![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A line of mouse cells N15 is switched to a solution of N14. Cells in G1, before being switched to N14 medium look like... |
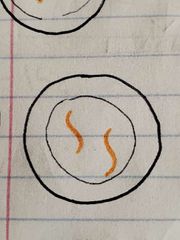
|
|
|
A line of mouse cells N15 is switched to a solution of N14. Cells in G2, after being switched to N14 medium look like... |
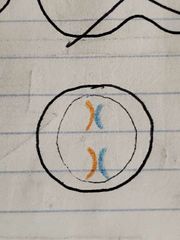
|
|
|
A line of mouse cells N15 is switched to a solution of N14. Cells in Anaphase of mitosis, after being switched to N14 medium look like... |
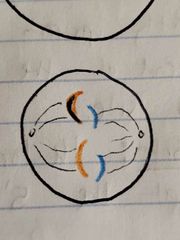
|
|
|
A line of mouse cells N15 is switched to solution of N14. Cells in Metaphase I of meiosis, after switching to N14 medium look like... |
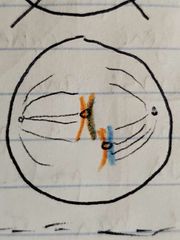
|
|
|
A line of mouse cells N15 is switched to suction of N14. Cells in Anaphase II of Meiosis, after switching to N14 medium look like... |
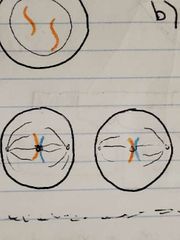
|
|
|
|
|
|
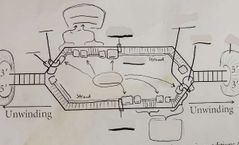
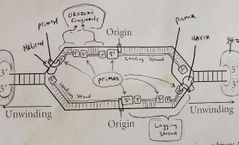
What will happen to replication if DNA Ligase was restricted? |
Newly synthesized segments would not be stuck together but replication would occur. |
|
|
What will happen to replication if DNA Polymerase I was restricted? |
The initial short chain of nucleotides in the newly synthesized strand would not be created but replication would still occur. |
|
|
What will happen to replication if DNA Polymerase III was restricted? |
DNA replication would not occur. |
|
|
What will happen to replication if Primase was restricted? |
DNA replication would not occur. |
|
|
What will happen to replication if Initiator Protein was restricted? |
DNA replication would not occur. |
|

|
Two bands |
|

|
Antiparallel nucleotide stands. |
|

|
Initiator protein, helicase, single-strand-binding protein, DNA gyrase. |
|

|
At the beginning of every Okazaki fragment. |
|

|
DNA Polymerase I |
|

|
The size of eukaryotic genomes, the linear structure of eukaryotic chromosomes, and the association of DNA with histone proteins. |
|

|
Chromosomes would shorten each generation. |
|

|
Recombination is important for generating genetic variation. |

