![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what's the difference between active and passive transport
|
active-cell expends energy, low to high concentration
passive- cell does not expend energy, high to low concentration |
|
|
list 4 types of passive transport
|
osmosis, diffusion, facilitated diffusion, ion channel
|
|
|
diffusion will eventually cause the molecules to be in what state
|
equilibrium
|
|
|
what is equilibrium
|
a balance of concentration inside and outside of the cell
|
|
|
do particles stop moving at equilibrium
|
no, the rate becomes equal inside and outside
|
|
|
what is osmosis
|
the diffusion of water from high to low, a type of passive transport
|
|
|
what happens when a cell is is placed in a hypotonic environment
|
more water outside the cell, water moves inside
|
|
|
what happens when a cell is placed in a hypertonic environment
|
more water inside the cell, water moves out
|
|
|
what happens to a cell in a isotonic environment
|
same amount of water inside and outside of the cell, no movement
|
|
|
what does a contractile vacuole do for single celled organisms
|
it removes water from a cell
|
|
|
what's the difference between plasmolysis and cytolysis
|
plasmolysis- inside a plant cell, hypertonic solution cell membrane separates from the cell wall
cytolysis-inside an animal cell, hypertonic solution the cell ruptures |
|
|
what do carrier proteins do in facilitated diffusion
|
helps the molecules move through a membrane, it makes channels
|
|
|
what is required for active transport
|
ATP or energy
|
|
|
what`s the difference between endocytosis and exocytosis
|
endocytosis- brings things in
exocytosis- takes things out |
|
|
moves large molecules or even entire cells into the cell membrane
|
phagocytosis
|
|
|
the energy needed to power the sodium-potassium pump, endocytosis, and exocytosis is provided by what
|
mitochondria/ATP
|
|
|
how does a phagocyte destroy bacteria
|
the phagocyte allows lysosomes to fuse with vesciles that contain bacteria and virsuses. The enzymes within the lysosomes destroy the bacteria abd vacuoles
|
|
|
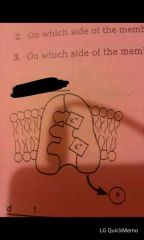
why is it important that ions being transported across a cell membrane be shielded from the interior of the lipid bilayer
|
the lipid bilayer is hydrophobic on the outside and hydrophillic on the inside, so it dissolves ions
|
|
|
why are the vesicles formed during pinocytosis much smaller than those formed during phagocytosis?
|
during pinocytosis solutes or fluids are being moved, during phagocytosis large molecules or whole cells are being moved
|
|
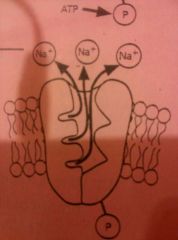
|
3
|
|
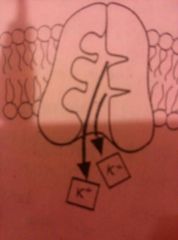
|
6
|
|
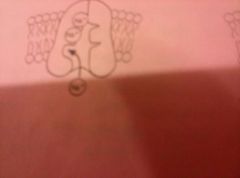
|
1
|
|

|
2
|
|
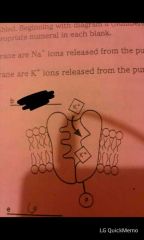
|
4
|
|
|
5
|
|
|
what is diffusion driven by
|
the molecule`s kinectic energy
|

