![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Macromolecule
|
Molecule that consists of thousands of covalently connected atoms that form a molecular colossus with a mass of over 100,000 daltons.
|
|
|
|
Polymer
(H) |
A long molecule consisting of many similar, or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. Carbohydrates, protiens, and nucleic acids.
(H) |
From the Greek "Polys", meaning "many", and "Meris", meaning, "part"
|
|
|
Monomer
(H) |
The repeating building blocks of a polymer.
(H) |
From the Greek "monos", meaning "one", and "meris", meaning "part".
|
|
|
Condensation Reaction
|
A reaction in which two molecules become covalently bonded to each other through the loss of a small molecule, usually water; also called a dehydration reaction.
|
|
|
|
Hydrolysis
(H) |
A chemical process that lyses, or splits, molecules by the addition of water.
(H) |
Essintially the reverse of a dehydration reaction.
|
|
|
Carbohydrates
|
A sugar (monosaccharide) or one of its dimers (disaccharides) or polymers (polysaccharides).
|
|
|
|
Monosaccharides
(H) |
The simplest carbohydrate, active alone or serving as a monomer for disaccharides and polysaccharides. Also known as simple sugars, with a molecular formula generally some multiple of CH2O. Ex. Glucose(C6,H12,O6)
(H) |
From the Greek "monos", single, and "sacchar", sugar.
|
|
|
Disaccharide
(H) |
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis, AKA, a glycosidic linkage.
(H) |
Maltose is formed by the linking of two molecules of glucose.
|
|
|
Glycosidic Linkage
|
A covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction.
|
|
|
|
Polysaccharides
|
A polymer of up to over a thousand monosaccharides, formed by dehydration reactions.
|
|
|
|
Starch
|
A polysaccharide storage of plant cells, is a polymer consisting entirely of glucose monomers.
|
|
|
|
Glycogen
|
A polysaccharide storage of animal cells. A polymer of glucose that is like amylopectin but more extensively branched.
|
|
|
|
Cellulose
|
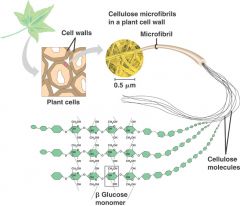
A structural polysaccharide of cell walls, consisting of glucose monomers joined by B-1, 4-glycosidic linkages.
|
|

