![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does it mean that muscles are extensibility?
|
It contracts and extends w/ out damage
|
|
|
What does it mean that muscles are elastic?
|
Ability to return to original shape after contract/extend
|
|
|
What muscle is striated?
|
Cardiac and skeletal
|
|
|
What is the term for involuntary muscle?
|
Smooth and cardiac
|
|
|
What are 4 layers, starting w/ the layer surrounding muscle fibers?
|
Endomysium - Perimysium - Epimysium - Deep fascia (they are all extensoins of deep fascia)
|
|
|
What is the plasma membrane that surrounds each muscle fiber?
|
Sarcolemma
|
|
|
What is a muscle fiber composed of? What are these composed of?
|
Myofibrils of myofilaments
|
|
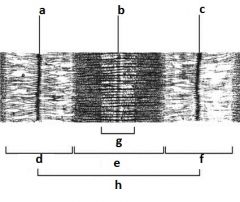
|
A - z disc
B - M line C - z disc D - I band E - A band F - I band G - h zone H - sacromere |
|
|
What protein positions the THICK myofilaments?
|
TITIN
|
|
|
What protein positions Thin myofilaments?
|
α-Actinin and Nebulin
|
|
|
Which of the following change in muscle contraction? A, I H?
|
I and H change NOT A
|
|
|
Which protein is the major component of THICK myofilaments?
|
Myosin
|
|
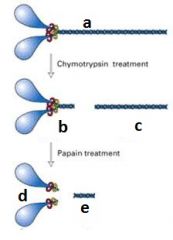
|
A - heavy chain of Myosin
B - HMM C - LMM D - S1 E - S2 |
|
|
What is the funciton of S1 unit of Heavy Chain of Myosin?
|
Bind ATP - and Thick/Thin binding
|
|
|
What is the function of LMM?
|
It is part of the heavy chain of myosin, it binds myosin's together
|
|
|
What is the major component of thin myofilaments? What is this component composed of?
|
F-Actin of G-actin molecules
|
|
|
What do Myosin heads bind to?
|
The active site of g-actin molecules on thin filaments
|
|
|
What proteins are present in Thick filaments? Function?
|
Myosin ONLY
|
|
|
What proteins are present in Thin filaments? Function?
|
Actin,
Tropomyosin - stabilize the helix, masks some active molecules Troponin |
|
|
What are the components of Troponin?
|
Troponin C - calcium
Troponin I - binds actin to prevent actin-myosin interaction Troponin T - binds to tropomyosin |
|
|
What is the job of Troponin I?
|
Bind to actin, prevent actin-myosin
|
|
|
What is the job of Troponin T?
|
Bind to tropomyosin
|
|
|
What is the job of Troponin C?
|
Bind to calcium
|
|
|
Where does the calcium come from taht acts in muscle contraction? How is it made available?
|
It is stored in the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum of Muscles. It is released when an Action potential travels down a T-tubule. This is caused by ACh being released from the pre-synaptic membrane and binding to the post-synaptic clefts
|

