![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
circle
|
the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point
|
|
|
center
|
the point that the set of points are equidistant to
|
|
|
radius
|
a segment whose endpoints are the center and any point on the circle
|
|
|
chord
|
a segment whose endpoints are on a circle
|
|
|
diameter
|
a chord that contains the center of the circle
|
|
|
secant
|
a line that intersects a circle in two points
|
|
|
tangent
|
a line in the plane of a circle that intersects the circle in exactly one point
|
|
|
point of tangency
|
the point at which a tangent intersects the circle
|
|
|
example of chord, radius, diameter, and center
|
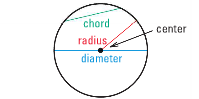
|
|
|
example of secant, tangent, and point of tangency
|
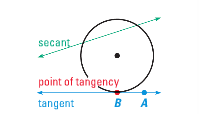
|
|
|
theorem 10.1
|

|
|
|
theorem 10.2
|
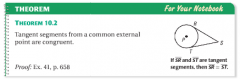
|
|
|
central angle
|
(of a circle) is an angle whose vertex is the center of the circle
|
|
|
minor arc
|
an arc that measures less than 180 degrees
|
|
|
major arc
|
the rest of the circle that isn't the minor arc
|
|
|
semicircle
|
an arc with endpoints that are at the end points of a diameter
|
|
|
measuring arcs example
|

|
|
|
postulate 23: Arc Addition Postulate
|

|
|
|
theorem 10.3
|

|
|
|
theorem 10.4
|

|
|
|
theorem 10.5
|

|
|
|
theorem 10.6
|

|
|
|
inscribed angle
|
an angle whose vertex is on a circle and whose sides contain chords of the circle
|
|
|
intercepted angle
|
the arc that lies in the interior of an inscribed angle and has endpoints on the angle
|
|
|
theorem 10.7: Measure of an Inscribed Angle Theorem
|

|
|
|
theorem 10.8
|

|
|
|
inscribed polygon
|
a polygon where all vertices lie on a circle
|
|
|
circumscribed circle
|
a circle that contains the vertices of a shape
|
|
|
theorem 10.9
|

|
|
|
theorem 10.10
|

|
|
|
theorem 10.11
|

|
|
|
theorem 10.12
|

|
|
|
theorem 10.13
|
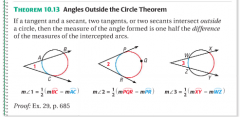
|
|
|
theorem 10.14
|

|
|
|
segments of a chord
|
the two segments of each chord formed when two chords intersect in the interior of a circle
|
|
|
secant segment
|
a segment that contains a chord of a circle, and has exactly one endpoint outside the circle
|
|
|
external segment
|
the part of a secant segment that is outside the circle
|
|
|
theorem 10.15: Segments of Secants Theorem
|

|
|
|
theorem 10.16: Segments of Secants and Tangents Theorem
|

|
|
|
locus
|
a locus in a plane is the set of all points in a plane that satisfy a given condition or set of given conditions
|
|
|
the equation of a circle with radius=r and center at the origin
|

x²+y²=r²
|
|
|
the standard equation of a circle
|

(x-h)²+(y-k)²=r²
|

