![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
hypertrophy |
increase in size of cells (or subcellular structure); usually results in increase in organ size
response of permanent cells like skeletal muscle, myocardium/cardiomyocytes |
|
|
atrophy |
reduced size of an organ or tissue resulting from decrease in cell size and number |
|
|
hypertrophy example due to hormones |
myometrium (smooth muscle of the uterus) during pregnancy |
|
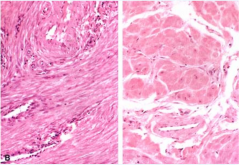
ID the structure and what is the difference between them |
myometrium, the one on the right is hypertrophied due to pregnancy hormones |
|
|
physiologic myocardial hypertrophy happens when? |
occurs through exercise/conditioning |
|
|
hyperplasia |
increase in number of labile cells like epithelia (skin, mucosa, glands, liver) and bone marrow precursors
stimuli include hormones, virus-derived and other growth factors, inflammatory cytokines (inflammatory directing chemical) |
|
|
pathologic myocardial hypertrophy |
probably due to hypertension |
|
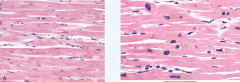
|
myocardial hypertrophy in the second image (notice the boxy nuclei) |
|
|
labile cells |
capable of replication |
|
|
endometrial hyperplasia |
excess estrogen; causes abnormal uterine bleeding |
|
|
prostate hyperplasia |
DHT (testosterone derivative) |
|
|
keloid |
excessive scar in wound healing (excess fibroblasts produce collagen) |
|
|
psoriasis |
inflammatory proliferation of epidermal squamous cells due to cytokines |
|
|
warts |
human papilloma virus causes hyperplasia |
|
|
what cell undergoes hyperplasia until puberty and then undergo hypertrophy |
fat cells |
|
|
atrophy |
reduced size of organ-tissue due to decrease in cell size and number |
|
|
marasmus |
starving slide |
|
|
common cause of pathologic atrophy |
age-related atrophy |
|
|
pathologic atrophy caused by disuse |
localized loss of muscle in cast, generalized loss of muscle with bed rest |
|
|
pathologic atrophy caused by loss of endocrine stimulation |
menopausal atrophy of breast, endometrium, vaginal epithelium |

