![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
132 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
PLATE TECTONICS
|
Converging = mountains - come together Diverging = rift valleys - pull apart Transformation = earthquakes Subduction = volcanoes - one below another |
|
|
CHONPS
|
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur |
|
|
EROSION · |
Wind, Water, Ice, & Gravity MOVES sediment; Plants help by holding soil in place |
|
|
CHEMICAL CHANGES
|
Rusting, Burning, Digesting, Bubbling, Fizzing, Unexpected Temp Change |
|
|
CONVECTION
|
SUN produces energy; Warm air rises, cold air sinks; Winds; Ocean currents |
|
|
Physical change |
chewing, cutting |
|
|
extinction |
Cause - DESTRUCTION of HABITAT by humans |
|
|
Habitat |
where an organism lives |
|
|
Weather |
Low pressure = lousy (rainy, cloudy)
High pressure = happy (sunny) |
|
|
Fossil Fuels |
Coal, Oil, Natural Gas Nonrenewable |
|
|
BIODIVERSITY |
variety of plants and animals in an ecosystem.
|
|
|
SUSTAINABILITY |
healthy ecosystem b/c large # of plants & animals (biodiversity) |
|
|
Cell Characteristics
|
Prokaryotic = no nucleus Eukaryotic = has a nucleus Autotrophic – makes own food Heterotrophic – hunts food |
|
|
Excretory |
Filters waste (kidney)
|
|
|
Balanced Forces |
NO movement OR constant velocity |
|
|
Unbalanced Forces |
cause motion |
|
|
HURRICANES are caused by
|
LOW PRESSURE WARM WATER (tropics) SUMMER and FALL |
|
|
Succession
|
Lichens & Moss -> Soil -> grass/weeds ->
shrubs->small trees -> big trees |
|
|
Evidence of Plate Tectonic Theory |
1. Continents fit like puzzle pieces
2. Fossils on opposite sides of oceans.
3. Major landforms on multiple continents |
|
|
TIDES
|
Caused by pull of moon’s gravity
|
|
|
Spring Tide |
Straight (sun, moon, earth) Super High, Super Low |
|
|
Neap tide |
Moon at 90 (Ninety) degree angle from the earth |
|
|
GALAXY
|
Made of Billions of stars; Milky Way is one
|
|
|
Milky Way |
disk shaped (spiral) galaxy
|
|
|
Stars |
make up a galaxy |
|
|
Nebula |
gas and dust that form a star gas and dust made from dying stars
|
|
|
Density |
mass / volume |
|
|
Speed |
distance / time |
|
|
Force |
mass x acceleration |
|
|
Velocity |
speed AND direction |
|
|
NEWTON’S LAWS
|
1. Inertia
2. Force = Mass X Acceleration
3. Every action has equal and opposite reaction |
|
|
Inertia |
object at rest stays at rest |
|
|
Force |
Mass X Acceleration |
|
|
Potential and Kinetic Energy |
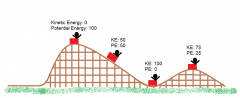
|
|
|
Proton |
positive - inside nucleus - "big" mass |
|
|
Neutron |
neutral - inside nucleus - "big" mass |
|
|
Electron |
Negative - outside nucleus - TINY mass |
|
|
Atomic Mass calculation to find neutrons |
Mass
- Atomic # =
Neutrons |
|
|
Periodic Table
|
Periods = rows, energy levels
Groups (family) = columns, similar properties, same valence electrons |
|
|
Periods |
rows, energy levels |
|
|
Groups |
columns, similar properties same # valence electrons |
|
|
GROUP 18 |
NOBLE GAS; Not reactive |
|
|
METALS
|
Left of stair-step line
- luster (shiny)
- conduct electricity
- malleable and ductile
|
|
|
NON-METALS
|
Right of stair-step line
- no luster
- no conductivity
good insulator |
|
|
Element |
found on periodic table |
|
|
Compound |
made up of 2 or more elements (two or more capital letters) |
|
|
C6H12O6
|
1 compound
3 elements
24 atoms |
|
|
LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MASS
|
Balancing an equation; same # of atoms of each element is found on reactant and product side |
|
|
Atoms in a chemical reaction are NEVER LOST OR GAINED, they are only REARRANGED |
LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MASS |
|
|
2 Plant Cell Differences
|
CELL WALL
CHLOROPLAST |
|
|
CELL ORGANELLES
|
Mitochondria– Power plant. Energy
Vacuole– water storage
Nucleus– has genetic material (DNA, chromosomes, genes) |
|
|
Mitochondria |
Power plant; Energy |
|
|
Vacuole |
water storage |
|
|
Nucleus |
has genetic material (DNA, chromosomes, genes) |
|
|
Sexual Reproduction |
2 parents; diverse offspring |
|
|
Asexual Reproduction |
1 parent; uniform offspring |
|
|
PREDATOR |
hunts prey |
|
|
PREY |
eaten by predator |
|
|
PARASITE |
harms the host
|
|
|
HOST |
harmed by parasite |
|
|
Work |
force x distance Object must MOVE |
|
|
Acceleration
|
Changing speed OR direction OR both |
|
|
Chemical Change |
New Substance is formed
|
|
|
Endocrine |
regulates hormones (glands) |
|
|
Integumentary |
protects (skin, hair, nails) |
|
|
Circulatory |
transfers nutrients (blood) carries gases
|
|
|
Respiratory |
exchange of gases (lungs) |
|
|
The % OF ENERGY passed UP the Pyramid |
10 |
|
|
CELL THEORY
|
1. All life is composed of cells
2. Cells are the basic unit of life
3. Cells arise from other cells |
|
|
Atomic #
Protons
Electrons |
Always the same number!! |
|
|
Valence Electron
|
Determines reactivity; # of Electrons in outermost energy level; look at Group # |
|
|
SEASONS caused by
|
1. 23.5* tilt of earth
2. Earth's revolution around Sun 365 days
|
|
|
BIOTIC |
LIVING factors (plants, animals, fungi, bacteria) |
|
|
ABIOTIC |
NONLIVING factors (sunlight, water, temperature, or soil) |
|
|
METALLOIDS
|
ON the stair-step line
w/ properties of both metals & non-metals |
|
|
R * A * P |
Reactant --> Product; for balancing equations |
|
|
SUN
|
Medium sized star; Near edge of galaxy
Yellow = average temperature
Middle of the HR diagram |
|
|
Waxing Crescent |
btwn new moon & 1st quarter RIGHT bright & SKINNY |
|
|
new moon |
btwn waning crescent & waxing crescent |
|
|
first quarter |
btwn waxing crescent & waxing gibbous RIGHT side 50% bright |
|
|
full moon |
btwn waxing gibbous & waning gibbous |
|
|
waxing gibbous |
btwn 1st quarter & full moon RIGHT side bright & BIG |
|
|
waning gibbous |
btwn full & last quarter LEFT side bright & BIG |
|
|
waning crescent |
right before new moon LEFT side bright & SKINNY |
|
|
last quarter |
btwn waning gibbous & waning crescent LEFT side 50% bright |
|
|
Lunar Cycle (Moon Phases) |
28 DAYS for a FULL CYCLE |
|
|
prokaryotic |
no nucleus - pro no! |
|
|
eukaryotic |
has a nucleus - you yes! |
|
|
autotroph |
makes own food; producer |
|
|
heterotroph |
hunts food; consumer |
|
|
dependent variable |
the variable that changes in response to the independent variable |
|
|
independent variable |
the variable the scientist changes |
|
|
scientific method |
steps scientists use to test solutions to scientific problems |
|
|
atom |
smallest particle of matter that maintains properties of that element |
|
|
models |
representation of something too small or too large to be seen |
|
|
nucleus |
center of the atom |
|
|
symbol |
1 or 2 letters; represents an element |
|
|
family |
same as a group; they have similar properties and reactivity |
|
|
shell |
energy level; electrons found here |
|
|
group 1 |
alkali metals; MOST reactive; 1 Valence Electron |
|
|
group 2 |
alkaline earth metals; VERY reactive; 2 VEs |
|
|
group 17 |
Halogens; 7 Valence Electrons |
|
|
physical properties |
properties found using sight or touch |
|
|
conductivity |
able to conduct heat or electricity |
|
|
corrosive |
can be broken down by rust or acid |
|
|
reactivity |
ability to react with another element or substance |
|
|
density |
how heavy something is for its size |
|
|
solubility |
ability to be dissolved |
|
|
viscosity |
how thick a liquid is |
|
|
flammability |
ability to burn |
|
|
insulators |
NOT able to conduct heat or electricity |
|
|
luster |
ability to reflect light; shiny |
|
|
malleability |
ability to be made into foil |
|
|
yields |
reacts to; represented by the ARROW |
|
|
chemical equation |
shows a chemical REACTION using symbols --> |
|
|
chemical formula |
describes compound using symbols |
|
|
coefficient |
BIG number in front of a compound tells how many molecules |
|
|
mixture |
a combination of 2 or more substances that are not chemically combined |
|
|
Dissolving |
PHYSICAL Property |
|
|
subscript |
SMALL number lower right of the symbol tells how many atoms |
|
|
100% |
Full Moon % of lit side visible on Earth |
|
|
0% |
New Moon % of lit side visible on Earth |
|
|
sunlight, water, temperature, or soil |
Abiotic Factors |
|
|
plants, animals, fungi, or bacteria |
Biotic Factors |
|
|
Newton's 3rd Law |
Each action has an equal & opposite reaction |
|
|
Mountains & Trenches |
made at CONVERGENT |
|
|
Ridges & Rift Valleys |
made at DIVERGENT |
|
|
Faults and Earthquakes |
made at TRANSFORM |
|
|
population DECREASES |
population DIES |
|
|
Carnivores eat |
MEAT |
|
|
Herbivores eat |
PLANTS |
|
|
Omnivores eat |
Meat AND Plants |

