![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Structure of DNA and RNA |
Double helix and single strand |
|
|
Replication and when |
Cells divide to produce new cells ; the DNA has to be copied. Happens during interphase before meiosis. |
|
|
Protein synthesis: transcription |
Occurs in the nucleus, the process of how RNA is made from DNA |
|
|
Protein synthesis: translation |
Occurs in the cytoplasm, specifically on the ribosomes. mRNA exits the nucleus and goes to the ribosome with the "message" for DNA. It is then translated into an amino acid sequence. |
|
|
Mitosis |
- For growth - Somatic cells (body cells) - Makes 2 identical diploid cells (2N) each with two complete sets of chromosomes - Diploid -> diploid - In human: 46 chromosomes |
|
|
Meiosis |
- For reproduction - Gametes (reproductive cells -> sperm and egg) - Makes 4 unique haploid cells (N) each with one set of chromosomes - Diploid -> haploid - In human: 23 chromosomes |
|
|
When does Genetic mutation happen |
Nondisjunction during anaphase 1. An extra chromosome goes to one side of the cell. |
|
|
Chromosomal mutation |
A change involving part of or the whole chromosome. - Deletion: a piece of the chromosome breaks off - Duplication: part of the chromosome is doubled - Inversion: part of the chromosome is rotated - Insertion: a piece of the chromosome breaks out and is transferred to a non-homologus chromosome - Nondisjunction: addition or loss of a whole chromosome |
|
|
Mendelian genetics |
Inherited traits are transmitted by genes which occur in alternating alleles ; each inherited trait is expressed by two genes |
|
|
What does mitosis look like? |

|
|
|
What does meiosis look like? |
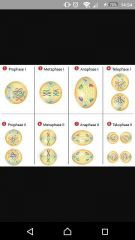
|
|
|
Genetic testing |
- Preimplantation: a small number of cells are taken from embryos and tested for certain generic changes - Prenatal: during pregnancy - Newborn screening: used just after birth to identify genetic disorders that can be treated early in life - Predictive and presymtomatic: used to detect gene mutations associated with disorders that appear after birth - Diagnostic: used to identify or rule out a specific generic or chromosomal condition |

