
|
|
Pain old carts |
Type- constant, uterus go hard ? Coming and going, stabbing, ache? Severity/location- Abdo- over uterus, lie down , under ribs, one side, back? Chest? Central, one side,back Head- frontal, crushing? Radiation Relieving |
|
|
Labour assessment |
Number of contractions in 10 minute period Strength How long do they last Does patient feel like pushing Anything hanging out between legs , cord? |
|
|
Labour assessment |
Number of contractions in 10 minute period Strength How long do they last Does patient feel like pushing Anything hanging out between legs , cord? |
|
|
Foetal assessment |
Is the baby moving normal or less Last time baby moved Dead babies can move like immobile object in fluid |
|
|
Obstetrics |
The health science that deals with pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum period, includes care of the newborn |
|
|
Obstetrics |
The health science that deals with pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum period, includes care of the newborn |
|
|
Baby’s circulation volume should be? At birth |
350ml |
|
|
Obstetrics |
The health science that deals with pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum period, includes care of the newborn |
|
|
Baby’s circulation volume should be? At birth |
350ml |
|
|
By cutting cord early you are reducing blood volume by ? |
150ml |
|
|
The loss of pregnancy or miscarriage can happen up to which week? |
24 weeks |
|
|
The loss of pregnancy or miscarriage can happen up to which week? |
24 weeks |
|
|
What is a threatened miscarriage? |
Light bleeding Little or no pain |
|
|
What is an inevitable miscarriage? |
More pain Bleeding rarely severe |
|
|
What is an inevitable miscarriage? |
More pain Bleeding rarely severe |
|
|
What is an incomplete miscarriage? |
Whole or part of placenta is retained |
|
|
When is miscarriage more common? |
Weeks 6-14 or within the first 12 weeks |
|
|
If a miscarriage occurs between 14-24 weeks what is the most likely cause? |
Underlying health condition |
|
|
What are the risk factors of miscarriage? |
Drugs/alcohol Smoking Obesity Age; under 30, 1 in 10 35-39, 2 in 10 Over 40 more than half |
|
|
What is an ectopic pregnancy and when does it occur? |
Fertilised egg implants outside womb 4-12 weeks gestation |
|
|
What are the risk factors to an ectopic pregnancy? |
Intra uterine device fitted Previous ectopic Smoking Increased maternal age IVF Sterilisation or reversal Pelvic inflammatory disease Chlamydia |
|
|
Management of ectopic? |
Maintain high suspicion of ectopic Correct C ABCD Treat for shock Pain relief Reassurance Time critical transfer |
|
|
What is antepartum haemorrhage? |
Bleeding from genital tract after 24 weeks Partial separation of placenta from uterine wall Caused by placental abruption or placenta praevia |
|
|
Estimating blood loss of APH |
Spotting: staining/streaking notes on underwear Minor; less than 50ml that has settled Major; more than 50ml |
|
|
Risk factors of APH? |
Over 40 years Complex medical problems Multigravida Previous C section Known placenta praevia Drugs Hypertension Coagulopathies History of APH Polyhydramnios |
|
|
Colour of blood for placental abruption? |
Darker in colour as it doesn’t exit straight away |
|
|
Different types of placenta praevia? |
Low placental implantation Partial placental praevia Complete placental praevia |
|
|
When can placental abruption happen? |
Any time after 20 weeks 50-80% of foetuses die, poor prognosis for ones that survive |
|
|
APH management |
Woody feeling blood present Baby has stopped moving for an extended period Treatment for shock , position left lateral Time critical transfer |
|
|
PIH or severe pre-eclampsia affects how many pregnancies? |
10-15% |
|
|
PIH is defined as a significant rise in BP after how many weeks gestation? |
20 weeks, with no signs of proteinuria or features of pre-eclampsia |
|
|
Pre-eclampsia is what and when does it occur? |
Development of hypertension >140 systolic >90 diastolic Proteinuria 20th week gestation |
|
|
Pre-eclampsia management? |
Maintain high suspicion of pre eclampsia Correct primary survey concerns Time critical features If BP is >140/90 speak to obstetrics If BP is >160/110 treat as time critical transfer |
|
|
Severe pre-eclampsia BP? |
>160/110 with proteinuria including one or more; Headache Visual disturbance Epigastric pain Confusion Oedema Nausea vomiting |
|
|
Severe pre-eclampsia management? |
Quick assessment and primary survey Time critical features Correct A and B problems SP02- target 94-98 Paramedic backup Do not administer fluids, risk of provoking oedema Time critical transfer to CLU |
|
|
What is eclampsia? |
Pre-eclampsia with convulsions Occurs after 24 weeks Can occur during pregnancy, labour, birth and up to 48 hours after delivery |
|
|
Eclampsia inset preceded by? |
Severe headache Dizziness Epigastric pain Vomiting Visual disturbance |
|
|
What is a cord prolapse? |
Cord below presenting part with intact membrane Preventing arterial and venous blood flow to foetus |
|
|
What is a cord prolapse? |
Cord below presenting part with intact membrane Preventing arterial and venous blood flow to foetus |
|
|
Management of cord prolapse? |
Avoid handling Use dry pad to get back in If longer do not attempt pushing in Knees to chest position Lateral position Pain relief Transfer with pre alert |
|
|
What is a cord prolapse? |
Cord below presenting part with intact membrane Preventing arterial and venous blood flow to foetus |
|
|
Management of cord prolapse? |
Avoid handling Use dry pad to get back in If longer do not attempt pushing in Knees to chest position Lateral position Pain relief Transfer with pre alert |
|
|
What is PPH? |
Most likely bleed from placenta site but can occur from any part of genital tract If uterine does not contract the myometrial fibres do not exert usual homeostatic compression of uterine muscles |
|
|
What is a cord prolapse? |
Cord below presenting part with intact membrane Preventing arterial and venous blood flow to foetus |
|
|
Management of cord prolapse? |
Avoid handling Use dry pad to get back in If longer do not attempt pushing in Knees to chest position Lateral position Pain relief Transfer with pre alert |
|
|
What is PPH? |
Most likely bleed from placenta site but can occur from any part of genital tract If uterine does not contract the myometrial fibres do not exert usual homeostatic compression of uterine muscles |
|
|
Blood loss for PPH? |
Primary :500ml or more within 24 hours of birth Secondary: PPH abnormal bleeding 24 hours to 12 weeks after birth |
|
|
What is a cord prolapse? |
Cord below presenting part with intact membrane Preventing arterial and venous blood flow to foetus |
|
|
Management of cord prolapse? |
Avoid handling Use dry pad to get back in If longer do not attempt pushing in Knees to chest position Lateral position Pain relief Transfer with pre alert |
|
|
What is PPH? |
Most likely bleed from placenta site but can occur from any part of genital tract If uterine does not contract the myometrial fibres do not exert usual homeostatic compression of uterine muscles |
|
|
Blood loss for PPH? |
Primary :500ml or more within 24 hours of birth Secondary: PPH abnormal bleeding 24 hours to 12 weeks after birth |
|
|
PPH management? |
Tone- uterus does not contract Tissue-retained products Trauma- uterine rupture, cervical or vaginal lacerations Thrombin- coagulopathies |
|
|
Complications of PPH? |
Trauma to perineum or genital tract, apply pressure with pressure dressing May lead to cardiovascular collapse |
|
|
Complications of PPH? |
Trauma to perineum or genital tract, apply pressure with pressure dressing May lead to cardiovascular collapse |
|
|
What is a uterine rupture ? |
Tear in uterus Commonly associated with previous c section Can occur in first pregnancy can lead to death of mother and baby |

