![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Law of independent assortment |
Genes that segregate independently do not affect each others inheritance; they are sorted at random |
|
|
Law of segregation |
Chromosomes are separated during meiosis and the gamete has an equal chance of inheriting either allele for each trait |
|
|
Test crosses |
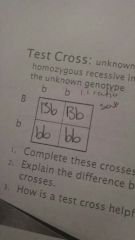
An unknown individual is crossed with a homozygous recessive individual to determine the unknown genotype |
|
|
Gene recombination |
New genes that result from crossing over and independent assortment |
|
|
Gene linkage |
Genes that are close to each other travel together |
|
|
Chromosome maps show? |
The order of genes on a chromosome |
|
|
Polyploidy |
-one or more extra sets of chromosomes -rarely happens in animals -normal for plants(makes them stronger) |
|
|
Gametes have ___ sets of chromosomes |
23(haploid) |
|
|
Zygotes have ___ sets of chromosomes |
46(diploid) |
|
|
Triploid |
-3 sets of chromosomes -lethal in humans |
|
|
Autosomal recessive traits don't... |
Appear on the sex chromosomes traits -ex:cystic fibrosis: caused by a defect in the gene for a membrane transport protein -Tay-sachs: absence of an enzyme that breaks down lipids in the brain -phenylketonuria: absence of gene that breaks down phenylalanine |
|
|
Huntingtons disease is a |
Dominant trait |
|
|
Incomplete dominance |
Neither trait is dominant so a third trait is made that is a blending of the two -ex:flower color |
|
|
Codominance |
-Both traits are dominant and a combination of both is shown -ex:sickle cell: some cells are normal while others are sickle shaped OR -neither trait is dominant |
|
|
Multiple alleles |
When there are more than two alleles for a given trait; each person will have two of those alleles -ex: blood type |
|
|
Sex linked trait |
Trait found in the genes the x chromosome has that the y doesn't -ex: colorblindness -ex:hemophilia |
|
|
Pedigree |
Chart of family history that shows how a trait is inherited over several generations; helps to predict genetic disorders -dominat pedigree has a colored in shape in every generation -receccive pedigree has one every other generation |
|
|
Polygenic inheritance |
Single trait controlled by many different genes -ex: skin color and height |
|
|
Difference between monohybrid and dihybrid |

|
|
|
Application of genetics |
Any practice that increases the frequency of a specific allele |
|
|
Selective breeding |
Breeding livestock, plants, or pets that display desired traits in order to increase the frequency of that trait |
|
|
Hybrid vigor/ hybridization |
Breeding things with different traits to produce offspring that have both traits; makes the offspring stronger |
|
|
Cloning |
Making an identical copy of a gene or an entire organism |
|
|
Gene therapy |
Inserting a normal gene into a person with an absent/abmormal gene; once inserted the normal gene begins to produce the correct protein/ enzyme which eliminates the disorder |
|
|
Stem cells |
Cells that have the potential to be specialized in structure or function -usually in embryos |
|
|
Recombinant dna |
Combined DNA from two organisms |
|
|
Transgenic orgsnisms |
Organisms that contain functional recombinant dna |
|
|
Steps for transgenic orgsnisms |

|
|
|
Genome |
Complete set of genes in an organisms dna |
|
|
Gene map |

Shows the location of the gene in the chromosome |
|
|
Gel electrophoresis |

|
|
|
Steps for gel electrophoresis |

|
|
|
Gel electrophoresis stuff |

-Since DNA is negatively charged its attracted to the positive end of the gel; the shortest DNA fragments move faster causing the DNA to be separated by length |

