![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

What is EMPLOYMENT? |
it is the term used to describe paid work.
|
|
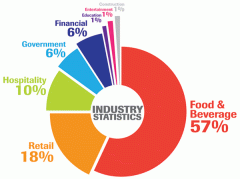
What are the FOUR types of work industries?
|
1. Primary
2. Secondary Industries 3. Tertiary Industries 4. Quaternary Industries |
|
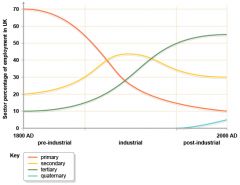
What is the EMPLOYMENT STRUCTURE? |
It is the % of people working in each of these 4 types of industries.
|
|

What is the PRIMARY SECTOR activities?
|
These involve the extraction of raw materials to be supplied to other industries.
|
|

What is the SECONDARY SECTOR activities?
|
These are where raw materials are assembled or manufactured to produce finished goods.
|
|

What is the TERTIARY SECTOR activities?
|
These are jobs which involve providing goods and services for the public.
|
|

What is the QUATERNARY SECTOR activities?
|
These include people who provide specialist information and expertise to all the above sectors.
|
|

What is the FORMAL SECTOR? |
These jobs are often controlled by the government or companies.
|
|

What is the INFORMAL SECTOR?
|
These jobs are ones where you don't pay taxes and often people find work for themselves.
|
|
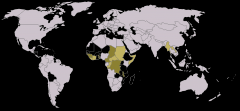
What is a LIC?
|
LOW-INCOME COUNTRIES
Occur largely in central Africa and in South and South East Asia |
|
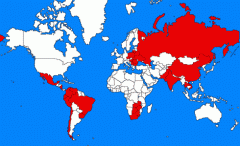
What is a MIC?
|
LOWER and UPPER MIDDLE-INCOME COUNTRIES
These two groups are most common in south America, North and South Africa, parts of the middle East, Eastern Europe and Asia. |
|
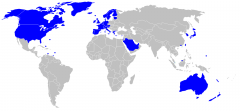
What is a HIC?
|
HIGH-INCOME COUNTRIES
Found mainly in North America, Western Europe and Australasia. |
|

What is PRIMARY ENERGY? |
Fuels that provide energy without undergoing any conversion process eg. coal, oil, wood.
|
|

What is SECONDARY ENERGY
|
eg. petrol, diesel, electricity which are made by processing (changing) primary fuels.
|
|

What is NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY? |
Non-renewable energy sources are finite. This means they cannot be replaced once they have been exhausted.
|
|
What are FOSSIL FUELS |
They have been formed from the fossilized remains of prehistoric animals and plants.
|
|
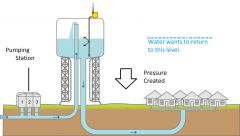
What is ABSTRACTION? |
is the REMOVAL of water from a RIVER, LAKE or GROUNDWATER for human use.
|
|
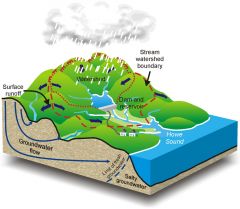
What is the WATERSHED?
|
is the DIVIDING LINE between one DRAINAGE BASIN and another.
|
|

What is an INTERLOCKING SPUR?
|
is a series of ridges projecting out on alternate sides of a valley and around which river winds its course.
|
|

What is meant by the ENERGY GAP?
|
it is the difference between a countries RISING DEMAND for ENERGY and its ability to PRODUCE the energy it NEEDS.
|
|
![What are the key words for a ZONE OF TRANSITION? (3)
[Burgess model of land use]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/56/79/98/5567998_m.png)
What are the key words for a ZONE OF TRANSITION? (3)
[Burgess model of land use] |
CENTRAL BUSINESS DISTRICT (CBD)
INNER CITY - zone of transition SUBURBS |
|

What is a MEGA-CITY?
|
a city with a population of over ten million people.
most MEGACITIES are found in the continent of NORTH and SOUTH AMERICA, having cities like SAO PAULO + NEW YORK |
|

What is URBANISATON?
|
it's the growth of towns and cities --> increasing proportion of countries population living in a URBAN AREA.
|
|
![Why does SÃO PAULO have RAPID URBANISATION?
[PUSH (5) & PULL (6) FACTORS]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/56/80/10/5568010_m.jpg)
Why does SÃO PAULO have RAPID URBANISATION?
[PUSH (5) & PULL (6) FACTORS] |
PUSH FACTORS:
1. not enough JOBS 2. FEW opportunities 3. NATURAL disasters - drought etc. 4. shortage of FOOD 5. UNHAPPY life PULL FACTORS: 1. BETTER way of life 2. HIGHER chances of JOBS - 40% of BRAZIL'S factories in SÃO PAULO 3. IMPROVED living conditions 4. EDUCATION 5. BETTER housing 6. medical care |
|
What types of SAMPLING STRATEGIES are there? (3)
|
1. SYSTEMATIC SAMPLING - this is at EQUAL intervals.
2. RANDOM SAMPLING 3. PRASMATIC - sensible and practical as you can make small changes. |
|

Data Presentation Techniques: |
1. This clearly shows you the AGE.
2. This shows you LAND USE. 3. This shows you the HEIGHT. 4. This shows you ENVIRONMENTAL QUALITY. |
|

What is a BROWNFIELD SITE? |
land that has been previously used --> unused so ready to be used.
|
|

What is a GREENFIELD SITE?
|
land that has not been used for URBAN DEVELOPMENT.
|
|
|
What is PHYSICAL WEATHERING?
|
This breaks rock down into smaller pieces. it is done by changes in temperature and by rainfall freezing and thawing in rock cracks.
|
|
|
What is CHEMICAL WEATHERING?
|
This causes rock to decay and disintegrate. It is largely done by slightly acidic rainfall sleeping into porous rock.
|
|
|
What is BIOLOGICAL WEATHERING?
|
The rocks of plans, especially tress, growing in cracks in the rocks gradually split the rock apart.
|
|
|
What is SLUMPING?
|
is when the bottom of a valley side slope is cut away by the river flowing at its base --> making the slope UNSTABLE
|
|
|
What is SOIL CREEP?
|
weather material moves slowly down slope under the influence of gravity. It collects at the bottom of the valley side and is eroded by the river
|
|
|
What is HYDRAULIC ACTION?
|
Water hits the river bed and banks with such force that material is dislodged and carried away --> good when high amounts of discharge
|
|
|
What is ABRASION?
|
The material being carried by a river is rubbed against the sides and floor of the channel. This “sandpaper” action widens and deepens the channel.
|
|
|
What is CORROSION?
|
Minerals in the rocks forming the sides of the river channel are dissolved by the water flowing past them.
|
|
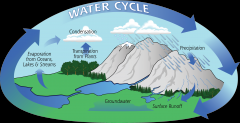
What is the HYDROLOGICAL CYCLE? + KEY WORDS (11) |
it recycles fresh water between the land, air and sea. |
|

What is URBAN RENEWAL?
|
it is the attempt to regenerate the inner city through industrial, housing and community schemes.
|
|

What was the LONDON DOCKLANDS like 100 years ago? (5) |
1. Steam ships
2. Importing and exporting 3. Many boats 4. A lot of activity 5. Ships from all over the world |
|

Why did the DOCKLANDS DECLINE? (3)
|
1. As boats became large the Thames become shallower because of the build up of silt. |
|

While the DOCKLANDS DECLINED what happened? |
- 1970-1980
30,000 jobs lost! - 1981 50% of Docklands DERELICT (over 1000 hectares) 21% UNEMPLOYMENT; male unemployment was 24% (twice the national average). One third of HOUSING unsatisfactory for human habitation Inadequate INFRASTRUCTURE of roads, rail, telephone and cable lines; the Docklands was kept deliberately inaccessible to protect the goods that were being stored. |
|

What is the LONDON DOCKLANDS an example of? |
urban regeneration/urban renewal
|
|
|
What is SUBURBANISATION? |
the outward spread of the urban area, often at towers densities compared with the older parts of a town or city |
|

What is ECOTOURISM? |
a type of tourism that aims to conserve fragile ecosystems and ensure that its benefits (jobs, income) stay within the local area. |
|
|
What is a STORM HYDROGRAPH? |
a graph showing changes to the discharge of a river after a storm/rainfall. |
|
|
What is LAG TIME? |
is the time between a peak rainfall and peak discharge i.e. it take time for rain water to reach the river. |
|
|
What is a HAZARD? |
Is defined as an event that threatens or actually causes damage and destruction to people, their property and settlement. |
|
|
What is a NATURAL HAZARD? |
is one produced by environmental processes and involves events such as storms, floods, earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. |
|
|
What is the TRANSECT |
is where a study is made along a certain path
e.g. Chichester, UK |
|
|
What is NATURAL CHANGE? |
depends on the balance of birth rates to death rates
more births than deaths = population increase
more deaths than births = population decrease |
|
|
what is FORCED MIGRATION? |
the coerced (foced) movement of a person or people away from their home or home region |
|
|
What is a TNC? |
Transnational Corporation - a company that has operations in more than one country (e.g. nike) |

