![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
114 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a triglyceride? |
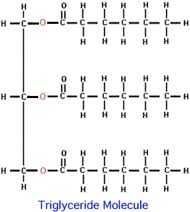
3 Fatty acids connected to a glycerol backbone. Formed by Ester bonds. |
|
|
Denatured Protein |
Physical Shape of protein is unfolded. The protein cant function. Is caused by extreme heat, pH, or mixing with chemicals |
|
|
What is a catalyst? |
It increases the rate of a RX |
|
|
Transgenic mice are...? |
Genetically modified mice |
|
|
Which body fluid best regulates body temperature? |
Blood |
|
|
Rough ER |
Endoplasmic Reticulum with Ribosommes attatched to it |
|
|
What type of cell makes up the mylen sheath of nerve cells? |
Swann Cells |
|
|
Is white or grey matter deeper in the brain? |
White matter is deeper. Grey matter is the superficial edge. |
|
|
What is Smooth ER |
An Endoplasmic reticulum without ribosommes. |
|
|
What brain lobe is most associated with memory? |
The Frontal Lobe |
|
|
What do Ribosommes do? |
Make protein |
|
|
What are the gaps inbetween the mylen sheath called? |
Nodes of Ranvier |
|
|
What is an Electrochemical gradient? |
Ion concentration changes from one side to another. |
|
|
Endocytosis |
The movement of food inside a cell |
|
|
What is Phagocytosis? |
A cell engolfing a large molecule. Like pacman |
|
|
What is pintocytosis? |
Movement of a liquid inside a cell |
|
|
Population Density Equation |
# of Organisms/Area |
|
|
What molecule is commonly referred to when speaking about blood sugar? |
Glucose |
|
|
What is an isomer of Glucose? |
Fructose |
|
|
What general structure of a lipid makes it a good energy source? |
The large amount of Carbon-Hydrogen bonds |
|
|
What do lipids not do? |
They don't dissolve in water |
|
|
How many H bonds are between A and T? |
2 Hydrogen bonds |
|
|
How many Hydrogen bonds are between C and G? |
3 Hydrogen bonds |
|
|
After one complete cycle of glucose, how much CO2 is formed? |
6 molecules of CO2 is formed |
|
|
What is the First law of Thermodynamics? |
Energy cannot be created nor destroyed |
|
|
What molecule contributes to the highest production of ATP? |
NADH |
|
|
Where does the Krebbs Cycle occur? |
In the mitochondrial Matrix |
|
|
Where does the Calvin Cycle occur? |
In the stoma of plants |
|
|
Mutualism |
Symbiosis that is beneficial to both organisms involved |
|
|
Paratism |
a non-mutual relationship between species, where one species, the parasite, benefits at the expense of the other. One benifits, other doesn't |
|
|
Commensalism |
Association where 2 organisms neither benefit nor harmed from the other |
|
|
Amensalism |
One species is destroyed, the other organism is unaffected |
|
|
Sympathetic Nervous System |
Part of the Autonomic Nervous system (non-Concious control). Sympathetic Nervous system is resposible for the fight or flight responses |
|
|
What is the Purpose of Homeostasis? |
To maintain a normal balance within the body. Examples include changes in Temperature, salt concentration, water concentration, and food intake |
|
|
Parasympathetic Pathway |
Part of the Autonomic Nervous System, the Parasympathetic Nervous System is responsible for the response of rest and digest. |
|
|
What is a C3 plant? SA |
C3 plants use the enzyme rubisco to collect CO2. Sometimes if it is hot or there is a high concentration of O2, rubisco will bind of O2 instead of CO2. This makes C3 plants inefficient in hot temperature. Examples of C3 plants include Evergreens, rice, and soybeans. |
|
|
What is a C4 plant? |
In C4 plants, the light-dependent reactions are separate from the calvin cycle. C4 plants also use an enzyme called PEP Carboxylase, which will never bind to O2. This makes sure that CO2 will only be used and photorespiration is minimized. EX Corn |
|
|
What is Chargaff's Rule? |
Adenine will bond with Thymine. Cytosine will bond with Guanine. |
|
|
What is a saturated fat? |
A fat with only single bonds, making it "saturated" with hydrogen |
|
|
What is the cell membrane made of? |
A Phospholipid bilayer |
|
|
What is free energy? |
Energy that is avaliable to do work |
|
|
What is activation energy? |
The amount of energy it takes to start a Reaction |
|
|
What is the structure of ATP? |
ATP, Adenosine triphosphate, consists of an adenosine bound to three phosphates |
|
|
What is reduction? |
Gain of electrons. GER |
|
|
What is oxidation? |
Loss of electron. LEO |
|
|
What is the biproduct of effective photosynthesis? |
O2 |
|
|
What is Photosystem 1? |
-Has the reaction centre of p700, absorbing wavelengths of 700nm. - produces NADPH |
|
|
What is Photosystem 2? |
-Has the reaction centre P680, absorbing wavelengths of 680 nm -Produces 02 and ATP |
|
|
What does hydrophobic mean? |
Not soluble in water. Clumps together if put in water. |
|
|
What does the breakdown of protein produce? |
Amino Acids |
|
|
What does the breakdown of starch create? |
Monosacharides |
|
|
What are CAM Plants? |
CAM plants minimize photorespiration and save water by separating these steps between night and day. During the night these plants open their stoma and PEP Carboxylase collects CO2. This is made into an organic acid until daytime, where it can be changed back into CO2 and photosynthesis can occur. EX Cactus |
|
|
What is a Codon? |
A sequence of three nucleotides that form a basic unit of the genetic code |
|
|
What is an exon? |
A segment of DNA or RNA containing information coding for a protein |
|
|
What is an Intron? |
A part of DNA or RNA sequence that does not code for a protein |
|
|
What is Uracil? |
Is one of the 4 nucleotide bases for RNA. Binds to Adenine and replaces Thymine. Uracil binds to Adenine |
|
|
What is Conservative Replication? |
Each 2 strands of parent DNA are replicated without strand separation. One stand is all new DNA, and the other is all old DNA. |
|
|
What is Semi-Conservative Replication? |
Every newly created helix contains one old stand and one new strand. |
|
|
What is Dispersive Replication? |
After Replication, Every helix contains randomly dispersed parts of new stands and old stands. |
|
|
What are Mutagens? |
Mutation causing agents. Physical Mutagens- X-Rays Chemical Mutagens- Nitrates, cigarette smoke |
|
|
What is Missense mutation? |
A single gene mutation that alters the amino acid sequence of a protein |
|
|
What is Silent Mutation? |
A type of single gene mutation where the amino acid sequence stays the same |
|
|
What is Nonsense Mutation? |
A type of single gene mutation that inserts a "stop" codon earluer than it was supposed to |
|
|
What is Frameshift mutation? |
AKA Strand slippage, it is a change in the reading frame that causes HUGE changes in the amino acid sequence |
|
|
What are single gene mutations? |
Changes of a nucleotide sequence in one gene. |
|
|
What is Point Mutation? |
The most frequent type of mutation. A single base pair is subsituted, inserted, or deleted. Can cause Silent, Missense, or Nonsense Mutation. |
|
|
What is the Error Rate of DNA replication? |
Between 1/10^6 and 1/10^9. It is very efficient. |
|
|
What is DNA? |
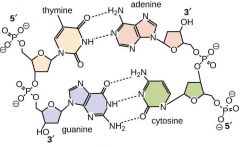
DeoxyriboNucleic Acid. -Hereditary information from ancestors -Contains all genetic information of an organism -Consists of Pentose Sugar, Nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group -For genes to be useful, they must be turned into proteins -Regions of DNA for specific attributes are called genes |
|
|
Nucleotides are held together by ________ bonds. |
Phosphodiester Bonds |
|
|
What is a Genome? |
The complete Genetic makeup if an organism |
|
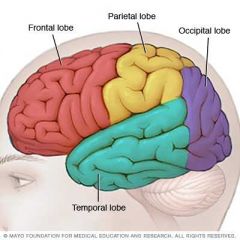
What do the lobes of the brain do? |
Frontal -Personality -Memory formation -Emotions Pariental -Senses -Perception Temporal -Hearing -Information Retrieval Occupital -Vision |
|
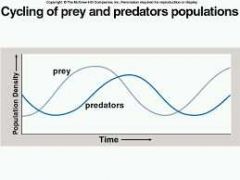
Predator Vs Prey Diagram |
When the prey is high, the next cycpe the predators will be high. They are directly related |
|
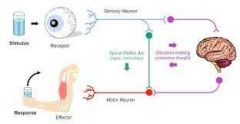
The Reflex Arc |
Order 1. Stimulus 2. Receptor 3. Sensory Neuron 4. Interneurons in spinal cord 5. Motor Neuron 6. Effector (muscles) 7. Response |
|
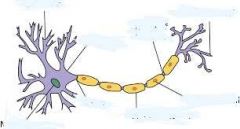
Diagram of Neuron |
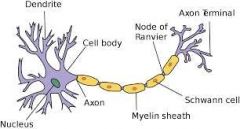
|
|
|
Diagram of the Overall Vertebrate Nervous System |
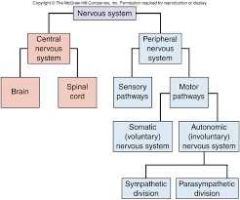
|
|
|
How Much ATP is made during cellular Respiration? |
38 ATP for every 1 Glucose |
|
|
What is the Central Dogma? |
1.DNA---->mRNA (through transcription) 2. mRNA ----> Protein (translation with Ribosomes) |
|
|
DNA VS RNA |
DNA -DeoxyribosNucleic Acid -Double Stranded -Stable -Found in Nucleus -ATGC RNA -RibosNucleic Acid -Single Stranded -Unstable -Found Everywhere in cell -AUGC |
|
|
What are the steps of Transcription? |
1. Initiation: RNA Polymerase binds to the DNA upstream to the gene that will be transcribed. The upstream region is a DNA sequence that tells RNA where to start transcribing, which is usually A's and T's as they only for 2 Hydrogen bonds. 2. Elongation: RNA polymerase binds to DNA and opens the Helix. mRNA is built and only one strand is used as the mRNA templare. The resulting mRNA has "U" instead of "T". 3. Termination: mRNA strand is synthesized until it reaches the end of the gene. (Terminator Sequence). mRNA is released. 4. Before the mRNA is released, a 5' Cap is added and a Poly-A tail to prevent it from being digested. Splicosomes cut out introns leaving only exons in the mRNA. |
|
|
What are the steps of Translation? |
mRNA is transported to ribosomes to be read in codons. 1. Initiation: Small ribosomal unit attatches to 5' cap and scans down. The Anticodon of tRNA attatches to the start codon. This sets the reading frame. Large ribosomal unit joins: -(P)Peptide site: where the first tRNA binds -(A)Amino Acid: Where the next tRNA will bind -(E)Exit: Where the tRNA will leave from. The ribosome is made of RNA and proteins 2. Elongation: The large ribosomal subunit catalyzes the peptide bond between the P site and the A site. -mRNA moves forward one codon. 3. Termination: Stop codon is reached, ribosome falls off. This creates a functional protein. tRNA is 80 nucleotifes that brings amino acids to the ribosome. |
|
|
What is growth Rate? |
Growth Rate = (present-past)/ past |
|
|
What is Death Rate? |
Death rate = # of deaths/ # of people |
|
|
What is carrying Capacity? |
The maximum number of organsms an enviroment can support |
|
|
Population Vs Community |
Population: Any group of individuals of the same species living in the same place. Community: 2 or more populations living in the same place. |
|
|
What does mRNA do? |
Carries copied genetic information from DNA to Ribosomes. |
|
|
What does tRNA do? |
Used to decifer what mRNA brought. |
|
|
What does rRNA? |
Production of ribosomes |
|
|
How many Amino acids are there? How mamy are Essential? |
20 Amino Acids. 9 are essential, in that our body cannot create them themselves. |
|
|
What are purines? |
Adenine and Guanine. |
|
|
How is mRNA modified before it leaves the nucleus? |
- A 5'Cap is added to protect mRNA -A poly-A tail is added ti protect mRNA -mRNA's introns are cut out, leaving only coding regions AKA exons. |
|
|
What does a Nucleotide consist of? |
-A phosphate -A simple sugar -A nitrogenous base |
|
|
________ Is the compacting of DNA. |
Supercoiling |
|
|
What is the Krebb's Cycle? |
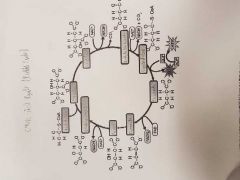
The Citric Acid Cycle 1. Citrate---> Iso-Citrate 2. Iso-Citrate ---(NAD+--->NADH)--> a-KetoGlutarate 3. a-KetoGlutarate --(NAD+--->NADH) --->Succinyl-CoA 4. Succinyl-CoA--(ADP-->ATP) (GDP-->GTP)--> Succinate 5. Succinate--(FAD-->FADH2)--> Fumarate 6. Fumarate---> Malate 7. Malate--(NAD+-->NADH)--> Oxaloacetate. 8. Oxaloacetate + Acetyl-CoA --> Citrate |
|
|
Anabolic Pathways are different from Catabolic Pathways, as Anabolic Pathways _______________. |
Require Energy |
|
|
The Mitochondrial inner Membrane Consists of ....... |
-Proton Pumps - ATP Synthase -A Lipid Bilayer -The Electron Transport Chain |
|
|
What does Glycolysis require and produce? |
Requires: - 6-Carbon Glucose chain Produces: - 2, 3 chain pyruvate - 2NADH - 2 ATP |
|
|
What does the Krebs Cycle Require and produce? |
Requires: - 2 Acetyl-CoA -O2 Produces: -6 NADH - 2 FADH2 - 2 ATP - CO2 |
|
|
What does the Calvin Cycle Require and produce? |
Requires: -ATP - CO2 - NADPH Produces: -G3P - ADP |
|

Where do the 4 cellular processes take place? |
Glycolysis: Cytoplasm outside of Cell Pyruvate Oxidation: Matrix Krebs Cycle: Matix Oxidative Phosphorylation: Inner Membrane |
|
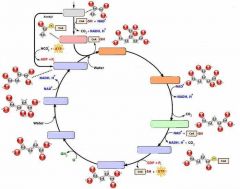
Label the Citric Acid Cycle |
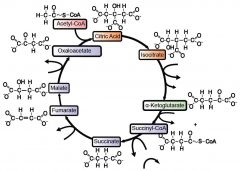
|
|
|
What is a competitive inhibitor? |
They bind to the active site of the enzyme, competing with the substance. |
|
|
What is a non-Competitive inhibitor? |
They bind to another part of the enzyme (non-active site) causing the enzyme to change shape and making the active site less effective. Inhibitors can be toxins, pesticides, poisons etc. |
|
|
An ________ is a substance that binds to the allosteric site and puts the enzyme into the active site |
Activator |
|
|
If a substance binds to the allosteric site and puts the enzyme into an inactive state, it is called an ________. |
Allosteric Inhibitor |
|
|
Compare Passive Transport Vs Active Transport |
Passive Transport: -No energy required - Molecules move to equalize gradient ( concentration, pressure, charge etc.) - Moves from high [ ] to low [ ] - EX: Diffusion, Osmosis Active Transport: - Requires Energy (ATP) - Move against concentration gradient -EX: Sodium-Potassium pump, Endocytosis, Exocytosis etc. |
|
|
What is the Negative Feedback? |
A process by which a mechanism is activated to restore conditions to their original state |
|
|
Channel Protein Vs Carrier protein. |
Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. Channel Protein: Always passive transport Carrier Protein: May be passive or active transport |
|
|
Catabolism Vs Anabolism |
Catabolism: Breaking large molecules into smaller particles Anabolism: Joining smaller particles into larger molecules |
|
|
What is the second law of Thermodynamics? |
During and process, the universe tends towards disorder. |
|
|
What are the different structures of proteins? |
Primary: The order of Amino Acids makes a line of peptide bonds. Secondary: Hydrogen Bonds form between the amino acid chain, forma the a-Helix and beta sheet Tertiary: More bonds between amino acid chain, imagine crumpled up ball of paper Quarternary: Forms when 2 or more amino acid chains fit together to make an overall 3D shape. |
|

Label The Chloroplast Diagram. |

|
|
|
Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes |
Similarities: -Require a point of replication -Follow the 5' --->3' direction -Both have continuous leading and discontinuous lagging strand -Both use DNA polymerase enzymes Differences: -Prokaryotes replicate faster -Prokaryotes have 1 point of replication, eukaryotes have thousands -DNA polymerase differ in structure and number |
|
|
What is a dipeptide bond? |
The bond that forms when 2 amino acids are connected. |
|
|
What is a nucleotide? |

Consists of a: Phosphate Nitrogenous base Pentose sugar |

