![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
85 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
how many vertebrae are there?
|
33
|
|
|
what are the different groups of vertebral column and their corresponding number of vertebrae?
|
From top to bottom: (cranial to caudal)
7 cervical vertebrae 12 thoracic vertebrae 5 lumbar vertebrae 5 sacral vertebrae (fused together) 4 coccygeal vertebrae (fused) |
|
|
zygapophysial joints
|
The synovial joints between superior and inferior articular processes on adjacent vertebrae are the zygapophysial joints
|
|
|
What are the the two major types of joints between vertebrae?
|
1. symphyses between vertebral bodies (inter vertebral discs)
2. synovial joints between articular processes |
|
|
what is the primary curvature of vertebral column?
|
Primary curvature (mostly in fetus and babies) is the one where the vertebral column is arranged in
concave fashion (from the anterior or ventral view). |
|
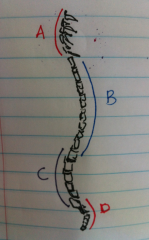
Identify the curvature in the image as primary (concave) or secondary (convex) for different parts of vertebral column.
hint : A and B are on the anterior side |
A. secondary or convex [cervical vertebrae]
B. primary or concave [thoracic vertebrae] C. secondary or convex [lumbar vertebrae] D. primary or concave [sacral and coccygeal vertebrae] |
|
|
what are the anatomical features of Vertebrae?
|
Total 7 anatomical features of vertebra ( note: not every vertebra has all these features )
1. Body (weight bearing part) 2. Vertebral arch (protective part) 3. Processes 4.Vertebral Foramen 5. Vertebral Canal 6. notches 7. Intervertebral foramen |
|
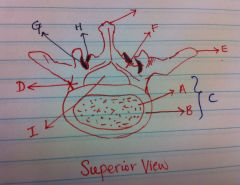
Vertebral Arch is composed of what two parts? identify them on the image.
|
1. Pedicles (two one on each side)
2. Lminae (two one on each side) On Image: ( D ) Pedicle the part of the arch which connects the transverse process and the lamina to the vertebral body. ( F ) Lamina dorsal part of arch connected to pedicles. |
|
|
how many processes are there in vertebra?
|
Total 7.
a. Articular processes (4) b. Transverse processes (2) c. Spinous process (1) |
|
|
Which vertebral processes are attached by Synovial joint?
|
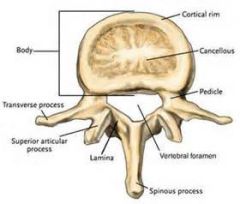
articular processes
bony part of synovial joint; contains 2 superior and 2 inferior facets for articulations with other vertebrae. |
|
|
What processes originate from the junction between the pedicle and the lamina
|
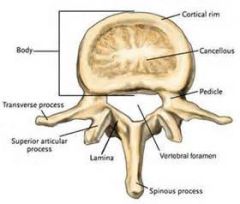
Transverse Processes
|
|
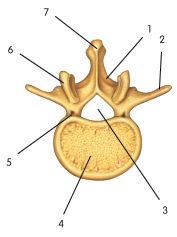
identify the Spinous process in the picture.
|
( 7 )
|
|
|
what is the function of spinous process?
|
Attachment for muscles and ligaments.
|
|
|
What is Vertebral foramen?
|
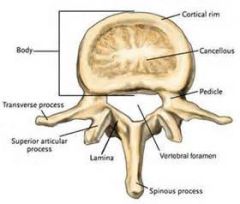
the opening in one vertebrae bounded by the body, the pedicles, and the laminae.
|
|
|
How is vertebral canal formed?
|
The vertebral or the spinal canal is formed by the successive vertebral foramina. This canal forms a continuous channel which contains the spinal cord, nerve roots, spinal nerves, meninges, and vessels.
|
|
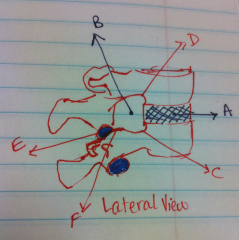
Name the notches in vertebra and identify them on the image.
|
a. Superior vertebral notch – small notch above the pedicle. [Labeled as "C" on image]
b. Inferior vertebral notch – small notch below the pedicle. [Labeled as "D" on image] |
|
|
How is intervertebral foramen formed?
|
an opening called "intervertebral foramen" is formed by superior and inferior vertebral notches of adjacent vertebrae; the dorsal root ganglia of spinal nerves lie in the intervertebral foramina, and it is in this area that the dorsal and ventral roots join.
|
|
|
what is Transverse foramina?
|
Foramina in the Cervical transverse processes of the first 6 cervical vertebrae; often present in C7. The foramina contain the vertebral arteries and veins.
|
|
|
what is the name for 1st Cervical Vertebra?
|
Atlas
|
|
|
what are some of the distinct features of Atlas (first cervical vertebra)?
|
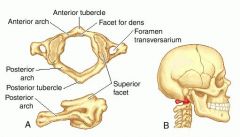
i. Lacks a body and a spinous process
ii. Contains an anterior arch and anterior tubercle, a posterior arch and posterior tubercle, and a lateral mass |
|
|
what is the name for 2nd cervical vertebra?
|
Axis
|
|
|
what are the distinct features of axis?
|
a. Dens (odontoid process)
b. Atlantoaxial joint – joint between the atlas and the axis’ dens |
|
|
which vertebra contains a long spinous process?
|
C 7 – vertebra prominens
|
|
|
which vertebrae have bifid spines?
|
Cervical vertebrae from C2 to C6 have bifid spines.
|
|
|
what are costal facets and where are they located?
|
Costal facets are located on the thoracic vertebrae for articulation with ribs; located on the body and on the transverse process.
|
|
|
how many costal facets are there on thoracic vertebra?
|
Total 6
2 superior, 2 inferior, and two transverse |
|
|
long slender spinous processes are the characteristic of which group of vertebrae?
|
Thoracic
|
|
|
Joint between the atlas (c1) and the axis’ (C2) dens is called?
|
Atlantoaxial ( if you have difficulty remebering this name think about a joint between ATLAS ..to...AXIAL
|
|
|
what is the function of Atlantoaxial joint?
|
Lateral rotation of atlas on axis (shaking head in "no" movement)
|
|
|
what is the shape of vertebral bodies in the middle of thoracic region
|
The bodies in the middle of the thoracic region are heart-shaped. ( from lab manual)
|
|
|
which vertebrae has the largest body size?
|
Lumbar
|
|
|
anterior and superior part of the body of S1 is called?
|
Sacral promontory
|
|
|
what is Sacral hiatus?
|
The aperture present where S5 lamina and spinous process are absent.
it leads into the sacral canal and is the inferior opening of the vertebral canal. |
|
|
to what part of the body is sacral vertebrae are attached?
|
Ilium or Pelvis
|
|
|
what joint attaches sacrum to pelvis?
|
Sacroiliac joint.
its a synovial joint. |
|
|
what is the common name for coccygeal vertebrae
|
tailbone
|
|
|
A defect allowing part of a vertebral arch to be separate from its body is?
|
Spondylolysis
|
|
|
what is spina bifida?
|
a defect of the vertebral arch resulting from the failure of fusion of the halves of the arch; usually occurs in L5 and/or S1
|
|
|
Name the three Abnormal curvatures of vertebral column
|
1. Kyphosis
2. Lordosis 3. Scoliosis |
|
|
Kyphosis
|
exaggerated thoracic curvature, sometimes referred to as “humpback” or "hunchback"
|
|
|
Lordosis
|
exaggerated lumbar curvature, due to the anterior rotation of the pelvis; sometimes referred to as “swayback”
|
|
|
Scoliosis
|
Abnormal lateral curvature of the vertebrae; often described as a “crooked” back.
|
|
|
what are the common ligaments of vertebral column?
|
a. Supraspinous
b. Interspinous c. Ligamentum Flavum d. Anterior Longitudinal e. Posterior Longitudinal |
|
|
what is a thin, continuous ligament that attaches to the tip of each spinous process from the sacrum to C7.
|
Supraspinous
|
|
|
what is the name of ligament that connects the tips of the spinous processes of cervical vertebrae from C7 to the skull,
|
Nuchal Ligament
|
|
|
which unite adjacent spinous processes in an oblique direction?
|
Interspinous
|
|
|
which ligament connects laminae of adjacent vertebrae
|
Ligamentum Flavum
|
|
|
function of Anterior Longitudinal ligament
|
Bind anterior surfaces of bodies and discs
|
|
|
function of posterior Longitudinal ligament
|
Bind posterior surfaces of bodies & discs; located in the vertebral canal ( pay attention to its location).
|
|
|
Intervertebral joints are what type of joints?
|
Cartilaginous (amphiarthrosis) - slightly moveable
|
|
|
function of intervertebral joints?
|
united to fibrocartilage (intervertebral disc)
|
|
|
what are the 2 parts of intervertebral disc?
|
(1) anulus fibrosus – the outer fibrous part composed of fibrocartilage arranged in concentric lamellae; attached to rims of vertebral bodies.
(2) nucleus pulposus – a gelatinous central mass that composes the “core” of the disc. |
|
|
reduction in height due to aging is related to _____________ .
|
dehydration and degeneration in the nucleus pulposus.
|
|
|
Name the synovial joints in vertebral column.
|
a. Costotransverse – the articulation between the rib tubercle and the transverse process of corresponding vertebrae.
b. Costovertebral – the articulation between the head of the rib and the costal facets of the vertebral bodies. c. Zygapophyseal joints (facet joints) – articulations between the articular processes of the vertebral arches. |
|
|
The gliding movements between the vertebrae are allowed due to what joints?
|
Zygapophyseal joints
|
|
|
where is the origination of spinal cord?
|
continuous with the medulla oblongata; superiorly, it begins at the foramen magnum
|
|
|
what is the name for the terminal end of spinal cord?
|
Medullary cone (conus medullaris), located inferior to the exit of the coccygeal nerve rootlets
|
|
|
where does the termination of spinal cord occurs?
|
It occurs at the intervertebral disc between L1 and L2; however, it can vary in its ending from T12 to L3.
|
|
|
why is spinal cord shorter than vertebral column?
|
During fetal growth, the spinal cord and vertebrae do not grow at the same rate; the vertebral column grows faster, leaving the spinal cord shorter than the vertebral column
|
|
|
specify the two regions of spinal cord enlargements?
|
1. Cervical Enlargement – from C4 to T1 segments of the spinal cord----- supply the upper extremities.
2. Lumbosacral Enlargement – from L1-S4 segments--supply the lower extremities. |
|
|
A collection of dorsal and ventral roots of the lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal spinal nerves that travel through the subarachnoid space are collectively called ____________.
|
Cauda Equina
|
|
|
what are the three types of arteries that supply blood to spinal cord.
|
1. Anterior spinal artery --distributed in ventral median fissure
2. Posterior spinal arteries --lies dorsal to the dorsal roots of the spinal nerves 3. Radicular arteries--supply to anterior and posterior nerve roots and also replenish the spinal arteries |
|
|
how many spinal veins are there?
|
3 anterior spinal veins and 3 posterior spinal veins
|
|
|
Spinal veins drain into __________________.
|
Radicular veins.
|
|
|
What are meninges?
|
3 membranes which surround the C.N.S. and the proximal portion P.N.S.
meninx - singular |
|
|
Name three meninges.
|
dura mater (outer most)
arachnoid (middle layer) pia mater (inner most) glued to spinal cord and brain cannot be separated. |
|
|
filum terminale of pia mater blends with filum of dura mater to form_____________________.
|
the coccygeal ligament
|
|
|
what is Filum terminale?
|
an extension of pia mater from the spinal cord’s conus medullaris to the coccyx.
|
|
|
lateral extensions of pia mater between the spinal nerve roots re called.
|
Denticulate ligaments
|
|
|
where does pia mater ends?
|
ends when the spinal cord ends between L1 and L2.
|
|
|
on the spinal cord spinal blood vessels are covered by which meninx
|
pia mater
|
|
|
the space between arachnoid and dura mater is called
|
subdural space
|
|
|
space between arachnoid and pia mater is
|
subarachnoid space
|
|
|
cerebrospinal fluid can be found in ____________________.
|
subarachnoid space.
|
|
|
Inferiorly, the arachnoid layer ends at what vertebral level?
|
S2
|
|
|
The subarachnoid space from L2-S2 is known as _____________.
|
lumbar cistern (location for lumbar puncture)
|
|
|
the space between vertebral foramina and dura mater is called ________________.
|
epidural space
|
|
|
what is dural sac?
|
It is a sheath of dura within the vertebral canal. Spinal nerves pierce the dural sac.
|
|
|
where does the dural sac ends?
|
The dural sac ends at S2.
|
|
|
The connective tissue that covers a peripheral nerve is called___________.
|
epineurium
|
|
|
what is the other location where spinal dura is present?
|
Spinal dura is present in the intervertebral foramina and along the nerve roots distal to the dorsal root ganglia....blends distally with epineurium.
|
|
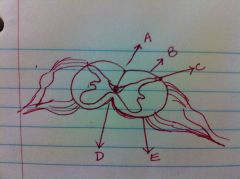
Name the topograpghy of spinal chord labeld in the image
|
A. dorsal median sulcus
B. dorsal intermediate sulci C. dorsolateral sulci D. ventral median fissure E. ventrolateral sulci |
|
|
Nucleus pulposus is derived from what embryonic structure?
|
Notochord
|
|
|
what embryonic structure makes dorsal root ganglionic cells
|
neural crest
|
|
|
spinal cord is derived from what embryonic structure
|
ectoderm or neruepithelium (neural tube)
|

