![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
DNA stands for...
|
Deoxyribonucleic acid
|
|
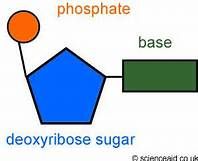
~Which stay the same and which change? |
Base changes and the phosphate and the deoxyribose sugar stay the same
|
|
|
Two types of nitrogenous bases are...
|
Pyrimidines- Single ringed & shorter Purines- Double ringed & longer |
|
|
Every nucleotide pair is composed of a...
|
Purine facing a Pyrimidine |
|
|
Base pairing occurs between... (The letters that go together and there H-bond) |
A & T (2 H-bonds) G & C (3 H-bonds) |
|
|
Extremophile
|
Higher G,C meaning its H-bonds are higher (3) which allows it to have more energy to break it...hydrogen higher breakage/strong
|
|
|
Apoptosis
|
Cellular death resulted from division problems
|
|
|
Mitosis (PMAT)
|
prophase- (DNA coils, chromatin turns into chromosomes, NM dissolves) metaphase- Line up along the middle), anaphase- spindle fiber shorten and pull chromosomes to the poles), telophase- Nm reforms , chromosomes turn back to chromatin
|
|
|
interphase
|
Resting point, G1, synthesis, G2 |
|
|
G1
|
Growth of contents |
|
|
Synthesis |
DNA duplicates
|
|
|
G2
|
size increases
|
|
|
|
|

