![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ovary
|
Organ that houses developing ova.
|
|
|
Follicles
|
Nutritive and secretory cells surrounding developing ova
|
|
|
Corpus Luteum
|
Secretory cells that reorganize to secrete sex hormones after ovulation; yellow body. forms after ovum is released from ovary.
|
|
|
Fallopian tube
|
duct that provides passages for ovum to the uterus; also known as uterine tube and oviduct.
|
|
|
Uterus
|
organ that provides for implantation of the embryo; contains muscular myometrium and highly vascularized endometrium.
|
|
|
Blastocyst
|
Last stage and what implants on uterus
|
|
|
Trophoblast
|
forms placenta
|
|
|
Fertilization
|
Occurs in oviducts, cillia move embryo towards uterus, joining of sperm and egg.
|
|
|
Gastrulation
|
Process in which the embryonic cells migrate and differentiate to form different germ tissues.
|
|
|
Ectoderm
|
Germ layer on outside of embryo; forms skin and nervous system
|
|
|
Mesoderm
|
Germ layer that fills the space between endo and ectoderms; forms all other tissues and muscles, bones,blood, lymph cells and organs
|
|
|
Endoderm
|
germ layer that forms the inner lining of the embryo; forms the lining of digestive respiratory reproduction and urinary systems
|
|
|
Extraembryonic Membrane
|
Four membranes that form placenta
|
|
|
Yolk Sac
|
No yolk, rich blood supply, contibuters to umbilical cord
|
|
|
What is ovulation?
|
Release of mature ovarian follicle from the ovary.
|
|
|
Ovum is surrounded by which two layers?
|
1. Zona pellucida (mucopolysaccharide cells)
2. Corona radiata (follicular cells of culumus oophorus) |
|
|
what is Culumus oo´phorus?
|
A mass of follicular cells surrounding the oocyte in the vesicular ovarian follicle.
|
|
|
What is peritoneal cavity?
|
The peritoneal cavity is the fluid-filled gap between the wall of the abdomen and the organs contained within the abdomen.
(The peritoneal cavity contains the pelvis, stomach, spleen, gall bladder, liver and the intestines) |
|
|
What is Secondary Oocyte?
|
An oocyte in which the first meiotic division is completed.
|
|
|
secondary oocyte is arrested at which stage of cell division? (hint: mitosis or meiosis?)
|
Second meiotic division
|
|
|
what do you call the funnel shaped opening of uterine tube?
|
infundibulum
|
|
|
what is the function of infundibulum?
|
to sweep released follicle into uterine tube.
|
|

identify the layers A and B around ovum.
|
A. Zona pellucida
B. Corona radiata |
|
|
what is the site of fertilization in uterine tube?
|
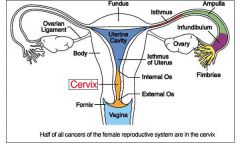
Ampulla of uterine cavity (right beneath infundibulum)
|
|
|
what happens during fertilization?
|
sperm penetrates through zona pellucida and corona radiata to fuse with nuclei of ovum (fusion of pronuclei)
|
|
|
what is the result of fertilization?
|
1. Restoration of diploid number of chromosomes (2n)
2. Determination of sex of zygote 3. Initiation of cleavage (early mitotic division) |
|
|
how many chromosomes are present in mature human gametes?
|
Total 23
22 - autosomes 1 - sex chromosome |
|
|
Morula
|
Pre-implantation development of embryo on day 4
12-16 cell stage Solid ball of cells each cell is called blastomere still surrounded by zona pellucida |
|
|
what is Blastocyst?
|
zygote on Day 5.
central cavity forms filled with fluid. cavity is surrounded by blastomere. early cell differentiation zona pellucida disintegrate...hatching happens |
|
|
how is blastocyst form?
|
by merging of extracellular spaces of zygote cells.
|
|
|
what are the two cell types in blastocyst?
|
1. Trophoblast - outer cell layer --contribute to placenta
2. Embryoblast- inner cell mass (located at the pole of blastocyst)-- makes body of embryo |
|
|
where does implantation takes place?
|
blastocyst free of zona pellucida will penetrate posterior wall of uterine cavity. Implantation must be completed by Day 12 of ovulation.
|
|
|
what is the process of implantation?
|
1. "sticky" Trophoblast destroys endometrial cells
2. Trophoblast proliferates, invades. |
|
|
what are the two subdivisions of Trophoblast?
|
1. Cytotrophoblast (mono nucleated with distinct cell boundaries)
2. Syncytiotrophoblast (multi nucleated) |
|
|
What is bilaminar disc?
|
The two layer disc formed by the segregation of embryoblast.
|
|
|
what are the two layers of bilaminar disc called?
|
1. Epiblast ( columnar cells )
2.Hypoblast (cuboidal cells) |
|
|
Epiblast give rise to what part of body?
|
Body of Embryo and Amnion.
|
|
|
hypoblast give rise to what part of embryo.
|
hypoblast does not make any body parts of embryo it gives rise to endoderm of umbilical vesicle (yolk sac)
|
|
|
what is Amnion?
|
intercellular cleft in epiblast that give rise to amniotic cavity on day 8.
|
|
|
why we call epiblast as pluripotent?
|
epiblast cells have potential to differentiate into different cell types.
|
|
|
Primary umbilical vesicle
|
an outgrowth of flattened cells from periphery of hypoblast and transform the blastocyst cavity to umbilical vesicle sac.
|
|
|
what forms between cytotrophoblast and the lining of amniotic cavity and yolk sac?
|
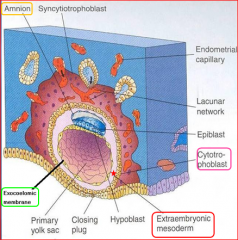
extraembryonic mesoderm
|
|
|
how is intraembryonic mesoderm form?
|
first the primitive streak and primitive node (Day 15) forms in the epiblast then some epiblast cell will migrate and invaginate.
|
|
|
which direction is the primitive node expand?
|
cranial end of primitive streak (primitive streak is present at tail end of baby)
|
|
|
what is prechordal plate?
|
firm attachment of ectoderm and endoderm
at cranial end of embryo. |
|
|
what is gastrulation?
|
Early (very important phase in embryonic development) in the embryonic development during which the single-layered blastula is reorganized into a trilaminar ("three-layered") structure known as the gastrula.
(know the process) |

