![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What did Gregor Mendel do? |
Experimented with peas to observe inheritance |
|
|
What is fertilization? |
When a sperm and egg come together to form an offspring |
|
|
What are true-breeding plants? |
They only produce offspring with the same traits (Homozygous Alleles) |
|
|
What did Mendel notice when he crossed true-breeding plants? |
-The first generation experienced the same traits as the parents -The second generation had all kinds of differences |
|
|
What were the pea plants with different traits called? |
Hybrids |
|
|
What is a genotype? |
The genes involving the influence of traits (can't see) |
|
|
What is a phenotype? |
The trait expressed as an influence of the genes involved, determined by genotype (can see) |
|
|
What is an allele? |
The segment of the gene in a chromosome that is responsible for influencing a trait. |
|
|
What is Homozygous? |
Containing the same alleles. Ex. AA, BB |
|
|
What is Heterozygous? |
Mixture of different alleles. Ex. Ab, Bb |
|
|
What is a gamete? |
Sex cell |
|
|
What is a somatic cell? |
Body cell |
|
|
What are the two laws that influence inheritance? |
Law of Segregation Law of Independent Assortment |
|
|
What is the Law of Segregation? |
During meiosis, alleles responsible for the same trait will separate |
|
|
What is the Law of Independent Assortment? |
During meiosis, homologous chromosomes assort themselves however they want on the metaphase plate |
|
|
What is Dominant/Recessive? |
In a heterozygous mix, ONLY the dominant phenotype will be observed Ex. Ab (A is dominant over b) |
|
|
What is Incomplete Dominance? |
-One allele is Partially dominant -In a heterozygous mix, both traits are BLENDED together to form a new phenotype |
|
|
What is Codominance? |
-Two alleles are equally dominant -In a heterozygous mix, BOTH phenotypes are expressed at the same time Ex. Blood Type (AB) |
|
|
What are Multiple Alleles? |
Different possible versions of a trait depending on what alleles are inherited Ex. Eye Color |
|
|
What are Polygenic Traits? |
-Show a spectrum of traits rather than 2 distinct phenotypes. -Expressed in a gradient Ex. Height & Skin Color |
|
|
Whats the difference between a monohybrid cross and a dihybrid cross? |
Monohybrid - one trait is examined Dihybrid - two traits are examined |
|
|
Who accidently discovered the influence of genes? |
Frederick Griffith |
|
|
What did Griffith do? |
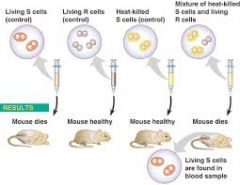
|
|
|
What did Griffiths experiment prove? |
Genetic material can be passed from bacteria cell to bacteria cell |
|
|
What did Oswald Avery do? |
Made an extract to digest certain molecules: Nucleic Acids, Lipds, Carbohydrates, Proteins |
|
|
What was found due to Avery's experiment? |
DNA is the material responsible for controlling genetics |
|
|
What did Hershey & Chase do? |
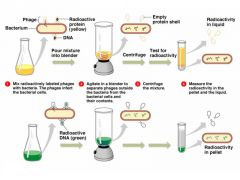
|
|
|
What were the two radioactive markers used in the Hershey-Chase experiment? |
P-32 (DNA) S-35 (Proteins) |
|
|
What was the purpose of the centrifuge in the Hershey-Chase experiment? |
To separate the heavier stuff from the lighter stuff |
|
|
What did the Hershey-Chase experiment prove? |
DNA is genetic material |
|
|
What did Chargaff notice? |
-The base concentration numbers varied from organism to organism -The relationship between Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, and Guanine seemed to be connected |
|
|
What did Rosalind Franklin do? |
Used X-Ray diffraction to take pics of DNA |
|
|
What did Watson & Crick do? |
They tried to create a 3D model of DNA |
|
|
How did Watson and Crick finally make the model? |
Watson was automatically able to read Franklin's X-Rays |
|
|
What is the basic structure of DNA? |
2 anti-parallel strands connected by nucleotide bases |
|
|
What is DNA's nickname? |
Double Helix |
|
|
What is a strand of DNA composed of? |
-Nitrogenous base -Deoxyribose sugar -Phosphate group |
|
|
What are the base pairs in DNA? |
Adenine + Thymine Cytosine + Guanine |
|
|
How are DNA backbones arranged? |
3' to 5' |
|
|
How many hydrogen bonds are between A&T, and C&G? |
A&T - 1 C&G - 2 |
|
|
What nucleotide bases are Purines? |
Adenine and Guanine |
|
|
What nucleotide bases are Pyridimines? |
Thymine and Cytosine |
|
|
Why do purines HAVE TO pair with a pyridimine? |
So the spaces between the strands are consistent. |
|
|
In DNA replication which direction will the new strand grow in? |
5' to 3' |
|
|
What are the main enzymes used in DNA replication? |
-Helicases -DNA polymerases |
|
|
What do helicases do? |
Spilt DNA |
|
|
What does DNA polymerase do? |
Connects the nucleotide bases from the parent strand to the new strand. |
|
|
What is a Karyotype? |
A visual representation of the number and appearance of chromosomes in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell |
|
|
What is the 23rd pair of chromosomes in a human karyotype? |
The sex chromosomes |
|
|
What does aneuploidy mean? |
An odd amount of chromosomes in a cell |
|
|
What is trisomy? |
Having 3 of the same chromosome |
|
|
What is a monoploidy? |
Half the normal number of chromosomes (Turner Syndrome) |
|
|
What causes monoploidy? |
Deletion of a chromosome |
|
|
Who invented the Central Dogma of Genetics? |
Francis Crick in 1956 |
|
|
What do DNA and RNA code for? |
DNA codes for RNA which codes for Proteins |
|
|
What are the two processes that make Proteins? |
Transcription & Translation |
|
|
What are the different types of RNA? |
mRNA tRNA rRNA |
|
|
What does mRNA do? |
Messanger RNA transfers info from the nucleus to the ribosome |
|
|
What does tRNA do? |
Brings amino acids to ribosome |
|
|
What is Transcription? |
Synthesis of DNA to RNA |
|
|
How many strands of DNA are made into RNA? |
1 strand |
|
|
How many genes does DNA code for? |
2, one for each strand |
|
|
Describe Transcription |
-DNA strands separate -RNA polymerase matches the exposed DNA base with the RNA counterpart on mRNA |
|
|
Where does the new RNA strand after transcription go? |
From the nucleus to the ribosome |
|
|
Describe Translation |
-The mRNA enters the ribosome and the codons are read in order to see which amino acids are needed -The strand is translated until a stop codon is reached -tRNA brings the appropriate amino acid to the mRNA strand |
|
|
What is the start codon in translation? |
AUG |
|
|
What makes a protein? |
Codons bonded by peptide bonds |
|
|
What happens when errors occur? |
MUTATIONS |
|
|
What are the 4 different types of point mutations? |
Silence, Missense, Nonsense, Frameshift |
|
|
What are the different types of single nucleotide base mutations? |
Substitution, Addition, Deletion |
|
|
What is the result of a silent mutations? |
-There's no phenotypic change -The amino acid stays the same |
|
|
What is the result of a missense mutation? |
One amino acid changes to another |
|
|
What is the result of a nonsense mutation? |
A stop codon is prematurely created |
|
|
What is a transversion mutation? |
Purine changes to Pyridimine and vice versa |
|
|
What is the result of an addition or deletion? |
Frameshift mutation |
|
|
What is the result of a frameshift mutation? |
The reading frame changes |
|
|
What is a Reading Frame? |
Splits DNA/RNA strands into triplets |
|
|
What causes mutations? |
Chemicals, Radiation, Something goes wrong during DNA replication, Nondisjunction (too many or too few chromosomes in gametes) |
|
|
What Trisomy is Down Syndrome? And what are its symptoms? |
Trisomy 21 Distinct facial appearance, developmental delays |
|
|
What is Klinefelter's Syndrome? And what are the symptoms? |
XXY Chromosome Low testosterone, reduced muscle mass, facial hair, and body hair. |
|
|
What Trisomy is Edward's Syndrome? |
Trisomy 18 Low birth weight, small abnormally shaped head |
|
|
What Trisomy is Patau Syndrome? |
Trisomy 13 Intestinal organs out of body, severe intellectual disabilities |

