![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What part of the body is home to more primary neoplasms that any other organ?
|
The colorectum (colorectal carcinoma accounts for ~10% of new cancers per year in men and women)
|
|
|
Sessile vs. Pedunculated polyp?
What is the most common type of polyp found in the colorectum? Do we have to be worried about malignancy? |
Pedunculated = has a stalk, Sessile = flat surface outgrowth
Hyperplastic polyp (90% of all polyps found), it is non-malignant. |
|
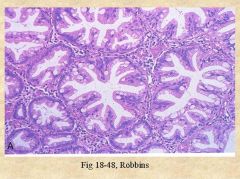
This histologic presentation is most consistent with a ______. What is the underlying pathogenesis of this condition?
What sydnrome can it be associated with? |
Hyperplastic polyp. Due to failure of cells to slough off. On histology you find abundant crypts lined by well-differentiated goblet cells.
Can be associaetd with hyperplastic polyposis syndrome. |
|
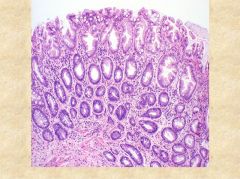
What is shown in this condition? Is it cancerous?
What mutations are associated with this? |
Juvenile Polyp- note the hamartomatous proliferation (mainly lamina propria) which encloses cystic dilations (of crypts). Non-malignant polyp. Seen in kids <5. Found in rectum.
SMAD4 mutation seen in Juvenile Polyposis syndrome. PTEN tumor suppressor mutation in Cowden syndrome.There is also a sporadic form. In patients |
|
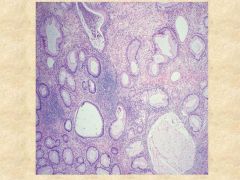
This is a histologic image of a polyp removed from the colorectum. What type of polyp is it?
Is it malignant? |
Peutz-Jeghers Polyp
Hamartomatous, non-malignant. It has bands of muscularis mucosa that proliferate and arborize through the polyp. Otherwise, normal histology. |
|
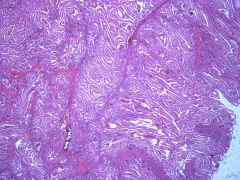
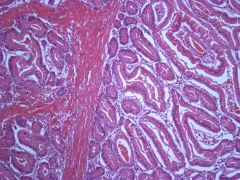
What is the classic presentation of a patient who has a polyp removed from their colorectum (shown here in histology)?
What is the inheritance pattern of this syndrome and the associated mutation? |
Peutz Jeghers (rare autosomal dominant). Patients may have menotic mucosal and skin pigmentation (esp. around lips and mouth).
Increased rsk for cancers- LKB1/STK11 mutation (codes for serine threonine kinase). But the polyp itself is not premalignant. |

