![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is light? |
A form of energy that you can see. |
|
|
What is a natural source of light? |
A natural source radiates light in all directions, and is not man-made. It is something that occurs naturally in nature. For example: Sun, stars, or fire. |
|
|
What is an artificial source of light? |
An artificial light source radiates light in all directions, and is man-made. For example: Light bulbs. |
|
|
What are photons? |
Photons are small bundles of energy that all light is made up of. Photons can be transformed into other types of energy. |
|
|
What is intensity? |
Intensity means how bright the light source is. If it is very bright, it has a high intensity, and if it is dim, it has a low intensity. The higher intensity something is, the more photons it has, meaning more energy can be transformed. |
|
|
What is an incandescent source? |
An incandescent source is the source of light that emits light when it is heated to a high temperature. The energy path for an incandescent source is Electrical Energy→Thermal Energy→Visible Light Energy |
|
|
What is a fluorescent source? |
The energy path for a fluorescent source is Electrical Energy→Energy Absorbed by Mercury Particles→Ultraviolet Light Energy→Energy Absorbed by Particles→Visible Light Energy, meaning that an electric current causes the mercury to vapor inside the tube and give off ultraviolet energy, and the phosphor coating on the inside of the tube absorbs the ultraviolet energy, and the coating glows, producing light immediately. |
|
|
Why is a fluorescent source hard to dispose of? |
A fluorescent source is hard to dispose of because of the toxic mercury inside. |
|
|
What is a phosphorescent source? |
A phosphorescent source is light energy stored by certain particles and released later as visible light later. For example: The star stickers on ceilings. |
|
|
What is a chemiluminescent source? |
A chemiluminescent source is light that can be released by chemical reactions. For example: Snap glow sticks. The energy path for a chemiluminescent source is Chemical Energy→Visible Light Energy. |
|
|
What is a bioluminescent source? |
A bioluminescent source is light emitted from chemical reactions inside living things. For example: Deep sea fish or fireflies. |
|
|
What are all objects that emit light called? |
All objects that emit light are called luminous. |
|
|
What is a ray? |
A ray is a straight imaginary line that represents the path of a beam of light. They are used in ray models or diagrams. |
|
|
How is a shadow made? |
A shadow is made in the absence of light from a certain light source, because light cannot bend around a opaque object. |
|
|
What is a transparent object? |
A transparent object is a completely clear or see-through object that light can pass through without being affected. For example: Glass, air, or the lenses of your eyes. |
|
|
What is a translucent object? |
A translucent object is an object through which light rays are deflected. This means you can still see the light, but not the objects behind it. For example: A piece of paper held up to a light bulb. |
|
|
What is an opaque object? |
An opaque object is an object through which light cannot pass. It will cast shadows behind it. The light rays are totally blocked. For example: Thick textbooks, humans, etc. |
|
|
How do you calculate the cost of lighting? |
Step 1: Convert watts (W) to kilowatts (kW). (W/1000)=x Step 2: Multiply kilowatts (kW) by hours (hrs). (x times # of hrs)=kW•hrs Step 3: Number of kilowatt hours (kW•hrs) x cents per hour = Money amount per hour of lighting. |
|
|
What is reflection? |
Reflection is the process in which light strikes a surface and bounces back off that surface. |
|
|
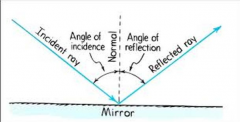
What is the incident ray? |
The ray that comes from a light source and strikes the surface. |
|
|
What is the reflected ray? |
The ray that bounces off the surface. |
|
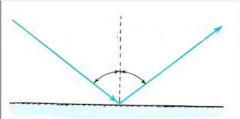
Label the ray diagram. |
|
|
|
What is the law of reflection? |
The angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence. |
|
|
What is the law of light? |
Light travels in straight lines. |
|
|
How does a smooth surface affect reflections? |
Smooth surface reflect light very uniformly. |
|
|
How does a rough surface affect reflections? |
Rough surfaces reflect light in a scattered manner because the normal lines point in different directions. This causes the reflected rays to be scattered and cannot form an image. |
|
|
What is a convex mirror?
|
It is a mirror that curves outward, or has a bulge. It is useful for seeing more objects in a space. Cars use them, as well as stores to keep an eye out for shoplifters. |
|
|
What is a concave mirror? |
It is a mirror that curves inward, or caves in like a shiny bowl. It projects the image upside down. |
|
|
What is refraction? |
Refraction is the bending of light when it travels from one medium to another. Light bends because it changes speed when going through materials with different densities. The bending of light makes objects appear to be in a different position from where it really is. |
|
|
What is the difference between light entering a more dense medium versus leaving it? |
When light goes from one medium to one that is more dense, it will bend TOWARD the line of normal. For example: Light entering water. When light exits a denser medium, light bends AWAY from the line of normal. For example: Light exiting water. |
|
|
How do the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction relate? |
When the angle of incidence increases, as does the angle of refraction. |

