![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
sexual reproduction |
requires a male gamete to fertilise a female gamete |
|
|
asexual reproduction |
when an organism reproduces through mitosis creating a clone |
|
|
gamete |
sex cell |
|
|
4 stages of mitosis |
Prophase - nucleus starts to break down Metaphase- chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell Anaphase- the chromosomes line up at opposite ends and are copied Telophase- two daughter cells are copied |
|
|
two other stages of mitosis |
Cytokinesis- cells split as the membrane surrounds each set Interphase- cloning of DNA and cell growth |
|
|
Meiosis |
cell division that results with four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell |
|
|
haploid |
one set of chromisomes |
|
|
what is the process of meiosis |

. |
|
|
how many divisions are there in a - mitosis b - meiosis |
a - 1 b - 2 |
|
|
how many cells are produced in a - mitosis b - meiosis |
a - 2 b - 4 |
|
|
what is dna |
strands of polymers made up of repeating nucleotides |
|
|
what are the 4 bases that join to each sugar |
A (adenine) T (thymine) C (cytosine) G (guanine) |
|
|
structure of a dna strand |
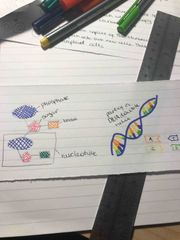
• double helix • sugar phosphate backbone • hydrogen bonds that hold bases together |
|
|
what are chromosomes |
long cooled up molecules of dna |
|
|
where are chromosomes found |
in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells |
|
|
What is protein synthesis |
Process by which amino acids are arranged into proteins |
|
|
Are the stages of protein synthesis |
1) DNA gets broken up by the rna 2) only one strand gets copied 3) the copy leaves the nucleus then travels through the cytoplasm to a ribosome 4) it then attaches to the ribosome (where protein synthesis happens) 5) tRNA comes in and pairs with the dna strand 6) the amino acids come together to make polypeptide which now becomes long enough to form whatever it needs to |
|
|
what did edwin chargraff discover |
that the amounts of A,T and C, G were the same |
|
|
what did edwin chargraff discover |
that the amounts of A,T and C, G were the same |
|
|
what did rosalind franklin discover |
that it had the double helix shape |
|
|
what did jerry donohue discover |
that hydrogen allowed the base pairs to be held together |
|
|
what did james watson and francis crick do |
won a nobel prize for compiling all of the other dna scientists work together |
|
|
what are the steps taken to extract DNA from fruit cells |
1-mash the fruit 2-add a salty detergent solution 3-heat at 60°C for 15 minutes 4-filter the mixture 5-add protease to the filtrate 6-slowly pour ice-cold ethanol into the solution 7-wins the precipitated DNA around a glass rod |
|
|
what are advantages and disadvantages of asexual reproduction |
+ there would be no adaptation change + there would be no homeric variation - they would be able to reproduce quicker - no mate is required |
|
|
why are scientists interested in regions of DNA besides genes |
-non coding regions are important in regulating protein expression -RNA polymerase enzymes able to bind to non coding regions |
|
|
describe the relationship between the bases in DNA sequence and the structure of a protein molecule |
it determines amino acids used the order leads to structure of protein |
|
|
information in a DNA strand can be transcribed to make a strand of mRNA. Describe how this mRNA strand is then used to make proteins |
• the TRNA carries amino acids • bases on the TRNA attaches to mRNA with an exact copy • mRNA is used to make proteins through translation • It leaves the nucleus to find a ribosome |
|
|
in a strand of mRNA, what does A bond to |
U (NOT T) |

