![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The Costal Zone |
|
|
|
Coast |
Where land meets sea |
|
|
Swash |
Forward movement up a beach |
|
|
Backwash |
Backward movement down a beach |
|
|
Fetch |
The stretch of open water over which the wind blows. The longer the fetch the more powerful the wave |
|
|
Weathering |
The disintegration of rock in their original place at or close to the surface |
|
|
Physical Weathering |
The disintegration of rock without any chemical changes taking place |
|
|
Chemical weathering |
Chemical changes occur when weathering takes place. |
|
|
Biological weathering |
Plants and roots grow and expand cracks. |
|
|
Sub-arial Process |
Includes weathering and mass movement |
|
|
Hydraulic power |
The weight and impact of water and air trapped in cracks, increasing pressure and cause the rock to break off |
|
|
Abrasion |
Sand and pebbles are thrown against rock face, causing pieces to break off and cause undercutting |
|
|
Attrition |
Particles carried by waves are reduced in size as they collide |
|
|
Solution |
Chemical action of rocks by sea water, rocks dissolve and carried by solution |
|
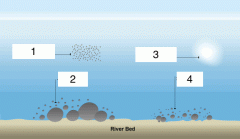
|
1- Suspension 2-Traction 3-Solution 4- Saltation |
|
|
Hows does LSD occur |
Material move up the beach at an angle in the swash controlled by prevailing wind, the material carried down the beach in the backwash |
|
|
Where do wave-cut notches occur |
Base of a cliff |
|
|
What is a Bar |
A bar is a spit which has grown right across a bay |
|
|
Mass movement |
Downhill movement of material due to gravity |
|
|
Constructive waves |
Strong swash, weak backwash |
|
|
Destructive waves |
Weak swash, strong backwash |
|
|
Slumping |
Downhill movement along a curved surface |
|
|
Spit |
Finger of new land made of sand jutting into sea. |
|
|
Salt marsh |
Low-lying costal marshes |
|
|
Wave-cut notch |
A small cut in a cliff |
|
|
Wave-cut platform |
A wide gently sloping rocky surface at the foot of a cliff |
|
|
Why are the Holderness cliffs collapsing |
Made from soft rock, (boulder clay) Beach is very narrow and thin ( wave-cut notch) Destructive waves Boulder clay is impermeable |
|
|
Boulder clay |
Soft clay left behind after glaciers |
|
|
Impermeable |
Doesn't allow water to soak through |
|
|
Managing retreat
|
controlled flooding of low lying costal areas |
|
|
Revetment |
Rock armour |
|
|
Some causes of rising sea levels |
Global warming Thermal expansion enhanced green house effect |
|
|
Problems caused by rising sea levels |
Costal flooding islands already disappeared storm surges salt water pools |
|
|
Abiotic |
Non-living organisms |
|
|
Biotic |
Living organisms |
|
|
Conditions needed for the development of sand dunes |
Regular supply of sediments Wide sandy beach Onshore winds Vegetation |
|
|
whats a psammosere? |
sand dune succsession |
|

|
1- Embryo dune 2- Fore dune 3- Yellow dune 4- Grey dune 5- Dune slack 6- Mature dune |
|
|
Some management strategies of Studland Heath |
close some areas for study only educating people about how dunes are fragile no BBQ's no noisy leisure activities |
|
|
Invader species |
Species which invade the pioneer species |
|
|
Pioneer species |
The first plant species to colonies an area |

