![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How can we tell if something is alive? |
All living things: 1. Need energy. 2. Respond and adapt to their environment. 3. Reproduce. 4. Grow. 5. Produce wastes. |
|
|
To get their energy, what is an animal's developed structures to help? |
Animals get their energy from food. They have a good sense of smell and claws, teeth, etc. to get their food. |
|
|
To get their energy, what is a plant's developed structures to help? |
Plants get energy from the sun and water and soil. They have leaves to absorb sunlight and roots to get water from soil. |
|
|
To respond and adapt to their environment, what is an animal's developed structures to help? |
Animals can adapt their eyesight depending on when they hunt. Raccoons have good night vision and feed at night; deer feed during the day and have good daytime vision. |
|
|
To respond and adapt to their environment, what is a plant's developed structures to help? |
Plants bend toward a light source to ensure they get the most light available. |
|
|
To reproduce, what is an animal's developed structures to help? |
Animals have live offspring. |
|
|
To reproduce, what is a plant's developed structures to help? |
Plants produce seeds. |
|
|
To grow, what is an animal's developed structures to help? |
Animals grow from young. |
|
|
To grow, what is a plant's developed structures to help? |
Plants can grow from a seed. |
|
|
To produce wastes, what is an animal's developed structures to help? |
Animals get rid of wastes like carbon dioxide. They get rid of waste such as feces and urine through the digestive track. |
|
|
To produce wastes, what is a plant's developed structures to help? |
Plants can get rid of gasses through a small pore in the leaves called stomota. |
|
|
All living things are made up of___________? |
All living things are made up of cells. |
|
|
If a group of cells all have a similar function, can they: a) become white blood cells b) become organs c) join together to form tissues like mussels |
c) join together to form tissues like mussels
|
|
|
True or False: Tissues can join together to form organs like your heart, lungs, veins, or arteries. |
True. |
|
|
With teamwork, organs can do what? |
Organs can group together and, with teamwork, form systems like your circulatory system, your digestive system, the lymph system, and your nervous system. |
|
|
What do cells do that ensures survival? |
Cells can be specialised into systems, but it is the co-operation of all these systems that ensure survival. |
|
|
What does magnification mean? |
Magnification means making and object appear larger. |
|
|
What is the limit to the size the human eye can see? |
0.1mm. |
|
|
Who is Anton van Leeuwenhoek? |
He was the first person to see organisms made of only one cell. He called these unicellular organisms 'animalcules.' |
|
|
What was Anton van Leeuwenhoek's profession? |
He was a Dutch linen merchant. |
|
|
When did Anton van Leeuwenhoek live? |
He lived from 1632 - 1723. |
|
|
What did Anton van Leeuwenhoek do for fun? |
His hobby was making magnifying glasses. |
|
|
What was Robert Hooke famous for? |
He discovered and gave us the name for cells. |
|
|
When did Robert Hooke live? |
1635 - 1703 |
|
|
What is the Latin name for "little rooms?" |
Cellulae |
|
|
What is the basis of all life? |
A cell is the basic unit of all life because of all the functions carried out by living things are carried out by their individual cells as well. |
|
|
Who developed the theory of the basis of all life? |
German botanist Matthias Scheiden and zoologist Theodore Schwann in 1839. |
|
|
What are the different types of microscopes and what are the limits of magnification? |
Compound light microscope (2,000X) Scanning electron microscope -SEM- (4,000X) Transmission electron microscope -TEM- (2,000,000) |
|
|
What is the Canadian connection to the electron microscope? |
To test their valuable new laboratory tool, two Canadians looked at the edge of a razor blade through different microscopes, the blade appearing smooth in one, and rough and jagged in the one magnified more. |
|
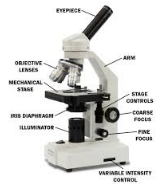
Label the microscope. |
|
|
|
What are the two categories that organisms can be grouped into? |
Multicellular and unicellular |
|
|
What is a multicellular organism? |
Many cells grouped together to do a specific function for the larger organism, like white blood cells or red blood cells. |
|
|
What is a unicellular organism? |
An organism that is only one cell. |
|
|
What features do both multicellular and unicellular organisms share? |
They each move, obtain food, and carry out other life functions through the use of small structures found withing the single cell called Organelles. |
|
|
What are Organelles? |
Structures inside the cell that have a specific function. |
|
|
What is the nucleus? |
It is the brain of the cell, it controls most of the cell's activities and holds most of the DNA. |
|
|
What is cytoplasm? |
It is the jelly-like material in which other parts float around in, it is similar to all the body fluids in a human. |
|
|
What is cell membrane? |
It surrounds the cell (like skin) and hold everything in place. It also plays a role in allowing things to pass in and out of the cell. |
|
|
What is a vacuole? |
It is a balloon-like space that holds surplus food, wastes, and other substances. |
|
|
What is a cell wall? |
It is in plant cells only, and it surrounds the cell membrane and gives support for the plant. (It is responsible for the hard structure a tree has when it has died.) It is made up of cellulose. |
|
|
What are chloroplasts? |
They are the structures that are responsible for photosynthesises to occur in plant cells only. They contain the chemical chlorophyll (which makes the plant green). |
|
|
What are the mitochondria? |
They are the "energy houses" of the cell. They take in food particles and break them down into chemicals which can create energy. Some cells have more mitochondria than others. They are found in both animal and plant cells. |
|
|
What are the lysosomes? |
They are the "suicide switch" of the cell. They are vacuole that contain toxic chemicals that when the cell has reached the end of it's life span, the nucleus sends out a signal to pop the ribosome and the cell kills itself. |
|
|
Why are cells so small? |
If the cell grows bigger, it needs more food and will produce more waste. In doing this, the waste and food need to travel to the cell membrane out or in. If the cell is bigger, the distance increases, and if you have a certain amount of food, you have to travel farther and expend more energy and need more food to replenish the energy. |
|
|
Most cells are the same __________? |
Size. Bacterial cells are on average 10x smaller than plant and animal cells. |
|
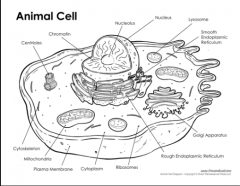
Label the animal cell. |
|
|
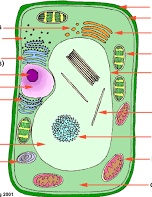
Label the plant cell. |
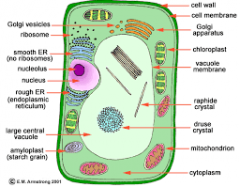
|

