![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
316 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Seismometers measure __________ __________. In a seismometer, a weight stays fixed due to _______, while the frame moves with the ground during an earthquake. Measurements from _____ seismic stations allow seismologists to determine epicenter location. |
earthquake vibrations intertia three |
|
|
We specify earthquake size by the _________ or _________. An increase of one magnitude number represents ___ increase in shaking, and a ___ increase in energy release. |
intensity magnitude 10x 32x |
|
|
represents damage caused |
intensity |
|
|
measurement of ground motion amplitude |
magnitude |
|
|
Most, but not all, earthquakes happen _____ _____ __________. Events occur in _____ and _________ _____, and along ____ ______ within _____ _________. Most catastrophic earthquakes happen as __________ __________ and along ___________ _________. |
along plate boundaries rifts collision zones weak faults plate interiors convergent boundaries continental transforms |
|
|
Earthquakes also cause devastation because ______ _______ topples buildings. But destruction can also be caused by __________, ________, and ________ ____________ triggered by the shaking. ____ and ________ may follow an earthquake. |
ground shaking landslides tsunamis sediment liquefaction Fire diseases |
|
|
Researchers can determine regions where earthquakes are more ______, but not exactly ____ and _____ an event will occur. Seismic hazard is _______ where seismicity has happened more __________ in the past and therefore has a _______ recurrence interval. |
likely when where greater frequently shorter |
|
|
Earthquakes are a fact of like on this dynamic planet. People in regions facing high seismic risk should build on ______ ______, avoid ________ ______, and design construction that can _______ _______. __________ ________ saves lives after an event. |
stable ground unstable slopes survive shaking Evacuation planning |
|
|
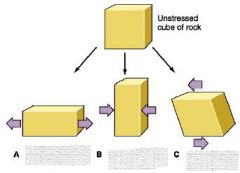
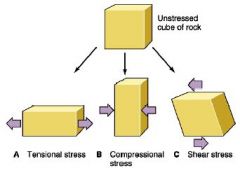
Three types of stress |
compression tension shear |
|
|
Stress can cause rocks to change _____, ________, and __________. During brittle deformation, rocks _____, whereas during ductile deformation, rocks ____ and _______ _______ ________. Strain is a measure of ____ ______. |
shape position orientation bend distort without breaking shape change |
|
|
cracks |
joints |
|
|
mineral-filled cracks |
veins |
|
|
fractures on which sliding occurs |
faults |
|
|
Brittle structures include ______, _____, and ______. Geologists distinguish among different kinds of faults based on the ________ ____________ across the fault. Faulting can _____ and _______ rock. |
joints veins faults relative displacement break scratch |
|
|
Folds are _____ or ______ designed by the shape of rock layers. Arch-like folds are __________, and trough-like folds are _________. Deformation can change the _____ and ___________ of grains, aligning them to produce a ______ ______ called foliation. |
bends curves anticlines synclines shape orientation planar fabric |
|
|
Mountain belts form in association with _________ _________ and _______. During continental collisions, and at some convergent margins, the crust ________, large ______ ______ and _____ form, and ________ ____________ develops. Rifting yields _____-_____ mountains. |
convergent collision rifting thickens thrust faults folds regional metamorphism fault-block |
|
|
Mountains exist where major ______ occurs. Beneath some belts, the relatively buoyant crust has _________, so the lithosphere ______ ______. Once uplifted, _______ sculpts ______ topography. Mountain belts may eventually _______ under their own weight. |
uplift thickened floats higher erosion rugged collapse |
|
|
_______ are portions of continents that consist of old (___________) and relatively stable crust. Parts of _______ may be covered by _________ ___________ ______. Variations in the dip and thickness of these strata define ________ ______, ______, and _____. |
Cratons Precambrian cratons Paleozoic sedimentary strata regional basins arches domes |
|
|
the present is the key to the past |
uniformitarianism |
|
|
The principle of _________________ implies that the Earth must be very ___, for geologic processes happen ______. Geologists distinguish between ________ age and __________ age. |
uniformitarianism old slowly relative numerical |
|
|
older or younger |
relative age |
|
|
how many years ago |
numerical age |
|
|
younger strata overlie older strata |
superposition |
|
|
younger features cut older ones |
cross-cutting relations |
|
|
fossil species occur in a predictable order |
fossil succession |
|
|
________-___ _____________ is based on geologic principles, including _________________, _____________, _____-_______ _________, and ______ _________. |
Relative-age determination uniformitarianism superposition cross-cutting relations fossil succession |
|
|
At a given location, sediments do no accumulate ____________, so ______________, surfaces representing intervals of nondeposition and/or erosionm can form. Because of unconformities, the geologic records at any given location is __________. |
continuously unconformities incomplete |
|
|
A _____________ _________ is a recognizable sequence of beds that can be mapped across a broad region. Geologists correlate formations __________ on the basis of ____ ____ and ______ _______, and portray the configuration of formations in a region on a ________ ___. |
stratigraphic formation regionally rock type fossil content geologic map |
|
|
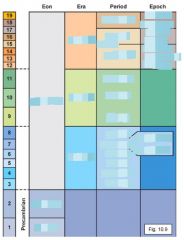
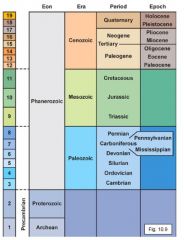
Correlation of stratigraphic sequences from around the world led to the production of a chart, the ________ ______, that represents the entirety of _____ _______. The column, developed using only ________-___ _________, is subdivided into ____, ____, _______, and ______. |
geologic column Earth history relative-age relations eons eras periods epochs
|
|
|
Isotopic dating specifies numerical ages in years. To obtain an isotopic data, we.... |
measure the ratio of parent radioactive isotopes to stable daughter products in a mineral. |
|
|
A date for a mineral gives the time at which the mineral... |
cooled below a closure temperature |
|
|
_________ _____ for sedimentary rocks come from ________ ______ of _____-_______ _______ _____. Such work led to the geologic time scale, assigning ages to periods. The oldest rock of Earth's crust is about ___ __. Dating of meteorites indicates the Earth is ____ __. |
Numerical dates isotopic dating cross-cutting datable rocks 4.0 GA 4.57 GA |
|
|
During the Haden (____ to ____ __), the Earth ______________ and the ____ formed. A rock record of this Eon _______ _____, because our planet's surface may have been _________ ______ and was __________ by __________. |
4.57 to 3.85 GA differentiated moon doesn't exist partially molten pulverized by meteorites |
|
|
During the Archean (____ to ___ __), the first continental crust formed from _________ ________ ____ and ___-____ _________, ______ filled the atmosphere _______ and life (_______ and ________) appeared. |
3.85 to 2.5 GA colliding volcanic arcs hot-spot volcanoes oceans changed archaea and bacteria |
|
|
During the Proterozoic (___ to ____ __), _______ formed and then _______ together to form _________ and, eventually ______________, which late riften apart. _____________ _________ appeared, and the atmosphere began to accumulate significant oxygen. |
2.5 to 0.54 GA cratons sutured supercontinents Multicellular
|
|
|
Break-up of the late Precambrian _____________ ushered in the _________. During the Paleozoic, _______ ____ covered continents, at times, and ____ ___________ and moved onto land. As the eon ended, collisions led to the assembly of _______. |
supercontinent Paleozoic shallow seas life diversified Pangaea |
|
|
During the Mesozoic, _________ roamed all continents. In North America, a __________ _____ ________ formed along the West Coast, eventually leading to the uplift of the _____ _________. Rifting of Pangaea produced the ________ _____. A ____ _________ _____ marks the end of the era. |
dinosaurs convergent plate boundary Rocky Mountains Atlantic Ocean Huge Meterorite impact |
|
|
The Cenozoic began when a huge meteorite impact may have caused ____ _________. During the Cenozoic, the ________ _____ of _____ rose, ______ _____ __________ became __________ and _______ diversified. Recently, ___ ___ ________ covered large areas. |
mass extinction mountain belts of today modern plate boundaries established mammals ice age glaciers |
|
|
Earthquakes usually don't happen in _________. |
isolation |
|
|
anything that happens before an earthquake |
foreshocks |
|
|
anything that happens after an earthquake |
aftershocks |
|
|
When can we tell foreshocks and aftershocks? |
After everything has been recorded |
|
|
_________ _ waves can be measured anywhere in the world. |
Magnitude 5 |
|
|
Seismometers are instruments that record ______ ______. |
ground motion |
|
|
Modern seismometers use a ______ and _______ ____. They record data _________. They are able to detect ____ _____ ground motion that people ______ _____. |
magnet electric coil digitally very small cannot sense |
|
|
Seismometers are on a big _______ slab and get ______. |
granite buried |
|
|
Three points for looking at seismometers |
Figure out when an earthquake occurred Where it occurred Have to have a network of seismometers |
|
|
We can locate where an Earthquake is more exactly by using _ and _ ____ arrival times. |
P and S wave |
|
|
The S-P interval will tell you the ________ of the earthquake from each station. |
distance |
|
|
How can you get the location of an Earthquake? |
From at least three stations, draw overlapping arcs to determine the location |
|
|
P and S-wave arrival times can be _______. |
graphed |
|
|
What is something other than Earthquakes that seismometers can measure? |
nuclear bomb testing |
|
|
Geophysics measures.. |
other stuff besides materials |
|
|
Is gravity always the same? Why or why not? |
No because different things are happening within the Earth |
|
|
What are three things that geophysics measures? |
ground motion, magnetism, and heat flow |
|
|
If the rock is homogenous, wave fronts are _______, in _____ ________. |
circles cross sections |
|
|
Energy in seismic waves is going out in all _________ __________. |
different directions |
|
|
Vp |
P-wave velocity |
|
|
Vs |
S wave velocity |
|
|
Body waves travel faster in ______ than in _________. |
Basalt Sandstone |
|
|
P-waves travel faster in ______ than in _______. |
solids liquids |
|
|
S-waves cannot travel through _______ or the _____ ____. |
liquids outer core |
|
|
P-waves will ____ ____ in the outer core. |
slow down |
|
|
If an earthquake is "late" getting to a seismometer, then you know there is an _______. With more Earthquakes and data, you can figure out ________ where it is. |
anamoly exactly |
|
|
After moving through a ____ ____, seismic waves return to their quicker speed. |
slow zone |
|
|
We get information about the Earth through _______ __________. |
seismic tomography |
|
|
________ ____________ shows hot spots and where stuff is warmer. |
Velocity Perturbation |
|
|
Seismic reflection is more concerned with the fact that your energy _______ ___ of some _________. |
bounces off interface |
|
|
Seismic reflection is looking at ______ of stuff that may not be at the _______. |
layers surface |
|
|
___________ are linked to plate tectonic boundaries. |
Earthquakes |
|
|
Shallow Earthquakes occur at... |
divergent and transform boundaries |
|
|
Intermediate and deep earthquakes occur at... |
convergent boundaries |
|
|
What occurs at divergent plate boundaries? |
Mid-ocean ridges |
|
|
Two types of faulting typify Mid-Ocean Ridges ,______ ______ at the ________ _____ ____ and ______-____ ______ along the _________. Mid-Ocean Ridge Earthquakes are _______ (<10 km deep) and ___ ______. |
normal faults spreading ridge axis strike-slip faults transforms shallow low energy |
|
|
have shallow, intermediate and deep earthquakes |
convergent plate boundaries |
|
|
Earthquakes go all the way down to the __________ _____. |
subducting plate |
|
|
Almost all shallow Earthquakes are in the _____. |
crust |
|
|
How can water mass redistribution effect earthquakes? |
1. Water is heavy 2. Water is fluid. 3. Water is pushing against the fault trying to open it. |
|
|
Two types of defomration |
folding and faulting |
|
|
What does deformation result in? |
displacement, rotation, and distortion |
|
|
a change in location |
displacement |
|
|
a change in spatial orientation |
rotation |
|
|
a change in shape |
distortion |
|
|
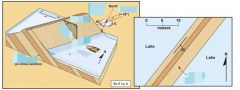
The geometry of ______ features created during rock deformation is easily described using ______ and ____. |
Planar strike and dip |
|
|
Lake water on a dipping bed of strata defines a ______ ____. |
strike line |
|
|
a line formed by the intersection of a horizontal plane with a tilted surface |
strike |
|
|
the angle of the tilted surface down from the horizontal |
dip |
|
|
Dip is ______ _____________ to strike. |
Always perpendicular |
|
|
no dip, 90* |
strike slip |
|
|
two points for strike slip faults |
vertical plane motion is horizontal |
|
|
Three types of faults |
strike-slip fautls dip-slip faults oblique slip faults |
|
|
moves diagonally |
oblique slip faults |
|
|
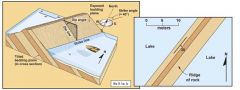
What do folds look at? |
limbs and hingeline |
|
|
|
|
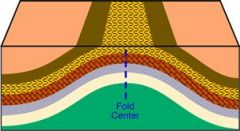
|
Anticline |
|
|
An anticline looks like an ____. The bed dips ____ from the hinge. |
arch away |
|
|
|
|
|
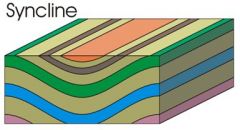
A syncline looks like a ______. The bed dips ______ the hinge. |
trough toward |
|
|
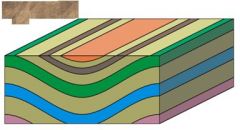
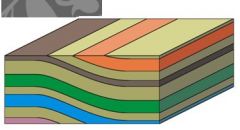
Six types of folds |
anticline syncline monocline basin plunging hinge dome |
|
|
|
|
|
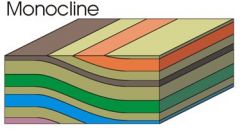
A monocline looks like a _____ ____ and is commonly ______ over a _____ _____. |
stair step draped fault block |
|
|
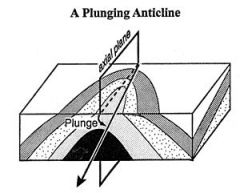
|
|
|
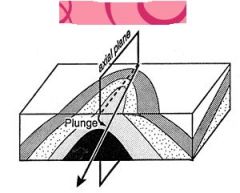
A plunging anticline has a ______ hinge. |
tilted |
|
|
|
|
|
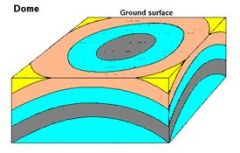
A dome has the shape of an __________ ____. Youngest layers are on the _______. |
overturned bowl outside |
|
|
|
|
|
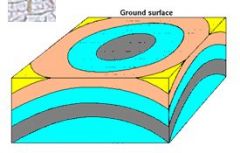
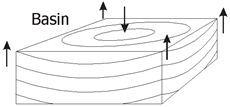
A basin has the shape of an _______ ____. The youngest layers are in the ______. |
upright bowl middle |
|
|
______ is the force, ______ is what happened. |
Stress strain |
|
|
______ causes ______ |
stress strain |
|
|
the change in shape caused by deformation |
strain |
|
|
There are several types of ______. |
strain |
|
|
sliding past |
shear |
|
|
the relationship between stress and strain |
rheology |
|
|
Three examples of rheology |
ductile elasticity brittle |
|
|
|
|
|
Four factors of rheology |
Temperature pressue compisition time |
|
|
More _______ further down in the Earth as the temperature gets higher |
ductile |
|
|
More pressure, more ______ |
ductile |
|
|
Some minerals are more prone to flow ___________ because of ________ _____. |
differently internal bonds |
|
|
Mantle is _____ and ______ |
solid liquid |
|
|
Stress rate has a big deal to do with how ______ will develop |
strain |
|
|
Can be brittle over a _____ time, then ______ over a long time. |
Short ductile |
|
|
Where is the boundary between brittle and ductile behavior? |
The lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary |
|
|
Thrust faults act to _______ and _______ mountain belts. |
Shorten thicken |
|
|
Thrusts can transport sheets of rock ________ of __________ and are common ________ at the leading edge of ________ ___________. |
hundreds of kilometers features orogenic deformation |
|
|
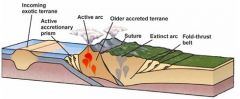
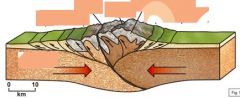
At some convergent margins, ___________ between the _________ and __________ plates uplifts a mountain range in which _________ occurs. Subduction may bring in ______ _______ ______ that collides and become incorporated in the _______. |
compression downgoing overriding volcanism exotic crustal blocks orogeny |
|
|
Four causes of mountain building |
convergent tectonic boundaries exotic terrains continental collision continental rifting |
|
|
Before you can have continental collision, you have to _______ the whole ______ part of the plate. |
subduct oceanic |
|
|
Exotic terrains consist of ______ ________ of continental crust that had a ________ geologic history before being sutured to the __________ _____ at a __________ ______. |
island fragments separate overriding plate convergent margin
|
|
|
curved faults |
listric |
|
|
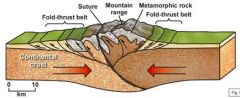
Continental collision consists of lots of _______, mostly in the ______. |
folding middle |
|
|
For continental collision, you are ridging into __________ fault. |
detachment |
|
|
rocks getting fused/sewn together |
suture |
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
During collision, continents _______ together and ______. Thrusting brings ___________ rock up to _________ levels. |
squeeze deform metamorphic shallower |
|
|
anything that's up relative to stuff that's down |
mountains |
|
|
As soon as you get to a ___ ____, sediments start to fill in. |
low spot |
|
|
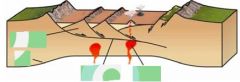
You end up with ______ of mountains when you're dealing with continental rifting. |
stripes |
|
|
_______ leads to the development of numerous ______ ________ ______. ____-______ _________ may also form. |
Rifting narrow mountain ranges Rift-margin mountains |
|
|
Basins are ___ _____ that fill with sediment. |
low areas |
|
|
Ranges are exposed to _____-_______ ______. |
fault-bounded blocks |
|
|
____ _______ rise to form mountains |
Rift margins |
|
|
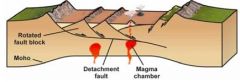
Convergent-margin horizontal ___________ causes horizontal __________ and vertical __________. These processes create a _____ _______ ____ beneath ________ ______. |
compression shortening thickening thick crustal root mountain ranges |
|
|
The Himalayas are the world's _______ ________ _____. The crust beneath them is almost _____ the normal thickness. |
highest mountain range twice |
|
|
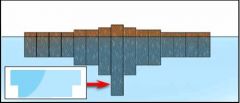
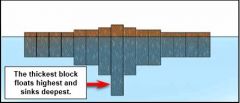
Because of ________, blocks of wood floating in water... |
isostasy sink to a depth such that the mass of the water displaced is the same as the mass of the block. |
|
|
What causes crust to go up? |
Uplift and gravity/buoyancy |
|
|
What causes crust to go down? |
Erosion and gravity |
|
|
state of balance between mass pushing down and pushing up |
isostasy |
|
|
India was created by the ___________ of ___ ______. |
convergence of two plates |
|
|
When India was created, the plates moved really ____. This created the ________. |
fast Himalayas |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
When India wrecked into EuroAsia, what happened? |
The EuroAsia plate caved in |
|
|
What is a passive margin? |
no faults or volcanoes |
|
|
Are passive or active margins stronger? |
passive |
|
|
When there are two plates of the same density, what happens? |
Mountains are created and one plate has to give. |
|
|
Three points for Arthur C Clarke. |
2001: A Space Odyssey Not a formal scientist Foresaw many things of our time |
|
|
Who made documentaries? |
Carl Sagan |
|
|
Three points for Steve Scarra |
There are three rovers on Mars Steve led two of them One is still working |
|
|
mission; satellite that can orbit planetary bodies |
Dawn at Ceres |
|
|
How far is the sun from the asteroid belt? |
2.7x the distance of the Earth from the sun |
|
|
What is the mission? |
We went to Vista and are now headed toward Ceres |
|
|
What is the largest asteroid in the asteroid belt? |
Ceres |
|
|
Name five planetary bodies |
satellites dwarf planets protoplanets planets sun |
|
|
What distinguishes Ceres from other bodies in the solar system? |
Ceres is a dwarf planet, the only mass in the belt that is considered this. May harbor life Ejecta, could give the origin of our species. |
|
|
carries the connotation of precursor; almost a planet |
protoplanet |
|
|
What does a protoplanet need to do to become a planet? |
Must clear the orbit, needs to be spherical be differentiated into different layers need enough mass for gravity to create uniform shape |
|
|
small, but are very close to being a planet |
dwarf planets |
|
|
Which body orbits planets? |
sattellites |
|
|
What insight might Ceres offer on our origin, as a planet and species? |
Tells about early geologic processes on earth origin of life
|
|
|
What do we know about Ceres that makes it like earth? |
it emits water vapor, and it has a rocky core |
|
|
What did Riftkin and his group observe on Ceres from Earth? |
It has carbonates and clay |
|
|
How can you tell which minerals are present on a body? |
By the shape of the spectrum |
|
|
collide together to form planets |
protoplanets |
|
|
components of planets that can be gaseous |
volatiles |
|
|
Water only amounts to about ___ of the Earth's mass |
3% |
|
|
What are the two immediate sources of volatiles on Earth? |
volcanos and oceans |
|
|
What was the first source of volatiles? |
Protoplanets, because they collided and released their gases |
|
|
essential for our planet |
volatiles |
|
|
How did we figure out what we know about Ceres? |
Mineral isotopes relative abundance will vary |
|
|
How differentiated is Ceres? |
We don't know and will try to find out with the Dawn mission |
|
|
What is the temperature on Ceres? |
about -105* C. |
|
|
H20 bonds layers together |
clay sillicates (phyllosilicates) |
|
|
We think Ceres might have a ________ core. |
metallic |
|
|
What do we need to know about Ceres? (4) |
gravity field, length from the sun, magnetic field mass density |
|
|
Ceres is about __ the density of water |
2x |
|
|
really cold setting; changes ice to gas |
cryovolcano |
|
|
What are the three reasons we chose Ceres over other similar cerrestrial bodies? |
1. It is the biggest protoplanet in the asteroid belt, so it has a higher chance of being differentiated. 2. Ceres can fill gaps about things we know about Earth. 3. Uniform size, safe to orbit for Dawn. |
|
|
What is the atmosphere like on Mars? |
1000 times thinner than the Earth's |
|
|
Three points for the atmosphere on Mars |
1. Thick enough to cause hydrothermal issues, but not enough to slow you down when you're landing 2. 95% carbon dioxide 3. The presence of life on Earth makes the difference |
|
|
The presence of biosphere on Earth determines ______. |
oxygen |
|
|
Mars is less _______ than Earth. |
massive |
|
|
Mars does not have a global ________ _____, so solar winds can _____ away atmosphere. |
magnetic field shear |
|
|
Mars has ________, but not _________. |
volcanos eruptions |
|
|
The volcanos on Mars are... |
two to three times the height of Mount Everest |
|
|
Four differences in the terrestrial crust of Mars and Earth |
plate tectonics sediment is not held together no water dust just keeps recirculating |
|
|
Why do we study geology? |
We are trying to figure out a record of what the Earth used to look like. |
|
|
Geologic history is the _________ of ______ in _____ of ________ ___ that have produced the ___, _________, and _________ that we see. |
succession events order relative age rock structure lanscape |
|
|
What does rock mean in the geologic history? |
explain processes of rock what chemistry is going on |
|
|
Where are the different rocks? |
structure |
|
|
Two points for landscape |
overall picture of it all what does the surface look like now |
|
|
What are the seven helpful rules for figuring out the relative ages of rocks? |
1. Uniformitarianism (vs. catastrophism) 2. Original horizontality 3. superposition 4. lateral continuity 5. Cross-cutting relationships 6. Baked contacts 7. Inclusions |
|
|
the way the world works now is the way it worked before |
uniformitarianism |
|
|
says that the things we see are the result of sudden changes happening all at once |
catastrophism |
|
|
Four examples of catastrophism |
big meteors super big volcano explosions floods fault slips |
|
|
What is typically what is going on in rock? |
slow and steady uniformitarianism |
|
|
What is correct, uniformitatianism or catastrophism? |
Both happen |
|
|
Principal of Original Horizontality |
Because sediments settle out of a fluid by gravity, they tend to accumulate horizontality. Sediment accummulation is not favored by slope. |
|
|
Superposition |
oldest at the bottom, youngest at the top |
|
|
Lateral continuity. |
Things get deposited in horizontal layers regionally. Layers are continuous over very large regions. |
|
|
Cross-cutting relationships |
If something is cutting across the continuous rock layers, the thing that is cutting is younger. |
|
|
If a dike cuts across sedimentary beds... |
the dike is younger |
|
|
Baked contacts |
The pluton baked the adjacent rock, so the adjacent rock is older. |
|
|
Inclusions |
Fragments of rock predate the rock; marbles are older than pudding. |
|
|
Fragments within an igneous rock intrusion are _____. |
older |
|
|
The pebbles of basalt in a conglomerate must be... |
older than the conglomerate |
|
|
Xenoliths of sandstone must be _____ than the basalt containing them. |
older |
|
|
Only __________ rocks are deposited. |
sedimentary |
|
|
Only _______ rocks are intruded. |
igneous |
|
|
surface representing a period of nondeposition or erosion that represents a gap in the geologic record |
unconformity |
|
|
What is a gap in the geologic record called? |
hiatus |
|
|
Two points for angular unconformity |
There is time missing in the rock area recognized by difference of dips in beds |
|
|
|
|
|
Three points for nonconformity |
recognize that something is missing sediments deposited over igneous or metamorphic rock recognized by contact between eroded igneous or metamorphic rock and sedimentary rock |
|
|
Three points for disconformity |
hardest to identify have time in between end up with sedimentary rocks that should not be next to each other |
|
|
There is no place where we have a ________ record, but there is a record for each time in ____ place. |
Complete some |
|
|
diagnostic of a particular geologic time |
index fossils |
|
|
Fossils are only found in... |
rocks that were deposited during the time the organism lived...not before, not after. |
|
|
Fossils are a... |
big part of how we put our time record together |
|
|
Six steps to the creation of a dinosaur fossil |
1. The dinosaur collapses and dies. 2. Footprints are left in the mud 3. Flesh rots away, bones remain 4. The water level rises; sediment buries the bones and footprints 5. A thick sequence of sediments accumulates over the bones; gradually the bones fossilize. 6. Erosion later exposes the later of strata containing the bones and footprints. |
|
|
What are three of the best ways to become a fossil and why? |
1. Have hard shells or other bits (soft tissue doesn't preserve well) 2. be buried rapidly (so you don't get eaten) 3. Be in an anoxic environment (so you don't become compost) |
|

|
Trilobite |
|
|
Sometimes you have the actual body (6 points) |
1. frozen 2. stuck in something 3. amber (fossilized tree sap) 4. mummified tissue 5. only works if it's pretty recent. 6. helpful for biologists, not geologists |
|
|
Sometimes just the hard bits get fossilized (five points) |
1. can learn a lot from individual pieces 2. made out of rocks (not bones) 3. Minerals in bones have been replaced 4. spongy bits get filled in 5. have essentially a statue of what used to be there |
|
|
have evidence that something used to be there, but you don't have any material from it |
trace fossils |
|
|
two examples of trace fossils |
footprints and carbon smudges |
|
|
Fossils comes in... |
all sizes, from microfossils to huge dinosaurs |
|
|
Mircrofossils are really important because they... |
get preserved very well. |
|
|
What gets preserved very well? |
pollen |
|
|
Fossils help us figure out... |
how life evolved. |
|
|
Most of the early organisms are ________ and ______. Everything else is _______. |
bacteria and archea Eukarya |
|
|
What were the first organisms to show up and when? |
Archea in the Archaen Period |
|
|
three points for Archea |
found today near hot springs (in volcanic centers) Thermofiles: okay with being really hot eat sulfur |
|
|
Mass extinctions occur when... |
a lot of species go extinct during a really short period of time. |
|
|
When did the dinosaurs go extinct? |
K/T Mass extinction |
|
|
Fossils tell us about the ___________ at that time, providing a _____ for the sediments they are found in. |
environment clock |
|
|
getting numerical ages aka isotopic dating |
geochronology |
|
|
change (decay) |
radioactive |
|
|
stay that way forever |
stable |
|
|
What do you need for geochronology? |
isotopes |
|
|
Which isotope is always radioactive? |
parent |
|
|
Which isotope is always stable? |
daughter |
|
|
Parent and daughter isotopes are... |
always in pairs. |
|
|
Two parent/daughter pairs |
potassium-->argon and calcium Rubidium-->strontium |
|
|
What happens with radioactive decaying? |
nucleus of the atom decays in a predictable way. |
|
|
The age of a rock represents... |
the amount of time since the system was closed |
|
|
Half life |
the amount of time it takes for half of the isotopes to decay; same for each half |
|
|
cannot be transported around |
closed system |
|
|
the isotopes are moving around |
open system |
|
|
Two points for closed system |
often related to temperature parent and daughter isotopes can no longer come and go from mineral grain |
|
|
For igneous rocks, closure temperature is... |
the time since cooling |
|
|
Steps to geochronology (4) |
1. Get a rock 2. Separate out the mineral grains you're interested in 3. Separate out the isotopes that you're interested in 4. Analyze the parent/daughter ratio |
|
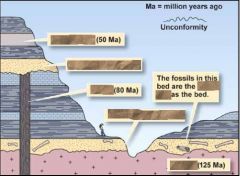
|
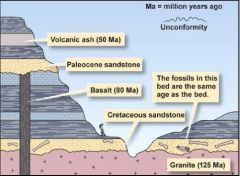
|
|
|
Three points for isotopic dating systems |
half-life must be close to the age of the material need a mineral that has isotopes in it prefer a closed system |
|
|
Why does isotopic dating only work well for igneous rocks? |
Metamorphic rocks have changed so it only tells us the date since metamorphism. If you date sedimentary rocks, you'd just be dating the clasts. |
|
|
We are dating the ____, not the ______. |
rock fossil |
|
|
When was the dinosaur age? |
254 Ma to 65 Ma (mesozoic era) |
|
|
What does the oceanic crust have that helps us? |
reversals of the magnetic field |
|
|
over time, where are the continents? |
Paleogeography (Paleotectonics) |
|
|
what's going on with the atmosphere, oceans, and global temperature? |
Paleoclimate |
|
|
Rocks from the moon show that the rock is mostly.... |
silicate, and moon formation happened after differentiation. |
|
|
In the Hadean, ____________ occured. |
differentiation |
|
|
Do we have rocks from the Hadean? |
No |
|
|
Once the atmosphere gets cool enough... |
the water vapor can create ocean (Hadean) |
|
|
In the Hadean, liquid water... |
condensed to form the ocean. |
|
|
The first evidence of oceans from marine sediment appeared... |
about 3.85 Ga (Hadean) |
|
|
Volcanic outgassing created a deadly atmosphere in the... |
Hadean |
|
|
In the Hadean, meteorites bombarded the surface around... |
4 and 3.9 Ga |
|
|
Three points for the Archean |
making oceans getting the first archea felsic rock that formed above subduction zones is welded to other felsic blocks during collisions |
|
|
What does proterozoic mean? |
before life |
|
|
incredibly old continental crust |
cratons |
|
|
When did our cratons form? |
Proterozoic |
|
|
In the Proterozoic, continents grew by the addition of ________ ____ and cooled and strengthened to become _______. |
volcanic arcs cratons |
|
|
How much of the Earth's crust was formed by the Proterozoic? |
90% |
|
|
Continental collision created... |
Proterozoic supercontinents |
|
|
How long ago was the Rodinia supercontinent formed and maintained? |
1 billion to 700 million years ago |
|
|
What was North America called in Rodinia? |
Laurentia |
|
|
When was the Pannotia Supercontinent formed and maintained? |
About 600 million years ago (didn't last long) |
|
|
What four major continents resulted from the rifting of Pannotia in the Phanerozoic era? |
Laurentia Gondwana Baltica Siberia |
|
|
Initially, in the Paleozoic era, both coasts were _______ margins. In the Middle Ordovician, __________ begins off of the east coast. |
passive subduction |
|
|
In the Paleozoic, transgressions and regressions... |
make inland seas and deposit sedimentary rocks.
|
|
|
Throughout the Paleozoic... |
things were wrecking into each other, becoming parts of continents, and making mountains. we were also making sedimentary layers |
|
|
The __________ orogeny was the first Appalachian orogenic pulse and the ______ ___ formed off of the west margin during the Paleozoic. |
Taconic antler arc |
|
|
The the Late Devonian, the _______ orogeny created a second pulse of Appalachian mountains that shed sediments onto the _______, forming the ________ _____. |
Acadian craton Catskill delta |
|
|
The largest collision occured when Gondwana smashed into ________ and ______. |
Laurentia Baltica |
|
|
During the early and middle mesozoic.... |
Pangaea (lasted about 100 million years) began rifting in the Triassic. |
|
|
By the ________, a narrow North Atlantic existed |
Jurassic. |
|
|
Where is the oldest sea floor in the Atlantic? |
The North |
|
|
In the late mesozoic, __________ continued along the west coast. The ________ ___ grew, exposed today as the ______ ______ batholith. The _____________ _____ forms the present day coast range. |
Subduction Sierran Arc Sierra Nevada accretionary prism |
|
|
In the late creataceous, climate continued to ____ and seas _______ the continents. The _______ interior sea way connected the ____ of ______ to the ___. |
warm flooded western Gulf of Mexico Artic |
|
|
In the late mesozoic, ________ national park was created, consisting of gigantic blocks of _______, which is an _________ ______ _______ rock. |
Yosemite granite intrusive felsic igneous |
|
|
In the Cretaceous, many of the faults did not reach the ______, instead _______ overlying strata into large __________ and uplifting the _____ ________ front range. |
surface folding monoclines Rocky Mountain |
|
|
The ________ Orogeny, in the Late __________, was unusual and resulted in the _____ _________. |
Laramide Cretaceous Rocky Mountains |
|
|
By the Late Creteceous, _____ has broken off from ________ and is heading toward ____. |
India Gondwana Asia |
|
|
The first ancestors of _______, resembling small ___-____ creatures, appeared in the ________. |
mammals rat-like Triassic |
|
|
During the Cenozoic, the ________ continents were heading for _________, creating the ________. |
Gondwana collision Himalayas |
|
|
When over subduction gets changed to Transform, we end up with ______ and ______. |
basins range |
|
|
Sediment in the middle of the __ comes from the fact that is used to be __________. |
U.S Underwater |
|
|
Four points for Middle Precambrian |
Carbon in the ocean start to have oxygen and photosynthesis Get to the point where oceans can no longer hold oxygen The excess of oxygen was preserved in banded iron formations |
|
|
Three points for Snowball Earth |
Right at the end of the Paleozoic Entire planet is glaciated Happened maybe a couple times |
|
|
Things will shells show up in the ________. |
Cambrian |
|
|
huge ramp-up of diversity |
cambrian explosion |
|
|
What probably costs the mass extinction at the end of the Permian? |
climate |
|
|
What happened for the K/T Mass Extinction? |
Meteorite impact we found the crater obvious when you look at gravity signature |
|
|
The first feathered birds occured in the... |
Early and Middle Mesozoic |

