![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Solid- A state of matter where the particles are packed together and regularly arranged. Liquid- A state of matter where the particles are close together and randomly arranged. Gas- A state of matter where the particles have no attractive forces between them and are randomly arranged. |
Solid -> Liquid = Melting Solid -> Gas = Sublimation Liquid -> Solid = Freezing Liquid -> Gas = Evaporation Gas -> Solid = Deposition Gas -> Liquid = Condensation |
|
|
Compound - Is made when 2 or more chemical elements are chemically bonded. Mixture - Is made when 2 or more compounds or elements are not chemically bonded. Element- A substance consisting of the same kind of atom. |
. |
|
|
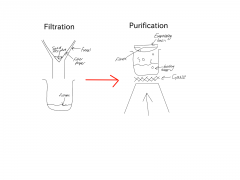
Filtration - Using a filter to separate insoluble substances from a liquid. Insoluble- A substance that does not dissolve in a certain liquid. Solution- Mixture made of solutes, formed when a substance has dissolved in a liquid. Solutes- a substance that dissolves in a liquid to make a solution. Solvent- A liquid in which a substance dissolves in to make a solution. Crystallisation- Separating solute from solution by evaporating the solvent. |
Filtrate- A solution that has passed through a filter. Residue- Material remaining in the filter after a mixture has passed through it. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- A Saturated solution contains the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in that amount of solvent. |
|
|
Chromatography Rf = Distance moved by spot -------------------------------------- Distance moved by solvent |
|
|
Distillation |
Fractional distillation The bunsen burner is used to heat the round flask. the liquid mixture starts to boil. The ethanol evaporates before the water because it has a lower boiling point, The water stays in the round flask. The ethanol vapour rises to the top of the flask- the thermometer reads to about 80 degrees. The ethanol vapour moves down the side arm to the condenser. The ethanol vapour condenses on the cool tube and turns back into a liquid. Ethanol collects in the conical flask. |
|
|
Health hazards 1. Liquid may fall- stand rather than sit. 2. Bunsen burner may be hot- wait for it to cool down. 3.Chemicals may get into eyes- Wear goggles. 4. Scarves/Hair/Ties may get set on fire- tuck into clothing |
. |
|
|
Drinking water Chemical reactions may be used to purify sewage water because there may be bacteria that filtration cannot get rid of. It would need to be checked regularly because pesticides, fertilizers etc may have gotten into the water. |
Sedimentation- Small particles are allowed to settle out Filtration- Water passes through beds of gravel and sand and small particles get left behind Chlorination - Kills microorganisms in the water |
|
|
Desalination- Producing pure water from saltwater -Heat salt water in first beaker - Water evaporates and condenses in second beaker |
. |

