![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are three 3 basic stages of transcription? |
1) Initiation 2) Elongation 3) Termination |
|
|
Def: Initiation |
When the transcription apparatus assembles on the promoter and begins the synthesis of RNA. |
|
|
Def: Elongation |
When the DNA is threaded through RNA polymerase, the polymerase unwinding the DNA and adding new nucleotides, one at a time, to the 3' end of the growing RNA stands. |
|
|
Def: Termination |
The recognition of the end of the transcription unit and separation of the RNA molecule from the DNA template. |
|

|

|
|
|
Chargaff Rule |
Percentages of adenine and thymine bases are almost equal in any sample of DNA. Purine : Pyrimidine 1:1 A=T and G=C A + G = C + T |
|
|
An RNA is composed of: A=23%, U=42%, C=21%, and G=14%. Is it double or single stranded? |
Single stranded, because A + G does not equal T + C. |
|
|
RNA: A=23%, U=42%, C=21%, and G=14%. What would be percentage of bases in DNA template stand? |
A=42%, T=23%, C=14%, and G=21%. |
|
|
The following is a single stranded DNA template:
ATTGCCAGATCATCCCAATAGAT
If DNA Polymerase reads from left to right, which end of the strand is 5' and which is 3'? |
3' ATTGCCAGATCATCCCAATAGAT 5' |
|
|
Give sequence and label polarity if RNA copied from this template:
ATTGCCAGATCATCCCAATAGAT |
5' UAACGGUCUAGUAGGGUUAUCUA 3' |
|
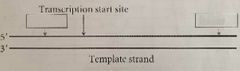
Label Promotor and Terminator |

|
|
|
Def: Promoter |
DNA sequences that define where transcription if a gene by RNA polymerase begins. |
|
|
Def: Transcription Start Site |
The location where transcription starts at the 5'-end of a gene sequence. |
|
|
Def: Exons |
Any part of a gene that will encode a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after have been removed by RNA splicing. |
|
|
Def: Introns |
A nucleotide sequence within a gene. They are a non coding intervening sequence of DNA within a gene that is transcribed into mRNA but is removed from the primary gene transcript and rapidly degraded during maturation of the RNA product. |
|
|
Def: 5' Untranslated Region (5' UTR) |
(a.k.a Leader Sequence/leader RNA) Is a region of an mRNA that is directly upstream from the initiation codon. This region is important for the regulation of translation of a transcript by differing mechanisms in viruses prokaryotes and eukaryotes. |
|
|
Def: 3' Untranslated Region (3' UTR) |
The section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that't immediately follows the translation termination codon. |
|
|
Def: AAUAA Consensus Sequence |
Found near the polyadenylation site of Eukaryotic mRNAs. This sequence is required for accurate and efficient cleavage and polyadenylation of pre-mRNAs in vivo. |
|
|
Def: Poly (A) Tail |
A long chain of adenine nucleotides that is added to a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule during RNA processing to increase the stability of the molecule immediately after a gene in a eukaryotic cell is transcribed, the new RNA molecule undergoes several modifications known as RNA processing. |
|
|
Def: 5' Cap |
A specially altered nucleotide on the 5' end of same primary transcripts such as precursor such as precursor messenger RNA. This process, known as 5' capping, is highly regulated and vital in the creation of stable and mature messenger RNA to undergo translation during protein synthesis. |
|

|
Transfer RNA (tRNA): attaches to an amino acid. |
|

|
The template strand is the DNA strand that is transcribed into an RNA molecule, whereas the nontemplate strand is not transcribed. |
|

|
The sigma factor recognizes the promoter and controls the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter. |
|

|
When DNA was hybridized to the mRNA transcribed from it, regions of DNA that did not correspond to RNA looped out. |
|

|
5' untranslated region |
|

|
It would be longer than normal. |

