![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
227 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Volcanoes erupt ____, ___________ ______, and ___. The character of a lava flow--whether it has ___ viscosity and spreads over a _____ area, or has ____ viscosity and builds a _____ over the ____, depends largely on its ___________. Pyroclastic debris includes ______, _______, ______, and _____. Some may fall over the countryside like snow, but some surge down the flank of a volcano as a ___________ ____. |
lava pyroclastic flow gas low large high mound vent composition pumice lapilli blocks bombs pyroclastic flow |
|
|
At a volcano, lava rises from a _____ _______ and erupts from chimney-like ________ or from _____-____ ________. Low viscosity ______ lava flows build ______ volcanoes. Fountaining basalt splatters ______ to build ______. Successive eruptions of ___________ ______ and lava build _______________ and explosions produce ________. |
magma chamber conduits crack-like fissures basalt shield tephra cones pyroclastic debris stratovolcanoes calderas |
|
|
Most volcanic activity takes place on _____ __________, but some occurs at ___ _____. The style of eruption depends on the setting. The sea hides _________-________ volcanoes, which erupt ______ ______. Volcanic arcs ____ ____ sea-level and may produce _______________. Oceanic hot spots produce ______ volcanoes. Continental hot spots and rifts produce both ________ and ________ eruptions. |
plate boundaries hot spots divergent-boundary pillow basalt rise above stratovolcanoes shield effusive explosive |
|
|
Volcanoes can be dangerous! The ____ _____, ___________ ______, __________, ___ _____ (______), __________, ___________, and ________ that can be produced during eruptions can destroy cities and farmland. ___ that enters the air can be a hazard for air travel |
lava flows pyroclastic debris explosions mud flows (lahar) landslides earthquakes tsunamis Ash |
|
|
Volcanoes don't erupt ____________ and don't ____ _______, so we can distinguish among ______, _______, and _______ volcanoes. Once a volcano ceases to erupt, erosion destroys its ________ shape. Geologists can provide ____-____ ___________ of eruptions so that people can take precautions. |
continuously last forever active dormant extinct eruptive near-term predictions |
|
|
The ___, _____, and ________ produced by explosive eruptions can be blown around the globe. This material can cause significant ______ _______. ________ _______, as well as other consequences of eruptions, may have impacted human evolution and civilization. |
ash gas aerosols global cooling Climatic effects |
|
|
Space exploration reveals that volcanism occurs not only on Earth, but has also left its mark on other ___________ planets and on the moons of giant planets. Satellites have detected active eruptions on moons of _______ and ______. |
terrestrial Jupiter Saturn |
|
|
Sedimentary Rocks differ from one another due to their ____ of ______ and/or ___________. Clastic rocks form from ________-________ ______ that broke off pre-existing rocks, limestones from ______ or ________ ____________, evaporites from ___________ ____ _____, and organic rocks from _____ ______ and other _______ ______. |
mode of origin composition cemented-together grains shells chemical precipitates evaporating sea water plant debris organic matter |
|
|
Sedimentary rocks occur in ____, because as conditions of deposition and/or sediment source ______ over time, sediment character changes. Geologists refer to a succession of ______ traceable over a region as a _____________ formation. The action of currents can produce sedimentary structures such as _______, ______, and _____ ____. |
beds change strata stratigraphic ripples scours cross beds |
|
|
Different types of sedimentary rocks accumulate in different depositional environments. Thus, strata deposited along a river _______ from strata deposited by ocean waves, by glaciers or in the deep sea. By studying sedimentary rocks at a location, geologists can ______ ____________ that existed in the locality in the past. |
differs deduce environment |
|
|
In certain geologic settings, Earth's surface sinks (subsides) to form a __________ that fills with ________. The depression with its thick fill of sediment is a ___________ _____. As sea level rises and falls, the coast, and therefore depositional environments, can _______. |
depression sediment sedimentary basin migrate |
|
|
Metamorphism takes place in response to changes in ___________, ________, ___________ of ___________ and _____, and/or ___________ with ____________ fluids. The process involves reactions that take place _______ _______, and can produce new ________ and ________. |
temperature pressure application compression and shear interaction hydrothermal without melting foliation minerals |
|
|
Geologists divide metamorphic rocks into classes based on whether the rock contains _________. Foliated rocks include _____, ______, and _____. Non-foliated rocks include ______ and _________. The type of metamorphic rock that forms depends on the __________ of metamorphism. Specific grades of metamorphic minerals form under ________ ___________ and _______ _______. |
foliation slate schist gneiss marble quartzite conditions specific temperature pressure ranges |
|
|
_______ (_______) metamorphism develops around igneous intrusions, due to ____ from the intrusion. _____________ (________) metamorphism develops beneath mountain ranges where rock undergoes ___________ and _____ at ____ ____________ and _________. _______ and ______ may eventually expose metamorphic rock in mountain ranges or continental shields. |
Thermal (contact) heat Dynamothermal (regional) compression shear high temperatures pressures Erosion uplift |
|
|
Most earthquakes happen when ______ builds sufficiently to cause sudden _________ of a fault, or ____ on a preexisting fault. The _____ is the point in the Earth where the slip occurs. The _________ is the point on the surface of the Earth directly above. |
stress formation slip focus epicenter |
|
|
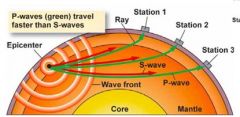
Earthquake energy travels as _______ waves. Body waves (_-_____ and _-_____) travel through the ________ of the Earth, whereas surface waves travel along the _______. Ground Shaking, due to arrival of waves, generally _________ with distance from the __________. |
seismic P-waves S-Waves interior surface decreases hypocenter |
|
|
Volcanic eruptions ____ _________ from inside the Earth to outside the Earth |
move materials |
|
|
|
|
|
molten rock that moves over the ground |
lava flows |
|
|
Flow style depends on _________ |
viscosity |
|
|
Viscosity depends on (4 things) |
composition, especially silica content temperature gas content crystal content |
|
|
The more ______ you have, the stickier stuff gets |
silica |
|
|
If lava is ______, it flows more easily. |
hotter |
|
|
If you add volatiles, it makes lava ____ viscous |
less |
|
|
Crystals happen between the _______ and ________ |
solidus and liquidus |
|
|
If there are more crystals, there is a _____ viscosity. |
lower |
|
|
_________ is the governing principle. |
Viscosity |
|
|
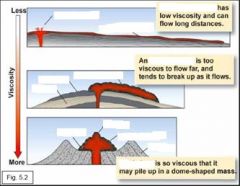
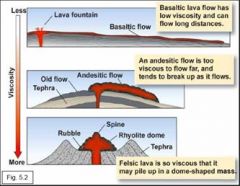
Basaltic lava flows (3 points) |
low viscosity (flows) surface texture reflects the timing of freezing relative to movement don't have much silica |
|
|
Four things formed by basaltic lava |
Pahoehoe A'a Pillow Basalts Columnar jointing |
|
|
crystallizing on the outside, flowing on the inside, "ropes" |
Pahoehoe |
|
|
broken up by subsequent flows, sharp and craggly |
A'a |
|
|
only happens underwater, solidifies quicker, way more common |
Pillow basalts |
|
|
Top bit of oceanic crust is made of ______ ______. |
pillow basalt |
|
|
look like long columns |
columnar jointing |
|
|
If ____ _____ form, lava can flow over greater distances |
lava tubes |
|
|
Lava tubes freeze ___ and _____ |
top and sides |
|
|
Rhyolite has the _______ SiO2 and is the ____ vicous lava. |
highest most |
|
|
Rhyolitic lava ______ flows. Rather, lava plugs the vent as a ____ ____. Sometimes, rhyolitic lava domes are _____ __. |
rarely lava dome blown up |
|

|
|
|
|
fragments blown out of a volcano; fiery bits |
pyroclastic debris |
|
|
Ash |
anything that is a tiny particle |
|
|
lapilli |
bigger than pea-sized |
|
|
blocks |
large fragments |
|
|
bombs |
streamlined (dollop of lava) |
|
|
Volcanoes often erupt large quantaties of _________. |
fragments |
|
|
Deposits include (4) |
pyroclastic debris preexisting rock landslide debris lahars |
|
|
Lava fragments that freeze in air |
pyroclastic debris |
|
|
blasted apart by eruption |
pre-existing rock |
|
|
blocks that have rolled downslope |
landslide debris |
|
|
transported as water rich slurries |
lahars |
|
|
___ gets knocked out by rain |
Ash |
|
|
Two points about Ash |
can get above where rainclouds are takes years to dissipate |
|
|
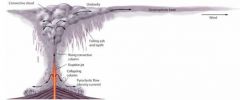
Pyroclastic flows go a lot ______ |
faster |
|
|
Three points about pyroclastic flows |
density/gravity current like an avalanche Volcanic hazard--> pyroclastic flow |
|
|
Lahar is a ___ pyroclastic flow |
wet |
|
|
Two points about Lahar |
more like concrete goes really really fast |
|
|
___ is a big part of what gets ejected from a volcano |
Gas |
|
|
Volcanic gas |
vapor and aerosols that exit a volcano |
|
|
Hazardous events at Yellowstone (from most to least frequent and least to most destructive) (4) |
small hydrothermal explosions strong earthquakes lava flows caldera-forming eruptions |
|
|
Several to many happen per century |
small hydrothermal eruptions |
|
|
one to several happen per century |
strong earthquakes |
|
|
about 100 happen per million years |
lava flows |
|
|
about one to two happen per million years |
caldera forming eruptions |
|
|
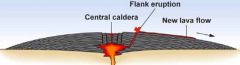
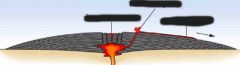
(shield volcano) |
|

|
Cindercone |
|
|
Stratovolcano |
|
|
anything that is coming out at the surface |
vent |
|
|
Volcanoes can ________ and make a _______ |
collapse caldera |
|
|
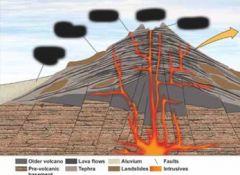
Four points about shield volcanoes |
less viscous has less silica (mafic) at a higher temperature broad and slightly dome-shaped |
|
|
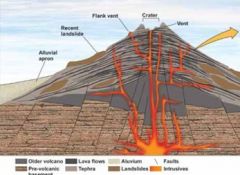
six points about stratovolcanoes |
large, cone-shaped steep slopes made of alternating layers of felsic lava, tephra, and debris often symmetric can be odd shapes have explosive eruptions |
|
|
Four things volcanoes do to signal eruption |
earthquakes deformation (deflating, inflating) heat flow gas chemistry (what isotropes?) |
|
|
Four ways to prepare for volcanos |
study eruption history decide which ones are the most hazardous set up monitoring systems plan before it happens |
|
|
awesome powerful and important |
sedimentary rocks |
|
|
Three points about sedimentary rocks |
not as abundant as igneous rocks oil and natural gas found in these soil for our gardens |
|
|
Which type of rock do we encounter most? |
sedimentary |
|
|
Sedimentary rocks do/don't make up very much of the Earth's crust |
don't |
|
|
Sedimentary rocks are important because... |
they do the most work as far as recording history. |
|
|
loose grains |
sediment |
|
|
loose grains cemented together |
sedimentary rock |
|
|
Four points about sediment |
comes from other rocks weathering and erosion Soil is not the same thing as sediment can be individual mineral grains or small chunks of rock |
|
|
Three types of weathering |
Physical Chemical differential |
|
|
Three points of physical weathering |
caused by trees anything physically happening abrasion (wind and glaciers) |
|
|
five points to chemical weathering |
rust used to be one material then it turned into another material oxidation done at an ion level dissolved; precipitated |
|
|
____ is not the same thing as sediment |
soil. |
|
|
What is on the top layer? middle layer? bottom layer? |
soil unconsolidated sediment bedrock |
|
|
As soon as the stuff is no longer connected to the main rock, it's ________. |
sediment |
|
|
As time goes on, sediment gets _______ and _______. |
smaller and rounder |
|
|
Biggest to smallest sediment sizes |
boulders cobbles pebbles sand silt clay |
|
|
differential weathering |
different layers weather different ways |
|
|
four classes of sedimentary rock |
biochemical clastic chemical organic |
|
|
biochemical |
cemented shells of organisms |
|
|
clastic |
loose rock fragments cemented together; most common |
|
|
chemical |
minerals that crystallize directly from water |
|
|
organic |
carbon-rich remains of once living organisms |
|
|
Two examples of biochemical sedimentary rocks |
limestone and chert |
|
|
Chert, which is made of ______, can be either ___________ (some plankton skeletons) or ________ (silica replacement of limestone; petrified wood), which is more common. |
silica biochemical chemical |
|
|
Three chemical sedimentary rocks (evaporites) |
salt gypsum travertine (chemically the same as limestone) |
|
|
Organic sedimentary rocks consist of everything except the _____. |
shell |
|
|
____ is its own subset |
Coal |
|
|
Three points about coal |
organic in layers didn't decompose |
|
|
Crystalline, but the crystals are so tiny that you cannot see them |
cryptocrystalline |
|
|
Three points about Petrified Wood |
agate got buried Water moved through it and replaced organic materials with silica |
|
|
Sedimentary rock processes |
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
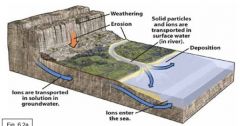
Clastic sedimentary rocks are created by _______ processes operating at Earth's surface |
several |
|
|
generation of detritus via rock disintegration |
weathering |
|
|
removal of grains from parent rock |
erosion |
|
|
dispersal of solid particles and ions by gravity, wind, water, and ice |
transportation |
|
|
setting out of the transporting fluid |
deposition |
|
|
the final stage of sedimentary rock formation is _____________ |
lithification |
|
|
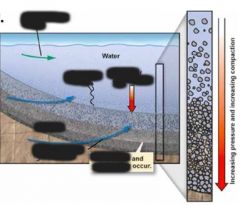
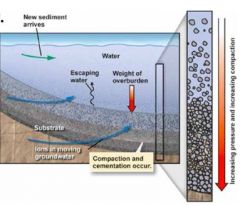
Lithification... |
transforms loose sediment into solid rocks |
|
|
Burial adds ________ to sediment, squeezing out ___ and _____, and __________ grains |
pressure water air compacting |
|
|
Minerals (often ______ or _______) precipitate from groundwater into ____ ______. This ______ glues sediment together. |
quartz calcite pore spaces cement |
|
|
Four ways to tell what type of sedimentary rocks we have |
grain sizes sorting well-rounded mostly silica or mostly carbonite |
|
|
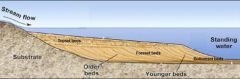
Sedimentary rocks come in ______/_______ beds |
layers/stratal |
|
|
______ often stands our clearly in sedimentary rock, appearing as _____ or _______ that can be traced _________ across an outcrop. |
Bedding bands stripes laterally |
|
|
____________ changes vary the stacking of rock features and create ______ ________ of rock that are ____________ over a region. |
Depositional unique packages recognizable |
|
|
Distinct rock units that are so unique that they can be recognized and mapped over large regions |
formations |
|
|
___________ are named for places where they are best exposed. |
Formations |
|
|
Geologic maps display the ____________ of __________. |
distribution of formations |
|
|
Three points about layers |
tells you how old stuff is shows chronologically what is going on stuff on top is newest, stuff on bottom is oldest |
|
|
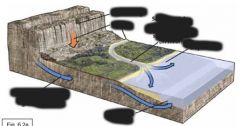
where sediment gets set down |
depositional environments |
|
|
terrestrial environments |
everything above sea level, including lakes and rivers |
|
|
marine environments |
everything below sea level |
|
|
The more ______ there is in the transport medium, the more _______ material it is able to carry. |
energy massive
|
|
|
Formula for Kinetic energy |
KE=1/2mv2 m=mass v=velocity |
|
|
two points about transport mediums |
will pick stuff up whenever you have enough energy to pick it up carry stuff for a ways until it runs out of energy |
|
|
Six points about glacial environments |
have to be accumulating more ice than you are melting pick up pretty much everything scoops everything along extra energy is in the bonds poorly sorted rocks conglomerates |
|
|
In a mountain stream environment, when glaciers melt and send more water, this is when ______ _________ will be moved. |
bigger sediments |
|
|
In a mountain stream environment, you have _____ grain sizes because the _____ grains are still going downstream |
large small |
|

|
Lake environments |
|
|
Sediment _____ ____ when it gets to the bottom. |
slows down |
|
|
When the river gets to the alluvial fan environment, it dumps ______ ____ __________ it has. |
pretty much everything |
|
|
Four points to alluvial fan environments |
not a place where there is a standard body of water sometimes floods anywhere water goes down a hill going to be sandstone |
|
|
Two points for alluvial fan sandstones |
minerals a little different than most sandstones close to source and did not have time to break down complex minerals |
|
|
Three points for sand dune environments |
air is the only transport material less energy carrying small stuff |
|
|
Cross beds are created by ______ and ____ ____ migration. |
rippes sand dune |
|
|
For sand dunes, Sand moves up the ______ ____ and piles up at the _____. Then it _____ ____ the _____ ____. The slip face moves ___________ and is buried by the next _________ of ____. The slip faces are preserved as _____ ____. |
gentle side crest slips down steep face downcurrent avalanche of sand cross beds |
|
|
weird features, characteristics, tells us that we were somewhere building dunes |
cross beds |
|
|
Four River (fluvial) environment points |
Fine sand, silt, clay are deposited on nearby flood plains fastest in the middle of the river cobbles would be in the middle (conglomerate) smaller grains would be at the edges (mudstones and sandstones) |
|
|
River environments ________ ________ of channelized ________ _________. Sand and gravel fill _______-__ ________ that often scour into previously deposited floodplain fines |
preserve evidence sediment transport concave-up channels |
|
|
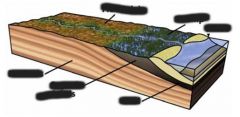
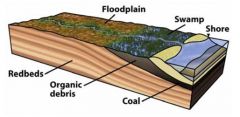
Lake (lacustrian) environment |
River slows down when it gets to the lake and loses almost everything |
|
|
|
|
|
Three points about coastal beach sands environment |
beach sands may preserve oscillation ripples mostly silica sand really normal sandstone |
|
|
Three points for shallow marine environments |
off of the coast, but not in the crazy deep ocean meters to tens of meters deep currents are indicated by the preservation of ripple marks and cross bedding
|
|
|
What kind of stuff is deposited at shallow marine environments? |
fine silts and muds turn into siltstones and mudstones shales carbonates |
|
|
Six points for deep marine environment |
no where near the coast at all no clastic stuff ton of water not that turbulent get plankton microfossils white cliffs of Dover |
|
|
Sea level rise creates a ___________ _______ of ______ |
predictable pattern of strata |
|
|
sea-level rises, coast shifts landward, |
transgression |
|
|
sea-level falls, coast shifts basinward |
regression |
|
|
What happens during transgression? |
depositional beds get finer |
|
|
What happens during regression? |
depositional beds get coarser |
|
|
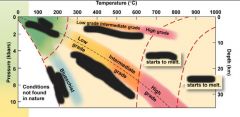
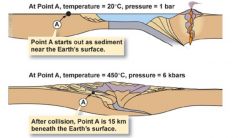
Metamorphism is a ____ _____ _____ of a _________ in response to ____________ of __________. |
solid state change protolith modification environment |
|
|
whatever the rock used to be |
protolith |
|
|
new minerals, new texture, but same chemical composition |
change |
|
|
chemical change, |
rearranging our atoms to be different |
|
|
|
|
|
Three rock cycles |
Limestone-->Marble sandstone-->quartzite shale-->slate-->phyllite-->schist-->gneiss |
|
|
Two point for solid state |
looking mostly at the crust relatively low pressure and temperature |
|
|
how changed it is |
Metamorphic grade |
|
|
slight change |
low grade |
|
|
high grade |
intense change |
|
|
Five points for modification of environment |
temperature pressure stress compression shear
|
|
|
If pressure is _____ on all sides, it'll just end up being a _______ ____. |
equal smaller rock |
|
|
(Compression/differential stress) Pressure is __________ on different sides, then the rock will appear _______ |
different squeezed |
|
|
(shear) pressure going two different ways, rock looks like a _____________. |
parallelogram |
|
|
two points for hydrothermal fluids |
this is not what is going on most of the time weird stuff happens |
|
|
READ ROCK CYCLES IN NOTEBOOK |
Do it. |
|
|
If it is purely __________ with no trace elements, skip directly to pure marble. |
Carbonates |
|
|
Six changes of a protolith |
recrystallization phase change neocrystallization pressure solution plastic deformation foliation |
|
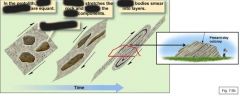
|
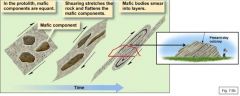
Compositional banding |
|
|
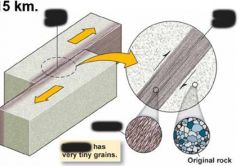
recrystallization |
tiny grains--> large new grains |
|
|
New minerals have the same chemical formula but different chemical structure |
phase change |
|
|
rock cycle for phase change |
lusite-->kyamite-->sillimanite |
|
|
Two points for Neocrystallization |
protolith-->metamorphic rock clay and quartz-->quartz, granet and mica |
|
|
shape changin |
pressure solution |
|
|
Two for pressure solution |
only happens in a compression environment spherical grains-->elliptical grains |
|
|
one point for plastic deformation |
Spherical grains-->elliptical grains |
|
|
Difference between plastic deformation and pressure solution |
In plastic deformation, the difference is that they are actually squashed. Growth rings are not cut out. |
|
|
Three points for foliation |
pages in a book folio means leaves folded |
|
|
___________ and _____ combine with elevated temperature and pressure to cause minerals and rocks to change shape _______ ________. |
Compression shear without breaking |
|
|
________ ________ are changed as minerals ______ or ________ and _____________ in preffered orientations. |
internal textures rotate dissolve recrystallize |
|
|
_____________ _______ can develop by extensive high-temperature shearing. |
Compositional banding |
|
|
Just look at it. |
|
|
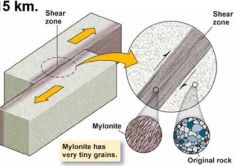
|
|
|
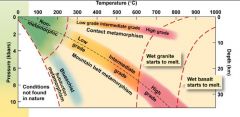
The types of metamorphism (3) |
continental collision (most common) orogeny (mountain building) regional metamorphism |
|
|
If ___________ only changes, then it's _______ metamorphism. |
temperature contact |
|
|
If some of the rock melts, metamorphic rocks can have "burn scars" of ________ ____. |
igneous rock |
|
|
____ _____ is getting buried at subducting oceanic plates. |
Cold Stuff |
|
|
Blueschists forms only at __________ margins with a ___________ _____ plate. |
Convergent subducting oceanic |
|
|
___________ _________ get scraped up |
accretionary prisms |
|
|
________ form only in shear zones (fault zones) |
Myolites |
|
|
occurs in unusual settings |
shock metamorphism |
|
|
Five points for shock metamorphism |
only in impact craters Rock turns to gas Eventually unvaporized Forms textiles sometimes Crazy extreme conditions |
|
|
Contact metamorphism is _________ than igneous rocks because it _______ ____. |
different doesn't melt |
|
|
Earth shaking is caused by a _____ _______ of ______, built up by _______ forces. |
rapid release energy tectonic |
|
|
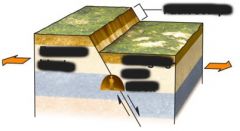
A fault is a place where ___ ______ meet |
two plates |
|
|
|
|
|
Line where two plates meet |
fault trace |
|
|
map description of where an earthquake starts |
epicenter |
|
|
3d idea of where an earthquake starts |
hypocenter |
|
|
amount that a place moves |
displacement |
|
|
permanent movement that persists |
slip, offset |
|
|
A fault is a |
planar surface |
|
|
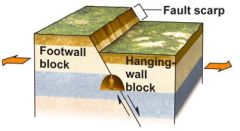
In a normal fault, the _________ wall moves ____ relative to the ________. It most often results from _________ (pull apart or stretching). |
hanging footwall extension |
|
|
In a normal fault, faulting causes rocks of different ages to become __________. |
juxtaposed |
|
|
In a reverse fault, the hanging wall moves __ relative to the footwall. It usually results from ___________ (squeezing or shortening) |
up compression |
|
|
The slope of a reverse fault is _____. |
steep |
|
|
A thrust fault is a special kind of _______ fault that has a _____ angle slope. It's a common fault type in _____________ ________ _____. |
reverse lower compressional mountain belt |
|
|
In a strike slip fault, one block ______ _________ past the other block. There is __ _________ ______ across the fault. |
slides laterally no vertical motion
|
|
|
Three points for strike-slip faults |
tend to be vertical no hanging wall or footwall there is no motion up or down |
|
|
Displacement |
is sometimes evident by offset or fences, roads, streams, etc. |
|
|
what am I going to look for? can be any type of rock |
marker bed. |
|
|
Earthquakes occur as the result of _____ ______. Earthquake energy is created when rocks _____ to form a ____ _____ or when a ___________ _____ is reactivated. |
fault motion break new fault preexisting fault |
|
|
Once faults are formed, they are always ____ _______ __________. |
weak crustal structures |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
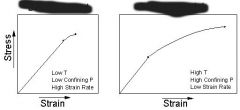
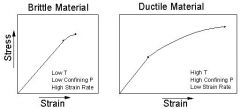
breaks; shallow; earthquakes |
brittle |
|
|
the material recovers its original shape after the stress is removed |
elastic behavior |
|
|
doesn't break, but is permanently changed (deep) |
ductile |
|
|
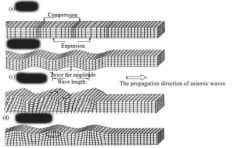
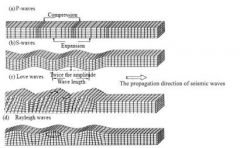
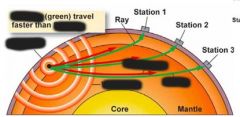
Body waves, travel through the middle of the Earth |
p-wave (primary) |
|
|
four points for p-waves |
like a slinky compressional or longitudinal wave fastest moving getting squished and stretched |
|
|
four points for s-waves |
second-fastest still going through the middle of the Earth shear happens in both directions |
|
|
Love wave |
most dangerous for buildings |
|
|
Rayleigh wave |
along the surface of the Earth |

