![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a gene? |
Classical Defintion An inherited factor that affects the charcteristics of an individual, Defined by its affect on the phenotype of the organism.
Molecualar Defintion PArt of chromosome involved in the transcription of DNA to RNA. |
|
|
What are telomers, their role? |
Telomers are end portions of the chromosomes, they're thought to protect our chromosomes. |
|
|
Function of telomerase? |
This enzyme is thought to prevent the ends of chromosomes from shortening during repeated rounds of cell division,
Present in stem cell and cancer cells |
|
|
Explain Dominant and reccessive alleles in terms of functionality. |
Generally:
Reccessive allele is Loss of function (LOF)
and dominant alleles are Gain of function (GOF). They'll have more funtion in the body
Normally single functional gene copy will be enough for the biochemistry of the body, Haplosufficiency
however if this is not the case it is refferred to as Haploinsuffiency, Where the single functional gene cannot meet beodies demands
|
|
|
Stages of Mitosis? |
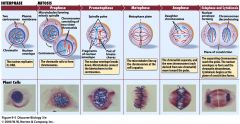
1) Early Prophase: Chromosomes condense, Mitotic spindle is formed from centrosome.
2)Late Prophase: Nuclear envelope breaks down, chromsomes attatched to miotic spindles
3)Metaphase: Chromosomes line up at equator of cell, sister chromatids attatch to opposite poles of miotic spindle
4) Anaphase: Cohesion between sister chromatids lost, and they're segregated to opposite ples by the miotic spindles shortening
Telophase: Chromsomes decondense, Nuclear envelope reforms, Cytokenesis Begins ( Cytoplasm splitting to form second cell) |
|
|
Meiosis? |
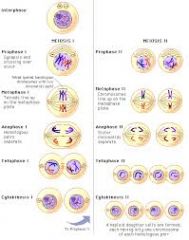
|
|
|
Whay are the gametes produced in Meiosis not genetically identical to one another? |
Chromosome orientation at metaphase 1 random,
Crossing-over shuffles segments of homologous chromosomes. |

