![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
99 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
cell
|
basic unit of life.
the average human body contains over 75 trillion cells. plants cell have cell walls & chloroplasts - animal cells do NOT |
|
|
prokaryotic
|
NO internal membrane to contain structures
e.g. bacteria |
|
|
eukaryotic
|
contains a membrane-bound structure
e.g. protists, fungi, plants & animals |
|
|
outer membrane/cell membrane/plasma membrane
|
dictator of cell. determines what what goes into or out of the cell
|
|
|
organelles
|
specialized parts that move around the cell and perform functions that are necessary for life.
e.g. nucleus, vacuoles, & mitochondria |
|
|
cytoplasm
|
gelatin-like material that fills the cell.
|
|
|
nucleus
|
membrane that contains the cell's hereditary information & controls the cell's growth & reproduction. the nucleus contains chromosomes
|
|
|
chromosomes
|
made up of DNA.
DNA determines the characteristics & traits of the organism. e.g. hair color, leaf shape |
|
|
vacuoles
|
storage containers of the cell. they may store waste or food until it is needed. in plant cells, there are large vacuoles that hold water
|
|
|
mitochondria
|
produces energy for the cell through a process called respiration
|
|
|
respiration
|
a series of chemical reactions that combine food and oxygen to create energy and waste by-product : carbon dioxide
|
|
|
cell wall
|
plants only!!
gives cell a firmer shape & support. made up of cellulose which provides fiber for our good health. |
|
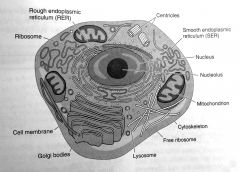
|
Animal Cell
|
|
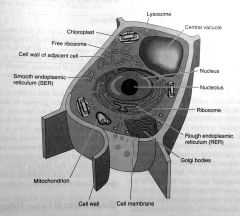
|
Plant Cell
|
|
|
biology
|
study of living things
|
|
|
Carle Linné
|
developed classification system used in modern biological science
|
|
|
Name the seven basic levels of classification
|
1. kingdom
2. phylum 3. class 4. order 5. family 6. genus 7. species Acronym : Keep Pond Clean Or Froggy Gets Sick |
|
|
binomial
|
two-word
|
|
|
the scientific name of an organism consists of:
|
a Genus name (always capitalized) and a
species name (always lower case) |
|
|
chloroplasts
|
are green & contain chlorophyll – which use the process of photosynthesis to make food.
|
|
|
photosynthesis
|
interact with light energy, combining carbon dioxide from the air with water to make food.
carbon dioxide + water = glucose + oxygen |
|
|
DNA
|
deoxyribonucleic acid. Determines how one looks and how one functions.
|
|
|
what is the DNA molecule composed of?
|
1. sugar component
2. phosphate component 3. four different bases (adenine paris with thymine & cytosine pairs with guanine) |
|
|
genes
|
parts of the DNA which determine the appearance & function of the new organism
|
|
|
mitosis
|
for cell division.
Nucleus divided once. 2 cells are formed. |
|
|
meiosis
|
for sex cell formation.
Nucleus divides 2x. 4 cells are formed. 23 Chromosomes in each new cell |
|
|
Asexual reproduction
|
is a mode of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single parent, and inherit the genes of that parent only (bacteria, the hydra & the eye of the potato)
|
|
|
sexual reproduction
|
the production of new living organisms by combining genetic information from two individuals of different types (sexes). In most higher organisms, one sex (male) produces a small motile gamete that travels to fuse with a larger stationary gamete produced by the other (female).
e.g. flowers, humans |
|
|
virus
|
A piece of hereditary material which contains nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) & a protein coat.
Viruses DO NOT have a nucleus or other organelles & CAN NOT produce energy. They are NOT plants, animals or bacteria. They NEED a host cell. |
|
|
Monera
|
1. one-celled or a colony of cells
2. producers, consumers, decomposers & parasites 3. move in water e.g. bacteria, blue-green algae |
|
|
Protista
|
1. one-celled or multicelled
2. producers & consumers 3. asexual & sexual reproduction 4. absorb food 5. have a nucleus (eukaryotic) 6. move with flagella e.g. plankton, algae, amoeba, protozoans |
|
|
Fungi
|
1. one-celled or multicelled
2. consumers (decomposers). 3. asexual reproduction & budding 4. absorb food 5. have a nucleus (eukaryotic) e.g. mushrooms, molds, mildew, yeast, fungi |
|
|
Plantae
|
1. multicelled
2. producers by photosynthesis e.g. angiosperms, gymnosperms, mosses, liverworts, ferns, flowers, bushes, vines, trees & other plants |
|
|
Animalia
|
1. multicelled
2. parasites & consumers 3. asexual & sexual reproduction e.g. sponges, worms, insects, starfish, mammals, fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, gorillas, humans |
|
|
producers
|
use an outside energy source, such as sunlight, to product energy. Most producers have chlorophyll, and most, but not all, are plants
|
|
|
consumers
|
cannot make their own energy - they need to eat other organisms
|
|
|
The five kingdoms of life are:
|
Monera
Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Most People Find Plants Attractive |
|
|
botany
|
scientific study of plants
|
|
|
vascular plants
|
transport roots to the stems and to the leaves by means of tubelike structures
|
|
|
nonvascular plants
|
absorb water only through their surfaces
|
|
|
gymnosperms
|
don't produce flowers
|
|
|
angiosperms
|
produce flowers
|
|
|
cotyledon
|
part of the seed that stores the food
|
|
|
monocots
|
seed that have one cotyledon (part of the seed that stores the food)
|
|
|
dicots
|
seeds that have two cotyledon (part of the seed that stores the food)
|
|
|
annuals
|
go through their entire life cycle in one growing season
|
|
|
biennials
|
two-year growing cycle. in year one the seed germinates, produces leaves & roots, & forms a compact stem for food storage. in year two the plant forms an elongated stem, produces flowers and fruits and then ends with seed production
|
|
|
perennials
|
live for many years
|
|
|
deciduous plants
|
lose their leaves in the winter
e.g. shrubs & trees |
|
|
evergreen plants
|
keep their leaves or needles throughout the year
|
|
|
roots
|
absorbing nutrients and water, anchoring the plant into the soil, holding up the stem and leaves & storing food
|
|
|
taproot system
|
one fat or sturdy main root
e.g. carrot, radish & parnsnips |
|
|
fibrous system
|
many branched roots
e.g. most grasses |
|
|
stem
|
the main trunk of the plant. carries nutrients, food & water through the plant via the vascular system
|
|
|
nodes
|
places in the stem where buds form
|
|
|
internodes
|
spaces between the nodes
|
|
|
vascular system
|
carries nutrients, food & water through the plant
|
|
|
phloem tubes
|
move food from the roots through the stem to the leaves
|
|
|
xylem tubes
|
move minerals and water. these tubes are surrounded by the cambium
|
|
|
cambium
|
the main tissue of the stem
|
|
|
cuticle
|
the protective layer on the leaves that reduces the evaporation of water from the plant. also helps protect the leaf from disease-causing organisms
|
|
|
stomata
|
tiny openings in the leafs that enable the plant to take in carbon dioxide & release oxygen into the atmosphere.
|
|
|
guard cells
|
cover the stomata openings (tiny openings in leaves) & regulate the exchange of water vapor, oxygen & carbon dioxide into & out of the stoma
|
|
|
pistil
|
the female portion of the flower. emcompasses the stigma, style & ovary.
|
|
|
stigma
|
the surface that captures and holds pollen
|
|
|
style
|
the area between the stigma & the ovaries
|
|
|
stamen
|
male portion of the flower
|
|
|
sepals
|
enclose various flower parts
|
|
|
fruit
|
ripened ovary or group of ovaries containing seeds
e.g. peanuts, sunflower seeds, barley, walnuts, tomatoes, grapes, oranges, apples, raspberries, cucumbers, squash, corn eggplants & strawberries |
|
|
parts of a flower
|
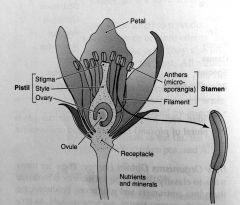
|
|
|
photosynthesis
|
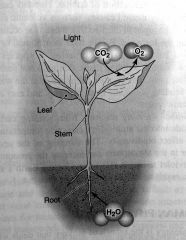
|
|
|
DNA molecule
|
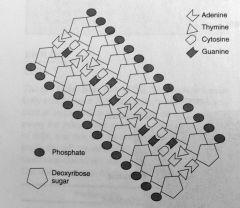
|
|
|
gravitropism
|
a plants response to gravity.
e.g. the roots of plants respond positively to gravity |
|
|
phototropism
|
plants growing toward light
|
|
|
vertebrates
|
animals that have a back bone
|
|
|
invertebrates
|
animals that do NOT have a back bone
|
|
|
mollusks
|
a type of invertebrate that has developed a hard shell
|
|
|
exoskeletons
|
invertebrates that have a tough coating made of chitin on the outside of their bodies
|
|
|
anthropods
|
have jointed legs & a segmented body.
e.g. spiders (arachnids), centipedes & millipedes e.g. insects such as beetles & butterflies |
|
|
crustaceans
|
are anthropods
e.g. shrimp, lobsters & crabs |
|
|
herbivores
|
animals that eat primarily plants
|
|
|
carnivores
|
animals that feed mostly on meat
|
|
|
omnivores
|
eat both plants & meat.
e.g. humans |
|
|
canine teeth
|
are sharp.
meat eaters have jaws & teeth that are designed for tearing & crushing |
|
|
molars
|
have a flattened surface for grinding
|
|
|
cold-blooded
|
its body temperature follows or matches the external temperature around it
|
|
|
warm-blooded
|
can control their body temperature
|
|
|
biosphere
|
the sum of all the places on Earth where life can exist
|
|
|
ecosystem
|
collection of all the living creatures and nonliving features or conditions in a particular environment
|
|
|
ecology
|
the study of ecosystems-the interactions between and among these living creatures and nonliving features
|
|
|
biodiversity
|
the variety of life forms that exist. biodiversity tends to increase as one approaches the equator
|
|
|
habitat
|
a geographic area with conditions that support the continued reproduction of the species
|
|
|
global warming
|
resulting from sending carbon dioxide into the atmosphere that can raise temperature & affect biodiversity
|
|
|
give examples of monera:
|
bacteria, blue-green algae
|
|
|
give examples of protista:
|
plankton, algae, amoeba & protozoans
|
|
|
give examples of fungi:
|
mushrooms, molds, mildew, yeast, fungi
|
|
|
give examples of plantae:
|
angiosperms, gymnosperms, mosses, ferns
|
|
|
give examples of animalia:
|
sponges, worms, insects, starfish, mammals, fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, gorillas, humans
|
|
|
what is the cell wall made of
|
cellulose - which is not digestible by humans
|

